Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding Wildlife Behavior
- III. Benefits of Positive Human-Wildlife Interaction
- IV. Examples of Successful Human-Wildlife Interaction Projects
- V. Responsible Wildlife Tourism Practices
- VI. Wildlife Conservation and Habitat Restoration
- VII. Coexistence Strategies for Conflict Resolution
- VIII. Best Practices for Wildlife Photography and Filming
- IX. Wildlife Rehabilitation and Rescue
I. Introduction

Welcome to the world of positive human-wildlife interaction! In this article, we will explore the numerous benefits of coexistence between humans and wildlife. As our society becomes more aware of the importance of preserving our natural environment, it is crucial to understand the positive impact that humans can have on wildlife and vice versa.
Human-wildlife interaction refers to the various ways in which humans and wildlife come into contact and interact with each other. This interaction can occur in both urban and rural settings, and it encompasses a wide range of activities, from observing wildlife in their natural habitats to participating in conservation efforts.
There are several reasons why positive human-wildlife interaction is beneficial for both humans and wildlife. Firstly, it allows us to gain a deeper appreciation and understanding of the natural world. By observing and learning about different species, we can develop a sense of awe and wonder for the diversity of life on our planet.
Secondly, positive human-wildlife interaction can contribute to the conservation and preservation of wildlife populations. By actively engaging with wildlife, we can raise awareness about the importance of protecting their habitats and implementing sustainable practices.
Lastly, human-wildlife interaction can have positive impacts on our mental and physical well-being. Spending time in nature and observing wildlife has been shown to reduce stress levels, improve mood, and increase overall happiness.
In the following sections of this article, we will delve deeper into the specific benefits of positive human-wildlife interaction. From promoting biodiversity to fostering a sense of stewardship, there is much to explore and discover in the realm of coexistence between humans and wildlife.
II. Understanding Wildlife Behavior
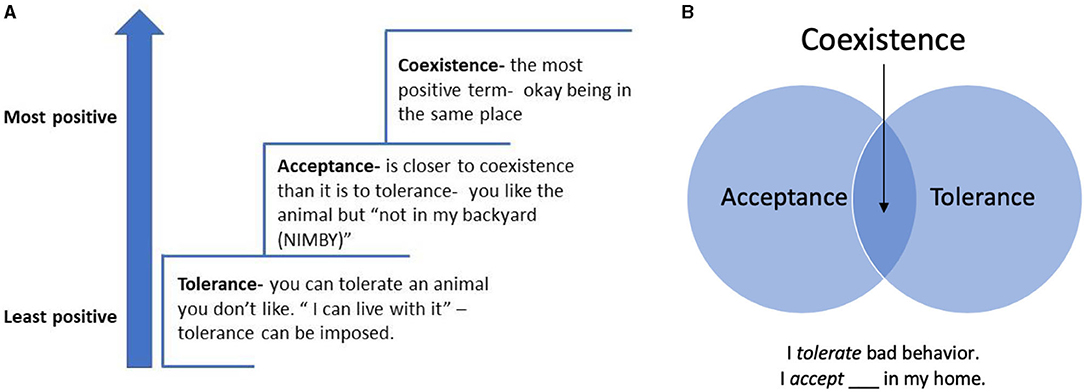
A. Factors influencing wildlife behavior
Wildlife behavior is influenced by a variety of factors that shape their interactions with their environment and other species. Understanding these factors is crucial for promoting positive human-wildlife interactions and ensuring the coexistence of humans and wildlife.
1. Habitat: The habitat in which wildlife species live plays a significant role in shaping their behavior. Different habitats provide varying resources, such as food, water, and shelter, which influence the behavior of wildlife species. For example, predators may exhibit different hunting strategies and social behaviors depending on the availability of prey in their habitat.
2. Seasonal changes: Wildlife behavior can also be influenced by seasonal changes. Animals may migrate, hibernate, or change their feeding patterns in response to seasonal variations in temperature, food availability, or breeding opportunities. Understanding these seasonal patterns is essential for managing wildlife populations and conserving their habitats.
3. Social structure: Many wildlife species exhibit complex social structures, which impact their behavior. Social hierarchies, mating systems, and cooperative behaviors are examples of social factors that influence wildlife behavior. For instance, in a pack of wolves, dominant individuals may exhibit different behaviors compared to subordinate individuals.
4. Predation risk: The fear of predation can significantly affect wildlife behavior. Animals may alter their foraging patterns, movement, or reproductive strategies to minimize the risk of predation. This can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem, as changes in predator-prey dynamics can impact the abundance and distribution of species.
5. Human disturbance: Human activities can have a profound impact on wildlife behavior. Noise pollution, habitat destruction, and direct interactions with humans can disrupt natural behaviors and cause stress to wildlife species. Understanding the effects of human disturbance on wildlife behavior is crucial for implementing effective conservation strategies.
B. Impact of human activities on wildlife behavior
Human activities have both direct and indirect impacts on wildlife behavior. As human populations continue to expand and encroach upon natural habitats, it is essential to understand these impacts to mitigate negative effects and promote coexistence.
1. Habitat loss and fragmentation: One of the most significant impacts of human activities on wildlife behavior is habitat loss and fragmentation. Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion result in the destruction and fragmentation of natural habitats, forcing wildlife to adapt to new environments or face extinction. This disruption can alter migration patterns, feeding behaviors, and social interactions.
2. Noise pollution: Noise pollution from human activities, such as construction, traffic, and recreational activities, can disrupt wildlife behavior. Animals rely on acoustic signals for communication, finding mates, and detecting predators. Excessive noise can interfere with these vital behaviors, leading to reduced reproductive success and increased stress levels.
3. Light pollution: Artificial lighting from urban areas can disrupt the natural light-dark cycle, affecting wildlife behavior. Nocturnal animals may experience altered feeding, mating, and migration patterns due to the presence of artificial light. This disruption can have cascading effects on ecosystems, impacting predator-prey relationships and plant-animal interactions.
4. Direct interactions: Human-wildlife interactions, both intentional and unintentional, can have significant impacts on wildlife behavior. Feeding wildlife, approaching too closely, or attempting to interact with wild animals can disrupt their natural behaviors and lead to habituation or aggression. It is important to respect wildlife and maintain a safe distance to minimize disturbance.
5. Climate change: Climate change is a global phenomenon that affects wildlife behavior on multiple levels. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and altered seasonal cycles can disrupt the availability of resources, migration patterns, and breeding behaviors. Understanding the impacts of climate change on wildlife behavior is crucial for implementing effective conservation strategies.
III. Benefits of Positive Human-Wildlife Interaction
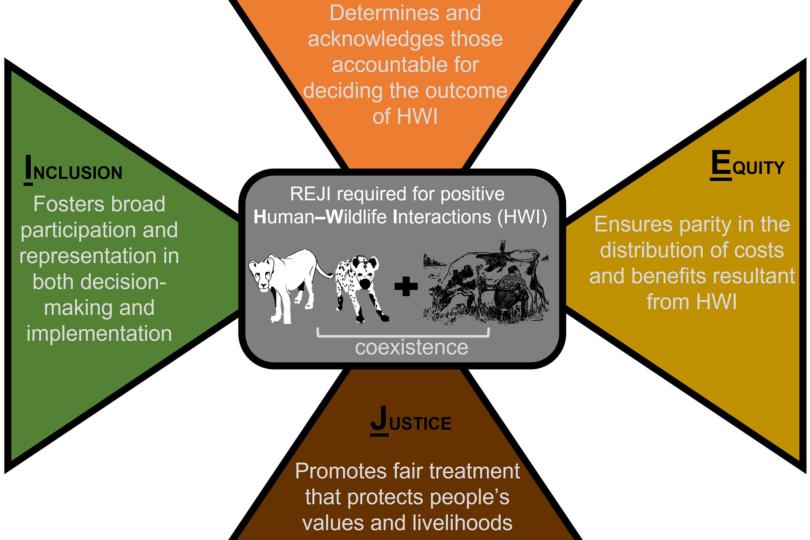
Positive human-wildlife interaction offers a range of benefits that extend beyond the individual and have a positive impact on society as a whole. These benefits can be categorized into four main areas: ecotourism and economic benefits, conservation and biodiversity preservation, education and awareness, and psychological and emotional benefits.
A. Ecotourism and economic benefits
One of the key benefits of positive human-wildlife interaction is its contribution to ecotourism and the resulting economic benefits. When humans have the opportunity to interact with wildlife in a positive and sustainable manner, it attracts tourists from around the world. These tourists not only contribute to the local economy through their spending on accommodation, food, and transportation, but they also support the conservation efforts in the area.
Ecotourism provides a sustainable source of income for local communities, which in turn incentivizes them to protect and preserve the natural habitats of wildlife. By creating jobs and generating revenue, positive human-wildlife interaction helps to alleviate poverty and improve the overall well-being of communities living in wildlife-rich areas.
B. Conservation and biodiversity preservation
Positive human-wildlife interaction plays a crucial role in conservation and biodiversity preservation. When humans have the opportunity to interact with wildlife in a positive and respectful manner, it fosters a sense of connection and responsibility towards the natural world. This connection often leads to increased support for conservation initiatives and a greater understanding of the importance of biodiversity.
By engaging with wildlife in a positive way, humans become more aware of the threats and challenges faced by different species. This awareness can drive individuals, communities, and governments to take action to protect and preserve wildlife habitats. Positive human-wildlife interaction also provides opportunities for scientific research and monitoring, which contribute to our understanding of ecosystems and help inform conservation strategies.
C. Education and awareness
Positive human-wildlife interaction is a powerful tool for education and raising awareness about the importance of wildlife conservation. When humans have the opportunity to observe and learn about wildlife in their natural habitats, it sparks curiosity and a desire to learn more. This curiosity can be harnessed to educate people about the ecological role of different species, the threats they face, and the actions that can be taken to protect them.
Through guided tours, educational programs, and interactive experiences, positive human-wildlife interaction provides a platform for sharing knowledge and fostering a deeper understanding of the natural world. This increased awareness can lead to behavioral changes and a greater commitment to sustainable practices that benefit both wildlife and the environment.
D. Psychological and emotional benefits
Positive human-wildlife interaction has significant psychological and emotional benefits for individuals. Interacting with wildlife in a positive and respectful manner can evoke a sense of awe, wonder, and connection with the natural world. These experiences have been shown to reduce stress, improve mental well-being, and enhance overall quality of life.
Spending time in nature and engaging with wildlife can also promote physical health by encouraging outdoor activities and exercise. Whether it’s birdwatching, hiking, or participating in wildlife conservation projects, positive human-wildlife interaction provides opportunities for individuals to engage in meaningful and fulfilling experiences that contribute to their overall well-being.
IV. Examples of Successful Human-Wildlife Interaction Projects
In this section, we will explore three case studies that highlight successful human-wildlife interaction projects. These projects not only demonstrate the positive outcomes of coexistence between humans and wildlife but also showcase the importance of conservation efforts in preserving our natural world.
A. Case study: Gorilla trekking in Rwanda
Gorilla trekking in Rwanda has become a popular ecotourism activity that allows humans to interact with these magnificent creatures in their natural habitat. The Volcanoes National Park in Rwanda is home to several habituated gorilla families, and visitors have the unique opportunity to observe them up close.
As an avid wildlife enthusiast and conservationist, I had the privilege of participating in a gorilla trekking expedition in Rwanda. The experience was truly awe-inspiring, as I witnessed the intricate social dynamics of the gorilla families and their remarkable intelligence.
During the trek, we were accompanied by experienced guides who ensured that we followed strict guidelines to minimize our impact on the gorillas and their environment. These guidelines included maintaining a safe distance, refraining from touching the gorillas, and avoiding direct eye contact.
Through responsible tourism practices and the revenue generated from gorilla trekking permits, Rwanda has been able to invest in conservation efforts and protect the gorilla population. This has led to a significant increase in gorilla numbers over the years, showcasing the positive impact of human-wildlife interaction projects.
B. Case study: Whale watching in Canada
Whale watching is another example of a successful human-wildlife interaction project that promotes conservation and education. Canada, particularly the coastal regions of British Columbia, is renowned for its diverse marine life, including various whale species.
During my visit to British Columbia, I had the opportunity to embark on a whale watching tour. The tour was led by knowledgeable guides who provided valuable insights into the behavior and conservation status of the whales we encountered.
Whale watching tours in Canada adhere to strict guidelines to ensure the safety and well-being of both the whales and the participants. These guidelines include maintaining a respectful distance, reducing vessel speed, and minimizing noise pollution.
By engaging in responsible whale watching practices, tourists contribute to ongoing research and conservation efforts. The revenue generated from these tours is often reinvested in marine conservation initiatives, such as habitat protection and research programs.
C. Case study: Elephant conservation in Thailand
Thailand is home to a significant population of Asian elephants, and various conservation projects have been implemented to protect these majestic creatures. One such project is the Elephant Nature Park, located in the northern part of the country.
During my visit to the Elephant Nature Park, I witnessed firsthand the dedication and passion of the staff in providing a safe and nurturing environment for rescued elephants. The park focuses on rehabilitation, education, and promoting responsible elephant tourism.
Visitors to the park have the opportunity to observe elephants in their natural habitat, participate in feeding and bathing activities, and learn about the challenges they face in the wild. The park also advocates against activities such as elephant riding and promotes ethical elephant tourism practices.
Through initiatives like the Elephant Nature Park, Thailand has made significant progress in raising awareness about elephant conservation and improving the welfare of captive elephants. These projects highlight the positive impact of human-wildlife interaction in promoting conservation and fostering a deeper understanding of these incredible animals.
V. Responsible Wildlife Tourism Practices
Responsible wildlife tourism practices are crucial for ensuring the well-being of both wildlife and their habitats, as well as supporting local communities and conservation efforts. As an avid wildlife enthusiast and conservationist, I have had the privilege of witnessing the positive impact of responsible wildlife tourism firsthand. In this section, I will delve into the key aspects of responsible wildlife tourism, including minimizing disturbance to wildlife habitats, ethical guidelines for wildlife encounters, and supporting local communities and conservation efforts.
A. Minimizing Disturbance to Wildlife Habitats
One of the fundamental principles of responsible wildlife tourism is minimizing disturbance to wildlife habitats. This involves adopting practices that minimize our impact on the natural environment and ensure the preservation of wildlife habitats for future generations. Here are some key strategies to achieve this:
- Respecting boundaries: When visiting wildlife habitats, it is essential to respect designated boundaries and follow any guidelines or regulations set by local authorities or conservation organizations. These boundaries are put in place to protect sensitive ecosystems and minimize disturbance to wildlife.
- Staying on designated trails: By sticking to designated trails, we can minimize our footprint and avoid trampling on delicate vegetation or disturbing wildlife habitats. Straying off the trails can lead to habitat destruction and disrupt the natural behaviors of wildlife.
- Minimizing noise and disturbance: Loud noises and sudden movements can startle wildlife and disrupt their natural behaviors. It is important to maintain a respectful distance and avoid any actions that may cause unnecessary stress or disturbance to the animals.
- Proper waste disposal: Responsible wildlife tourism also involves proper waste disposal to prevent pollution and habitat degradation. Visitors should always carry out any trash they generate and dispose of it in designated bins or recycling facilities.
B. Ethical Guidelines for Wildlife Encounters
Interacting with wildlife can be a thrilling experience, but it is crucial to ensure that these encounters are conducted ethically and with the well-being of the animals as a top priority. Here are some ethical guidelines to follow when encountering wildlife:
- Observe from a distance: It is important to maintain a safe distance from wildlife to avoid causing stress or harm to the animals. Using binoculars or zoom lenses can allow for a closer view without intruding on their space.
- Do not feed or touch: Feeding wildlife can disrupt their natural diet and behavior, and it can also make them dependent on humans for food. Touching animals can transmit diseases and may cause them distress. It is best to admire wildlife from afar and let them remain wild.
- Do not disturb nesting or breeding areas: During certain times of the year, wildlife may be nesting or breeding. It is important to respect these sensitive periods and avoid approaching or disturbing these areas to ensure the survival and well-being of the species.
- Follow local guidelines: Different wildlife species may have specific guidelines or regulations in place to protect them. It is essential to familiarize yourself with these guidelines and follow them to ensure responsible and ethical wildlife encounters.
C. Supporting Local Communities and Conservation Efforts
Responsible wildlife tourism goes beyond minimizing disturbance and ethical encounters. It also involves actively supporting local communities and conservation efforts. By doing so, we can contribute to the long-term sustainability of wildlife habitats and ensure the well-being of both wildlife and local communities. Here are some ways to support local communities and conservation efforts:
- Choose responsible tour operators: When planning wildlife tours or activities, opt for tour operators that prioritize responsible practices and contribute to local conservation efforts. Look for operators that support local communities and employ knowledgeable guides who prioritize the well-being of wildlife.
- Learn about local cultures: Take the time to learn about the local cultures and traditions of the communities living in or near wildlife habitats. Respect their customs and support local businesses, such as purchasing locally made crafts or products.
- Contribute to conservation organizations: Many conservation organizations rely on donations and support from individuals to carry out their important work. Consider making a contribution to these organizations or volunteering your time to support their initiatives.
- Spread awareness: Use your experiences and knowledge to raise awareness about responsible wildlife tourism and the importance of conservation. Share your stories and insights with others, both online and offline, to inspire more people to engage in responsible practices.
By practicing responsible wildlife tourism, we can ensure that future generations will also have the opportunity to witness the beauty of wildlife in their natural habitats. Let us embrace the principles of minimizing disturbance to wildlife habitats, following ethical guidelines for wildlife encounters, and supporting local communities and conservation efforts. Together, we can make a positive impact on the coexistence of humans and wildlife.
VI. Wildlife Conservation and Habitat Restoration
As a passionate advocate for wildlife conservation and habitat restoration, I firmly believe in the importance of protected areas and wildlife corridors. These designated spaces play a vital role in preserving biodiversity and ensuring the survival of various species.
A. Importance of Protected Areas and Wildlife Corridors
Protected areas, such as national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and nature reserves, serve as havens for wildlife. They provide a safe and secure environment where animals can thrive without the threat of human interference or habitat destruction. These areas are carefully managed to maintain the delicate balance of ecosystems, allowing for the coexistence of different species.
Wildlife corridors, on the other hand, are essential for connecting fragmented habitats. They act as pathways that enable animals to move freely between different areas, facilitating gene flow and promoting genetic diversity. By establishing and maintaining wildlife corridors, we can mitigate the negative effects of habitat fragmentation and ensure the long-term survival of species.
Both protected areas and wildlife corridors are crucial for conserving biodiversity. They provide refuge for endangered species, protect critical habitats, and support the overall health of ecosystems. By safeguarding these areas and maintaining connectivity between them, we can preserve our natural heritage for future generations.
B. Restoring and Preserving Natural Habitats
One of the key aspects of wildlife conservation is the restoration and preservation of natural habitats. Human activities, such as deforestation, urbanization, and pollution, have significantly impacted ecosystems worldwide. It is our responsibility to reverse these detrimental effects and restore the balance of nature.
Restoring natural habitats involves various strategies, including reforestation, wetland rehabilitation, and habitat enhancement. By replanting trees, reintroducing native plant species, and creating suitable conditions for wildlife, we can recreate thriving ecosystems. This not only benefits the flora and fauna but also contributes to climate change mitigation and water resource management.
Preserving natural habitats is equally important. It involves protecting existing ecosystems from further degradation and ensuring their long-term sustainability. This can be achieved through the implementation of sustainable land-use practices, strict regulations, and community involvement. By working together, we can safeguard the habitats that support countless species and maintain the delicate balance of nature.
C. Promoting Sustainable Land-Use Practices
Sustainable land-use practices are essential for the conservation of wildlife and the preservation of natural habitats. These practices aim to minimize the negative impacts of human activities on the environment while meeting the needs of the present and future generations.
One of the key principles of sustainable land-use is the promotion of biodiversity-friendly agriculture. This involves adopting farming techniques that prioritize the conservation of natural resources, minimize the use of chemicals, and protect wildlife habitats. By implementing agroforestry, organic farming, and integrated pest management, we can create a harmonious relationship between agriculture and nature.
Another important aspect of sustainable land-use is the responsible management of forests and other natural resources. This includes sustainable logging practices, protected area management, and the prevention of illegal wildlife trade. By ensuring the sustainable use of these resources, we can maintain the integrity of ecosystems and support the livelihoods of local communities.
Furthermore, sustainable land-use practices also encompass urban planning, infrastructure development, and waste management. By incorporating green spaces, promoting energy efficiency, and reducing waste generation, we can create sustainable cities that coexist with nature.
VII. Coexistence Strategies for Conflict Resolution
Human-wildlife conflict is a complex issue that arises when the needs and behaviors of humans and wildlife intersect, often resulting in negative consequences for both parties. As an experienced wildlife conservationist and researcher, I have witnessed firsthand the causes and impacts of this conflict and have dedicated my career to finding effective solutions. In this section, I will explore the various strategies that can be employed to foster coexistence between humans and wildlife, focusing on non-lethal methods and community-based conservation initiatives.
A. Human-wildlife conflict causes and impacts
Understanding the causes and impacts of human-wildlife conflict is crucial in developing effective coexistence strategies. One of the primary causes of conflict is habitat loss and fragmentation, as human activities such as agriculture, urbanization, and infrastructure development encroach upon wildlife habitats, forcing animals to seek resources in human-dominated landscapes. This often leads to crop damage, livestock predation, and even threats to human safety.
Another significant cause of conflict is competition for resources. As human populations continue to grow, the demand for land, water, and food increases, putting pressure on wildlife populations and their habitats. This competition can result in resource depletion, affecting the survival and well-being of both humans and wildlife.
The impacts of human-wildlife conflict are far-reaching. For communities living in close proximity to wildlife, conflict can lead to economic losses, food insecurity, and increased poverty. Additionally, the loss of crops and livestock can have devastating effects on the livelihoods of farmers and pastoralists, exacerbating existing socio-economic inequalities.
From an ecological perspective, conflict can disrupt natural ecosystems and biodiversity. When wildlife populations are threatened or killed in response to conflict incidents, it can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to cascading effects on other species and ecological processes.
B. Non-lethal methods for managing conflicts
Recognizing the need for sustainable and humane approaches to conflict management, non-lethal methods have gained prominence in recent years. These methods aim to mitigate conflict by reducing negative interactions between humans and wildlife, without resorting to lethal measures. Here are some effective non-lethal strategies:
- 1. Electric fencing: Installing electric fences around agricultural fields and livestock enclosures can deter wildlife from entering and causing damage. The mild electric shock serves as a deterrent without causing harm to the animals.
- 2. Predator deterrents: Various deterrents, such as flashing lights, noise devices, and scent repellents, can be used to discourage predators from approaching human settlements or livestock enclosures.
- 3. Livestock guarding animals: The use of trained guardian animals, such as dogs or llamas, can help protect livestock from predation. These animals establish a presence and deter potential predators.
- 4. Early warning systems: Installing motion sensor cameras or using trained detection dogs can provide early warning of wildlife presence, allowing farmers or communities to take preventive measures before conflicts escalate.
- 5. Habitat management: Implementing habitat management practices, such as creating buffer zones or restoring wildlife corridors, can help reduce human-wildlife interactions by providing alternative habitats and resources for wildlife.
C. Community-based conservation initiatives
Recognizing the importance of engaging local communities in conservation efforts, community-based conservation initiatives have emerged as a successful approach to mitigating human-wildlife conflict. These initiatives involve active participation and empowerment of local communities in decision-making processes and the implementation of conservation measures. Here are some key components of community-based conservation initiatives:
- 1. Education and awareness: Providing education and raising awareness about the importance of wildlife conservation and the benefits of coexistence can help foster positive attitudes towards wildlife among local communities.
- 2. Livelihood diversification: Supporting alternative livelihood options, such as ecotourism, sustainable agriculture, or handicraft production, can reduce communities’ dependence on resources that may attract wildlife and contribute to conflict.
- 3. Conflict resolution mechanisms: Establishing community-led conflict resolution mechanisms, such as community wildlife committees or hotlines, can provide a platform for dialogue and mediation between affected parties.
- 4. Incentive-based programs: Providing incentives, such as compensation for crop or livestock losses, can help alleviate the economic burden on communities and promote tolerance towards wildlife.
- 5. Collaborative partnerships: Building partnerships between local communities, conservation organizations, and government agencies can enhance the effectiveness of conservation initiatives by leveraging collective knowledge, resources, and expertise.
By implementing these non-lethal methods and community-based conservation initiatives, we can foster coexistence between humans and wildlife, ensuring the long-term survival of both. It is essential to recognize that conflict resolution is a dynamic and ongoing process that requires continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation of strategies to address the evolving needs and challenges of both humans and wildlife.
VIII. Best Practices for Wildlife Photography and Filming
As an avid wildlife photographer and filmmaker, I have had the privilege of capturing stunning images and videos of various species in their natural habitats. Throughout my journey, I have learned the importance of respecting wildlife and their habitats, considering ethical considerations when capturing wildlife images, and promoting conservation through visual storytelling. In this section, I will share some best practices that I have developed over the years to ensure that my work contributes to the preservation of wildlife and their ecosystems.
A. Respecting wildlife and their habitats
When engaging in wildlife photography and filming, it is crucial to prioritize the well-being of the subjects and their habitats. Here are some key practices to follow:
- Do thorough research: Before venturing into the field, familiarize yourself with the species you intend to photograph or film. Understand their behavior, habitat requirements, and any specific guidelines or regulations in place for their protection.
- Maintain a safe distance: Respect the personal space of wildlife and avoid causing any distress or disturbance. Use telephoto lenses or binoculars to capture close-up shots without intruding on their natural behavior.
- Stay on designated paths: Stick to established trails and paths to minimize your impact on the environment. Avoid trampling vegetation or disturbing nesting sites.
- Minimize noise and movement: Sudden movements and loud noises can startle wildlife and disrupt their natural activities. Move slowly and quietly to blend into the surroundings.
- Leave no trace: Take all your trash with you and avoid leaving any signs of your presence. Dispose of waste properly and avoid littering.
B. Ethical considerations for capturing wildlife images
As wildlife photographers and filmmakers, we have a responsibility to maintain ethical standards in our work. Here are some important considerations:
- Observe without interfering: Document the natural behavior of wildlife without altering their actions or environment. Avoid baiting, trapping, or manipulating the subjects for the sake of a shot.
- Do not disturb nesting or breeding sites: Breeding and nesting periods are critical for the survival of many species. Refrain from approaching or disturbing these areas to ensure the well-being of the animals and their offspring.
- Avoid stressing wildlife: Be patient and allow wildlife to acclimate to your presence. If an animal shows signs of stress or discomfort, back off and give it space.
- Respect local regulations: Different regions may have specific rules and guidelines for wildlife photography and filming. Familiarize yourself with these regulations and adhere to them at all times.
- Consider the welfare of captive animals: If photographing or filming animals in captivity, ensure that they are kept in appropriate conditions and are not subjected to any form of mistreatment.
C. Promoting conservation through visual storytelling
Visual storytelling is a powerful tool for raising awareness about wildlife conservation. Here are some ways to effectively convey the importance of preserving our natural world:
- Highlight conservation success stories: Showcase the efforts and achievements of individuals, organizations, and communities in protecting and restoring wildlife habitats.
- Document environmental challenges: Shed light on the threats faced by wildlife and their ecosystems, such as habitat loss, climate change, and illegal wildlife trade. Use your images and videos to educate and inspire action.
- Capture the beauty and diversity of wildlife: Showcase the incredible variety of species and habitats to foster appreciation and empathy towards the natural world.
- Collaborate with conservation organizations: Partner with local or international conservation groups to amplify your message and support their initiatives.
- Engage with your audience: Use social media, blogs, or exhibitions to share your work and engage with a wider audience. Encourage dialogue and encourage others to get involved in conservation efforts.
By following these best practices, we can ensure that our wildlife photography and filming endeavors contribute positively to the conservation of our planet’s precious biodiversity. Let us capture the beauty of nature while also working towards its preservation.
IX. Wildlife Rehabilitation and Rescue
Wildlife rehabilitation centers play a crucial role in the conservation and protection of wildlife. These centers serve as a safe haven for injured, orphaned, or sick animals, providing them with the necessary care and treatment to recover and eventually be released back into their natural habitats.
One of the primary roles of wildlife rehabilitation centers is to provide immediate medical attention to injured animals. These centers have trained professionals, including veterinarians and wildlife rehabilitators, who assess the animals’ injuries and develop appropriate treatment plans. They may administer medication, perform surgeries, or provide physical therapy to aid in the animals’ recovery.
Moreover, wildlife rehabilitation centers also play a vital role in educating the public about wildlife conservation. They organize educational programs, workshops, and outreach events to raise awareness about the importance of protecting wildlife and their habitats. By engaging with the community, these centers aim to foster a sense of responsibility and empathy towards wildlife.
Wildlife rescue and rehabilitation involve several steps to ensure the well-being and successful release of animals. The process begins with the rescue of injured or orphaned animals, often reported by concerned individuals or wildlife authorities. Trained rescuers carefully capture the animals and transport them to the rehabilitation center.
Upon arrival at the center, the animals undergo a thorough examination to assess their overall health and determine the extent of their injuries. This examination includes physical examinations, X-rays, and blood tests. Based on the evaluation, the animals are placed in appropriate enclosures or cages that mimic their natural habitats as closely as possible.
The next step in the rehabilitation process is providing the animals with the necessary medical care. This includes administering medication, wound treatment, and physical therapy. The animals are closely monitored by the center’s staff to ensure their progress and adjust the treatment plans accordingly.
In addition to medical care, wildlife rehabilitation centers also focus on providing proper nutrition to the animals. They develop specialized diets that cater to the specific dietary needs of each species, ensuring they receive the necessary nutrients for their recovery.
As the animals regain their strength and demonstrate their ability to survive in the wild, they undergo a process called “pre-release conditioning.” This involves gradually reintroducing them to their natural behaviors, such as hunting or foraging, in controlled environments. The animals are closely observed during this phase to ensure they can fend for themselves before being released.
Success stories of wildlife rehabilitation are inspiring and demonstrate the positive impact these centers have on individual animals and overall conservation efforts. One such success story involves the rehabilitation and release of a bald eagle named Freedom. Freedom was found with a severe wing injury and was unable to fly. After months of intensive care and rehabilitation, including surgery and physical therapy, Freedom made a full recovery. He was successfully released back into the wild, where he continues to thrive.
Another remarkable success story is the rehabilitation of an orphaned baby elephant named Hope. Hope was rescued after her mother was killed by poachers. She was severely malnourished and traumatized. Under the care of a dedicated team of wildlife rehabilitators, Hope received round-the-clock care, including bottle feeding and emotional support. Today, Hope has grown into a healthy and thriving elephant, living in a protected reserve with other elephants.
These success stories highlight the importance of wildlife rehabilitation centers in giving injured or orphaned animals a second chance at life. They demonstrate the dedication and expertise of the staff involved in the rehabilitation process, as well as the positive outcomes that can be achieved through their efforts.
