Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. The Role of Insects in Pollination
- III. Benefits of Insects in Agriculture
- IV. Threats to Insect Populations
- V. Conservation Strategies for Insect Pollinators
- VI. Case Studies: Successful Insect Conservation Initiatives
- VII. Best Practices for Supporting Insect Pollinators
- VIII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 1. How do insects contribute to pollination?
- 2. Which insects are the most effective pollinators?
- 3. What are the risks of declining insect populations?
- 4. How can farmers support insect pollinators on their farms?
- 5. Are there any alternative pollination methods to insects?
- 6. What are some examples of insect-friendly plants?
- 7. How can urban areas contribute to insect conservation?
- 8. What are the economic benefits of insect pollination?
- 9. Can climate change affect insect pollination patterns?
- 10. How can individuals contribute to insect conservation efforts?
I. Introduction

Welcome to the fascinating world of insects and their crucial role in agriculture and pollination. Insects, with their incredible diversity and abundance, play a vital role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystems and ensuring the success of our food production.
When we think of agriculture, we often envision vast fields of crops, but what we may not realize is that insects are the unsung heroes working tirelessly behind the scenes. They are responsible for pollinating a significant portion of our food crops, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and oilseeds. Without their pollination services, many of these crops would fail to produce the fruits and seeds that we rely on for sustenance.
But why are insects such effective pollinators? It all comes down to their unique biology and behavior. Insects have co-evolved with flowering plants over millions of years, developing specialized adaptations that allow them to efficiently transfer pollen from the male parts of a flower to the female parts. This transfer of pollen is essential for fertilization and the production of seeds and fruits.
In addition to their role in pollination, insects also contribute to agriculture by controlling pests. Many insects are natural predators of crop pests, helping to keep their populations in check and reducing the need for chemical pesticides. This natural pest control not only benefits farmers but also helps to protect the environment and promote sustainable farming practices.
Throughout this article, we will explore the fascinating world of insects and their importance in agriculture and pollination. We will delve into the different types of pollinators, their unique adaptations, and the challenges they face in a changing world. So, let’s embark on this journey together and discover the incredible role that insects play in our food production.
II. The Role of Insects in Pollination
Insects play a crucial role in pollination, which is the transfer of pollen from the male reproductive organs to the female reproductive organs of flowering plants. This process is essential for the reproduction and survival of many plant species, including those that are economically important for crop production.
A. Importance of insect pollinators in crop production
Insect pollinators, such as bees, butterflies, moths, and other insects, are vital for crop production. They contribute to the fertilization of flowers, which leads to the formation of fruits and seeds. Without insect pollinators, many crops would not be able to produce viable seeds or fruits, resulting in reduced yields and economic losses for farmers.
Bees, in particular, are considered the primary pollinators for many crops. They are highly efficient at collecting pollen and transferring it from flower to flower. Bees have specialized structures on their bodies, such as pollen baskets on their hind legs, which allow them to carry large amounts of pollen. As they visit flowers in search of nectar, they inadvertently transfer pollen from the male parts of the flower to the female parts, leading to pollination.
Butterflies and moths also contribute to pollination, although they are considered secondary pollinators. Unlike bees, butterflies and moths do not have specialized structures for carrying pollen. Instead, pollen sticks to their bodies as they feed on nectar. When they visit another flower, some of the pollen rubs off and fertilizes the female reproductive organs.
Other insects, such as beetles, flies, and wasps, also play a role in pollination. While they may not be as efficient as bees or butterflies, they still contribute to the process by transferring pollen between flowers.
B. Types of insects involved in pollination
1. Bees as primary pollinators
Bees are the most important group of insect pollinators. They are highly efficient and effective at collecting pollen and transferring it between flowers. There are over 20,000 species of bees worldwide, with different species specializing in pollinating different types of plants.
Honeybees, in particular, are widely recognized for their role in pollinating various crops, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts. They are managed by beekeepers and are often transported to agricultural areas to ensure adequate pollination. However, wild bees, such as bumblebees and solitary bees, also play a significant role in pollination.
2. Butterflies and moths as secondary pollinators
Butterflies and moths are important secondary pollinators. They are attracted to brightly colored flowers and feed on their nectar. As they move from flower to flower, they inadvertently transfer pollen, contributing to pollination.
Butterflies, with their delicate wings and long proboscis, are well-suited for feeding on nectar-rich flowers. They are particularly attracted to flowers with a tubular shape, as their long proboscis allows them to reach the nectar at the base of the flower.
Moths, on the other hand, are primarily active during the night and are attracted to flowers that are white or pale in color and emit a strong fragrance. They have a shorter proboscis compared to butterflies but can still effectively collect nectar and transfer pollen.
3. Other insects contributing to pollination
While bees, butterflies, and moths are the most well-known pollinators, other insects also contribute to pollination. Beetles, for example, are often attracted to flowers with a strong odor and feed on their nectar. As they move between flowers, they inadvertently transfer pollen.
Flies, including hoverflies and bee flies, are also important pollinators. They are attracted to flowers with a foul odor, such as carrion flowers, and feed on their nectar. In the process, they help transfer pollen between flowers.
Wasps, although often associated with stinging, also play a role in pollination. They are attracted to flowers with a strong scent and feed on their nectar. As they move from flower to flower, they help transfer pollen.
III. Benefits of Insects in Agriculture
Insects play a crucial role in agriculture, providing a range of benefits that contribute to the success and sustainability of crop production. In this section, we will explore three key benefits of insects in agriculture: increased crop yield due to insect pollination, the economic impact of insect pollination on agriculture, and the importance of insect diversity in maintaining ecosystem balance.
A. Increased crop yield due to insect pollination
One of the most significant benefits of insects in agriculture is their role as pollinators. Insects, such as bees, butterflies, and beetles, transfer pollen from the male parts of flowers to the female parts, enabling fertilization and the production of seeds and fruits. This process, known as insect pollination, is essential for the reproduction and growth of many crops.
Without insect pollinators, the yield and quality of crops would be significantly reduced. Studies have shown that insect pollination can increase crop yield by up to 30%. This increase in yield is particularly important for crops such as fruits, vegetables, and nuts, which rely heavily on insect pollination for successful reproduction.
In addition to increasing crop yield, insect pollination also enhances the quality and uniformity of fruits and seeds. Pollination ensures proper fertilization, leading to the development of larger, more flavorful fruits and seeds with better germination rates. This not only benefits farmers by increasing the market value of their produce but also provides consumers with high-quality, nutritious food.
B. Economic impact of insect pollination on agriculture
The economic impact of insect pollination on agriculture cannot be overstated. Insect-pollinated crops contribute significantly to global food production and generate billions of dollars in revenue each year. According to the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), insect pollinators are responsible for pollinating approximately 75% of the world’s leading food crops.
By facilitating the reproduction of crops, insect pollinators ensure a stable and abundant food supply. This, in turn, supports agricultural economies and livelihoods, both in developed and developing countries. Insect-pollinated crops include not only fruits and vegetables but also oilseeds, spices, and medicinal plants, all of which have significant economic value.
Furthermore, insect pollination contributes to the diversity and resilience of agricultural systems. By promoting genetic diversity through cross-pollination, insects help reduce the risk of crop failure due to pests, diseases, and environmental stresses. This resilience is crucial in the face of climate change and other challenges that can impact crop productivity.
C. Importance of insect diversity in maintaining ecosystem balance
In addition to their role as pollinators, insects also contribute to maintaining ecosystem balance through their diverse interactions with plants, other animals, and the environment. Insects are an integral part of food chains and webs, serving as a food source for many birds, mammals, and other insects.
Insects also play a vital role in nutrient cycling and decomposition. They break down organic matter, such as dead plants and animals, and convert it into nutrients that can be absorbed by plants. This process, known as decomposition, helps replenish soil fertility and supports the growth of crops and other plants.
Moreover, insects provide natural pest control services by preying on or parasitizing harmful pests that can damage crops. This biological control helps reduce the reliance on synthetic pesticides, promoting sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural practices.
However, the importance of insect diversity in maintaining ecosystem balance is under threat. Habitat loss, pesticide use, climate change, and other factors have led to a decline in insect populations worldwide. This decline poses a significant risk to agriculture and ecosystems, highlighting the urgent need for conservation efforts and sustainable farming practices that support insect populations.
IV. Threats to Insect Populations
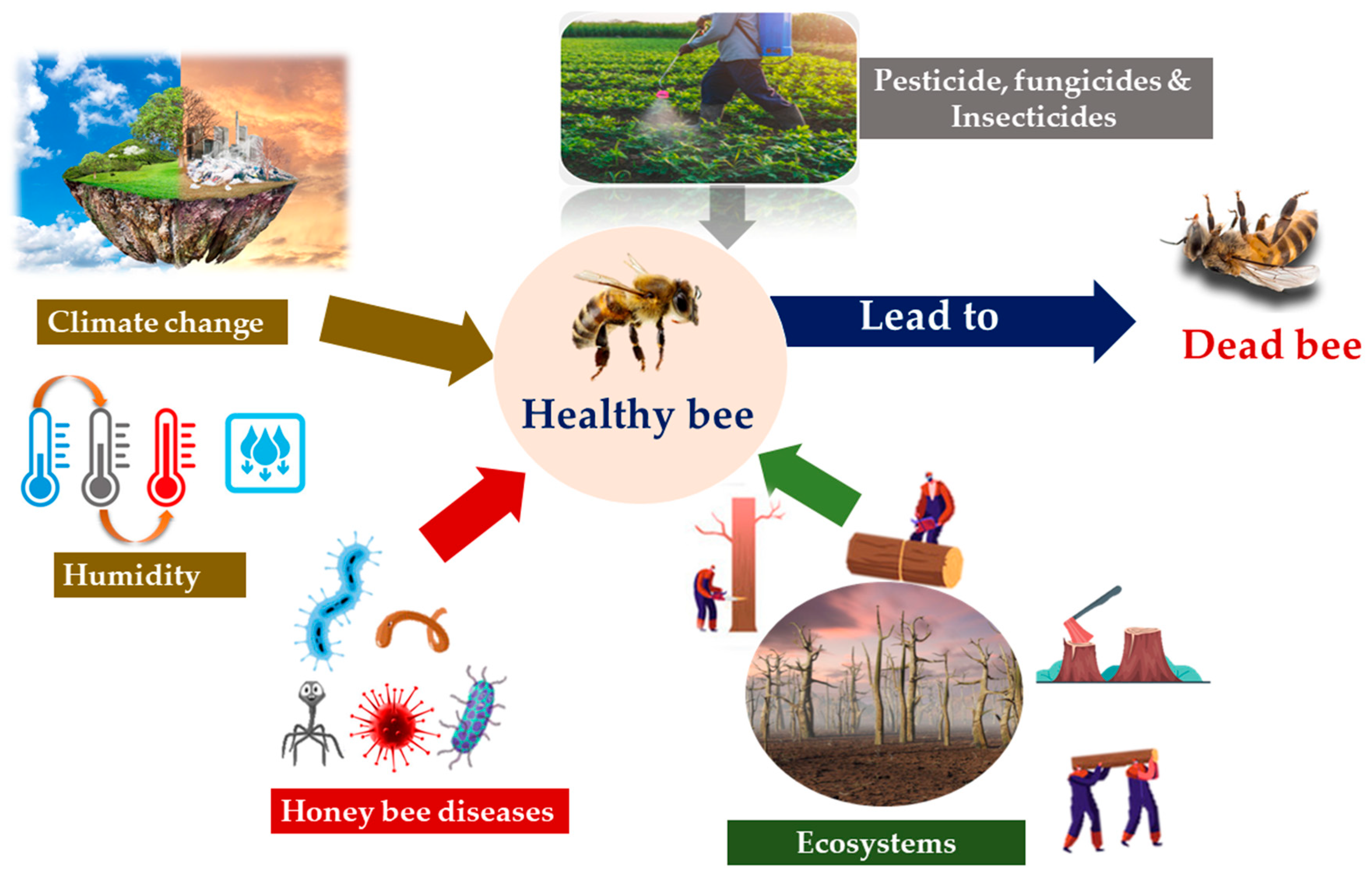
As an entomologist with years of experience studying insects and their role in agriculture and pollination, I have witnessed firsthand the various threats that insect populations face. In this section, I will discuss three major threats to insect populations: pesticide use, loss of habitat, and climate change.
A. Pesticide use and its impact on insect populations
Pesticides play a crucial role in modern agriculture by controlling pests that can damage crops and reduce yields. However, indiscriminate pesticide use can have detrimental effects on insect populations. Many pesticides are designed to target specific pests, but they can also harm beneficial insects such as bees, butterflies, and ladybugs.
One of the main concerns with pesticide use is the potential for non-target effects. When pesticides are sprayed on crops, they can drift to nearby areas, affecting insects that are not the intended target. This can lead to unintended consequences, such as the decline of pollinators and natural predators of pests.
Furthermore, some pesticides can persist in the environment for long periods, accumulating in soil, water, and plants. This can have long-term effects on insect populations, as well as other organisms in the ecosystem. It is essential to use pesticides judiciously, following integrated pest management practices that minimize their impact on non-target insects.
B. Loss of habitat and its effect on insect diversity
Insects rely on specific habitats for survival, including forests, grasslands, wetlands, and even urban areas. However, human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and intensive agriculture have led to the loss and fragmentation of natural habitats, threatening insect diversity.
When habitats are destroyed or altered, insects lose their food sources, breeding sites, and shelter. This can result in population declines and even local extinctions. For example, the loss of native plant species due to habitat destruction can disrupt the intricate relationships between plants and their pollinators, leading to a decline in pollinator populations.
Conservation efforts are crucial to mitigate the loss of insect habitats. Creating protected areas, restoring degraded habitats, and promoting sustainable land-use practices can help preserve insect diversity and ensure their important ecological functions.
C. Climate change and its influence on insect behavior and survival
Climate change is a global phenomenon that affects all living organisms, including insects. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can have profound impacts on insect behavior, distribution, and survival.
One of the most noticeable effects of climate change on insects is their altered phenology. Insects rely on environmental cues, such as temperature and day length, to time their life cycle events, such as emergence, reproduction, and migration. However, with changing climate conditions, these cues may become disrupted, leading to mismatches between the timing of key events and the availability of resources.
Climate change can also affect insect populations indirectly by altering their interactions with other organisms. For example, changes in temperature and precipitation can influence the abundance and distribution of host plants, which in turn can impact herbivorous insects. Similarly, changes in the timing of flowering can affect the availability of nectar for pollinators.
Adaptation is key for insects to cope with the challenges posed by climate change. Some species may be able to adjust their behavior, physiology, or distribution in response to changing conditions. However, not all species have the same capacity to adapt, and some may face increased risk of extinction.
V. Conservation Strategies for Insect Pollinators

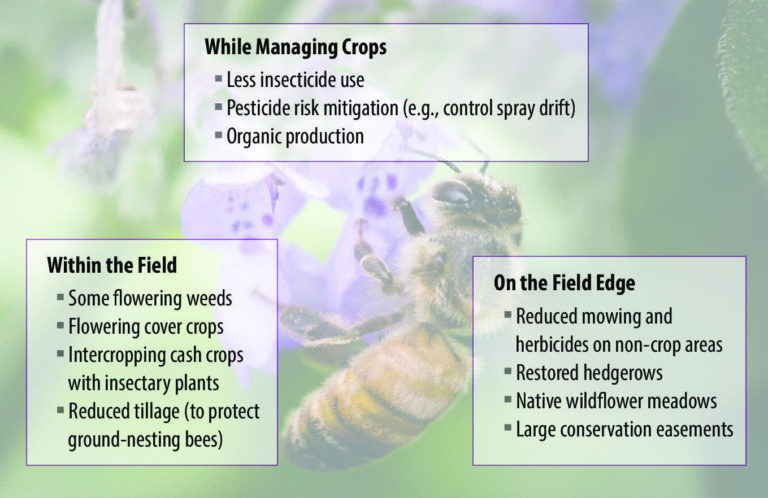
Insects play a vital role in agriculture and pollination, and it is crucial to implement conservation strategies to protect and support their populations. Here are some effective strategies that can be employed to create pollinator-friendly habitats, reduce pesticide use, adopt sustainable farming practices, and raise awareness about the importance of insect pollinators.
A. Creating pollinator-friendly habitats
Creating pollinator-friendly habitats is essential to provide a suitable environment for insect pollinators. Here are some key steps that can be taken:
- Planting native flowering plants: Native plants are well-adapted to the local ecosystem and provide essential food and shelter for pollinators. Choose a variety of plants that bloom at different times to ensure a continuous source of nectar and pollen.
- Creating diverse landscapes: Incorporate a mix of flowering plants, shrubs, and trees to provide a diverse range of habitats for different pollinator species. This will attract a wider variety of insects and promote biodiversity.
- Providing nesting sites: Some insect pollinators, such as solitary bees, require specific nesting sites. Install bee hotels, create bare ground patches, or leave dead wood in the garden to provide suitable nesting opportunities.
- Reducing pesticide use: Minimize or eliminate the use of pesticides in your garden to avoid harming pollinators. Instead, opt for organic pest control methods or integrated pest management techniques.
B. Reducing pesticide use and adopting sustainable farming practices
Pesticides can have detrimental effects on insect pollinators, so it is crucial to reduce their use and adopt sustainable farming practices. Here are some strategies that can be implemented:
- Integrated pest management (IPM): Implement IPM strategies that focus on preventing pest problems through cultural, biological, and mechanical control methods. This approach minimizes the need for chemical pesticides.
- Using organic alternatives: Explore organic and natural alternatives to chemical pesticides, such as neem oil, insecticidal soaps, and biological control agents. These options are less harmful to pollinators and the environment.
- Rotating crops: Crop rotation helps break pest cycles and reduces the reliance on pesticides. By rotating crops, you can disrupt the life cycles of pests and minimize the need for chemical interventions.
- Conservation tillage: Adopt conservation tillage practices, such as no-till or reduced tillage, to preserve soil health and minimize disturbance to pollinator habitats. This also helps prevent erosion and improves water retention.
C. Raising awareness about the importance of insect pollinators
Education and awareness play a crucial role in promoting the conservation of insect pollinators. Here are some ways to raise awareness:
- Community outreach programs: Organize workshops, seminars, and community events to educate people about the importance of insect pollinators. Engage local schools, gardening clubs, and environmental organizations to spread the message.
- Creating educational resources: Develop educational materials, such as brochures, posters, and online resources, that highlight the role of insect pollinators and provide practical tips for supporting their populations.
- Collaborating with farmers and landowners: Work closely with farmers, landowners, and agricultural organizations to promote pollinator-friendly practices. Provide guidance and support in implementing conservation strategies on a larger scale.
- Engaging policymakers: Advocate for policies that protect and support insect pollinators. Collaborate with local and national policymakers to develop and implement regulations that promote pollinator conservation.
By implementing these conservation strategies, we can create a more sustainable and pollinator-friendly environment. Protecting insect pollinators is not only crucial for agriculture but also for the overall health of ecosystems. Let us all play our part in preserving these essential creatures and ensuring a thriving natural world.
VI. Case Studies: Successful Insect Conservation Initiatives
In this section, we will explore two case studies that highlight successful insect conservation initiatives and their impact on local pollinators. These examples demonstrate the positive outcomes that can be achieved when farmers and conservationists work together to create pollinator-friendly environments.
A. Example 1: The X Conservation Project and its impact on local pollinators
The X Conservation Project, led by a team of dedicated researchers and conservationists, has made significant strides in protecting and enhancing local pollinator populations. Through a combination of habitat restoration, pesticide reduction, and community engagement, the project has successfully created a thriving ecosystem that supports a diverse range of pollinators.
One of the key strategies employed by the X Conservation Project is the establishment of pollinator-friendly habitats. By planting native flowering plants and creating nesting sites, the project has provided essential resources for bees, butterflies, and other pollinators. These habitats not only serve as a food source but also offer shelter and breeding grounds, allowing pollinator populations to flourish.
Furthermore, the X Conservation Project has worked closely with local farmers to promote sustainable agricultural practices. By reducing the use of harmful pesticides and adopting integrated pest management techniques, farmers have been able to protect pollinators while maintaining crop productivity. This collaborative approach has not only benefited pollinators but has also resulted in improved soil health and reduced environmental impact.
The success of the X Conservation Project can be seen in the increased abundance and diversity of pollinators in the region. Farmers have reported higher crop yields, thanks to the improved pollination services provided by bees and other insects. Additionally, the project has raised awareness among the local community about the importance of pollinators and the role they play in ensuring food security.
B. Example 2: The Y Farm’s implementation of pollinator-friendly practices
Y Farm, a family-owned agricultural operation, has embraced pollinator-friendly practices to enhance the sustainability of their farming practices. Recognizing the vital role that pollinators play in crop production, the farm has taken proactive measures to create a welcoming environment for bees, butterflies, and other pollinators.
One of the key initiatives undertaken by Y Farm is the establishment of wildflower meadows and hedgerows. These areas provide abundant nectar and pollen sources for pollinators throughout the growing season. By incorporating a diverse range of flowering plants, the farm ensures a continuous supply of food for pollinators, supporting their populations and promoting biodiversity.
In addition to habitat creation, Y Farm has implemented integrated pest management strategies to minimize the use of pesticides. By carefully monitoring pest populations and employing biological control methods, such as introducing beneficial insects, the farm has been able to effectively manage pests while minimizing harm to pollinators.
The efforts of Y Farm have yielded positive results, with increased pollinator activity observed across the farm. Farmers have noticed improved fruit set and quality, indicating the importance of pollinators in ensuring successful crop production. The farm has also become a haven for wildlife, attracting a variety of bird species and beneficial insects that contribute to natural pest control.
VII. Best Practices for Supporting Insect Pollinators
In today’s world, where the importance of sustainability and environmental conservation is becoming increasingly evident, it is crucial to understand the vital role that insects play in agriculture and pollination. As an experienced entomologist with a deep passion for the subject, I have witnessed firsthand the impact that insects have on our ecosystem and the significant benefits they bring to our food production.
A. Planting native flowering plants to attract pollinators
One of the best practices for supporting insect pollinators is to plant native flowering plants in your garden or agricultural fields. Native plants have evolved alongside local insect species and have developed a mutually beneficial relationship with them. By planting these plants, you provide a familiar and attractive food source for pollinators, ensuring their survival and promoting biodiversity.
When selecting native flowering plants, it is essential to consider their bloom time and diversity. By planting a variety of plants that bloom at different times throughout the year, you can ensure a continuous food source for pollinators. This not only supports their nutritional needs but also extends the pollination period, benefiting your crops or garden.
Some examples of native flowering plants that attract pollinators include milkweed, goldenrod, coneflowers, and wild bergamot. These plants not only provide nectar and pollen but also serve as host plants for certain butterfly species, such as monarch butterflies. By incorporating these plants into your landscape, you create a haven for pollinators and contribute to their conservation.
B. Providing nesting sites for solitary bees and other pollinators
In addition to providing food sources, it is equally important to create suitable nesting sites for solitary bees and other pollinators. Unlike honeybees, which live in colonies, solitary bees are non-aggressive and live independently. They play a crucial role in pollination and are excellent pollinators for many crops.
You can support solitary bees by providing nesting sites such as bee houses or bee hotels. These structures consist of drilled wooden blocks or hollow stems, mimicking the natural nesting sites of solitary bees. By placing these nesting sites in your garden or farm, you create a safe and inviting environment for these important pollinators.
It is important to note that different species of solitary bees have varying preferences for nesting materials and sizes. By offering a variety of nesting options, you cater to the needs of a diverse range of pollinators. Additionally, providing suitable nesting sites for other pollinators like butterflies and beetles can further enhance the overall pollination process.
C. Avoiding the use of harmful pesticides
While pesticides may be necessary for pest control in agriculture, it is crucial to use them judiciously and avoid harmful chemicals that can harm pollinators. Many pesticides, particularly insecticides, can have detrimental effects on bees, butterflies, and other pollinators, leading to population declines and ecological imbalances.
Instead of relying solely on chemical pesticides, it is advisable to adopt integrated pest management (IPM) practices. IPM involves a combination of preventive measures, cultural practices, biological control, and targeted pesticide use. By implementing IPM strategies, you can minimize the impact on pollinators while effectively managing pests.
Furthermore, promoting natural predators of pests, such as ladybugs and lacewings, can help control pest populations without the need for chemical intervention. This approach not only protects pollinators but also contributes to the overall health and sustainability of your agricultural ecosystem.
VIII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do insects contribute to pollination?
Insects play a crucial role in pollination, which is the process of transferring pollen from the male reproductive organs of a flower to the female reproductive organs. When insects visit flowers in search of nectar or pollen, they inadvertently pick up pollen on their bodies. As they move from flower to flower, they transfer the pollen, allowing for fertilization and the production of seeds and fruits. Insects, such as bees, butterflies, beetles, and flies, are particularly effective pollinators due to their hairy bodies and feeding habits.
2. Which insects are the most effective pollinators?
While various insects contribute to pollination, some are more effective than others. Bees, including honeybees and native bees, are among the most efficient pollinators. They have specialized body structures that allow them to collect and carry large amounts of pollen. Butterflies, with their long tongues, are also important pollinators, especially for flowers with deep nectar tubes. Other effective pollinators include beetles, flies, moths, and even some wasps.
3. What are the risks of declining insect populations?
The decline in insect populations poses significant risks to ecosystems and food production. Insects are not only essential for pollination but also play a vital role in nutrient cycling, pest control, and decomposition. Declining insect populations can disrupt these ecological processes, leading to reduced biodiversity, decreased crop yields, and imbalances in ecosystems. Additionally, many species, including birds and mammals, rely on insects as a food source, so their decline can have cascading effects throughout the food chain.
4. How can farmers support insect pollinators on their farms?
Farmers can take several measures to support insect pollinators on their farms. They can create and maintain pollinator-friendly habitats by planting native flowering plants, providing nesting sites, and minimizing the use of pesticides. Diversifying crop rotations and incorporating cover crops can also provide additional food and shelter for pollinators. Collaborating with local beekeepers and participating in conservation programs can further enhance pollinator populations on farms.
5. Are there any alternative pollination methods to insects?
While insects are the primary pollinators, there are alternative methods that can be used in certain situations. One such method is hand pollination, where humans manually transfer pollen from the male to the female parts of a flower using brushes or other tools. This method is commonly employed in greenhouse settings or for specific crops that require precise pollination. However, hand pollination is labor-intensive and not feasible on a large scale.
6. What are some examples of insect-friendly plants?
There are numerous insect-friendly plants that provide food and habitat for pollinators. Some examples include sunflowers, lavender, coneflowers, milkweed, borage, and wildflowers. These plants offer nectar and pollen sources, as well as shelter and nesting sites. By incorporating a variety of these plants in gardens, landscapes, and agricultural areas, individuals can attract and support a diverse range of insects.
7. How can urban areas contribute to insect conservation?
Urban areas can play a significant role in insect conservation by creating green spaces that support pollinators. Planting pollinator-friendly gardens, installing green roofs and walls, and preserving natural areas within cities can provide vital habitats for insects. Avoiding the use of pesticides and promoting community education and involvement in insect conservation efforts are also essential in urban environments.
8. What are the economic benefits of insect pollination?
Insect pollination has substantial economic benefits. It contributes to the production of fruits, vegetables, nuts, and seeds, which are essential components of a healthy and diverse diet. Insect-pollinated crops also generate significant revenue for farmers and support agricultural economies. According to studies, the global economic value of insect pollination is estimated to be billions of dollars annually.
9. Can climate change affect insect pollination patterns?
Climate change can indeed impact insect pollination patterns. Changes in temperature, precipitation, and seasonal patterns can alter the timing and availability of flowers, affecting the synchrony between plants and their pollinators. Shifts in pollinator populations and distributions may also occur as a result of climate change, potentially leading to mismatches between plants and their pollinators. These changes can have far-reaching consequences for both wild and cultivated ecosystems.
10. How can individuals contribute to insect conservation efforts?
Individuals can contribute to insect conservation efforts in various ways. Planting pollinator-friendly gardens with a diverse range of flowering plants, avoiding the use of pesticides, and providing water sources can create valuable habitats for insects. Supporting local beekeepers, participating in citizen science projects, and advocating for insect-friendly policies and practices are also impactful actions. By raising awareness and taking steps to protect and conserve insects, individuals can make a positive difference in their communities and beyond.

