Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding Human Trafficking
- III. Global Human Trafficking Statistics
- IV. The Impact of Human Trafficking
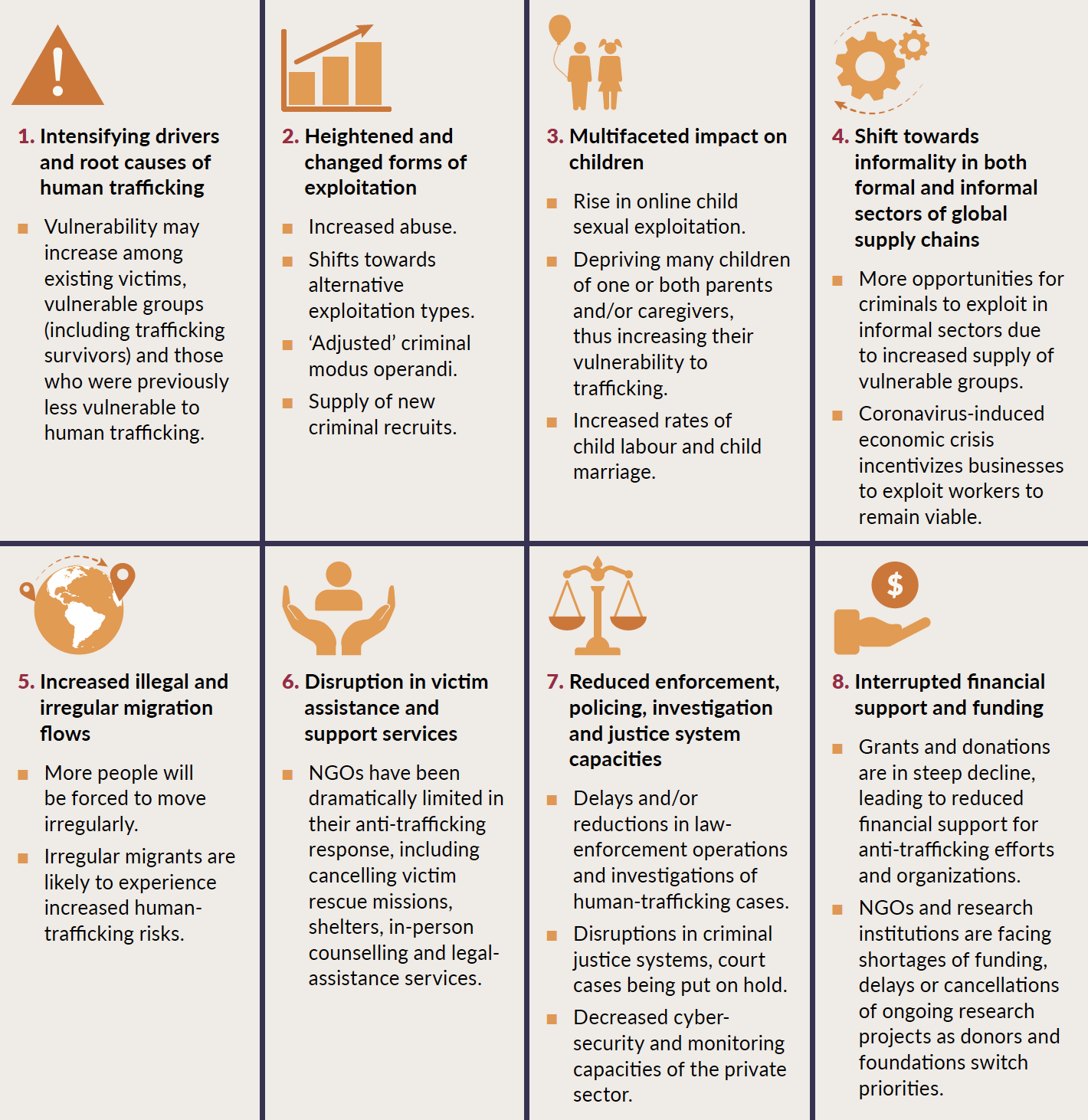
- V. Factors Facilitating Human Trafficking
- VI. The Role of Technology in Human Trafficking
- VII. International Efforts to Combat Human Trafficking
- VIII. Legal Frameworks and Law Enforcement
- IX. Prevention and Awareness
I. Introduction
Human trafficking is a global issue that affects millions of people every year. It is a form of modern-day slavery that involves the recruitment, transportation, and exploitation of individuals through force, fraud, or coercion. This heinous crime is driven by various factors such as poverty, inequality, and the demand for cheap labor and sexual services.
In this article, we will explore the impact of human trafficking and discuss ways to fight against it. We will delve into the devastating consequences faced by victims, the different forms of trafficking, and the underlying causes that perpetuate this crime. Furthermore, we will shed light on the efforts being made by governments, organizations, and individuals to combat human trafficking and support survivors.
By raising awareness and understanding the complexities of human trafficking, we can work towards preventing it and providing assistance to those affected. Together, we can contribute to the global fight against this grave violation of human rights.
II. Understanding Human Trafficking
Human trafficking is a grave violation of human rights that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a complex issue that requires a deep understanding of its various dimensions in order to effectively combat it. In this section, we will explore the different types of human trafficking and the factors that contribute to its prevalence.
A. Types of human trafficking
1. Sex trafficking:
Sex trafficking involves the recruitment, transportation, or harboring of individuals through force, fraud, or coercion for the purpose of sexual exploitation. Victims of sex trafficking are often subjected to physical and sexual abuse, forced into prostitution, and denied their basic human rights.
2. Labor trafficking:
Labor trafficking is the exploitation of individuals through force, fraud, or coercion for the purpose of forced labor. Victims of labor trafficking are often forced to work in industries such as agriculture, construction, domestic work, and manufacturing, under deplorable conditions and for little or no pay.
B. Factors contributing to human trafficking
1. Poverty and economic inequality:
Poverty and economic inequality play a significant role in the prevalence of human trafficking. Individuals living in poverty are more vulnerable to exploitation and are often lured by false promises of better opportunities and higher wages. Lack of economic opportunities and income disparities create a fertile ground for traffickers to exploit vulnerable individuals.
2. Gender inequality:
Gender inequality is a major contributing factor to human trafficking, particularly in the case of sex trafficking. Women and girls are disproportionately affected by trafficking, with many being forced into sexual exploitation. Discrimination, lack of access to education, and limited economic opportunities for women contribute to their vulnerability to trafficking.
3. Political instability:
Political instability and conflict create an environment conducive to human trafficking. Displaced populations, breakdown of law and order, and weak governance provide traffickers with opportunities to exploit vulnerable individuals. In such situations, traffickers often operate with impunity, making it difficult to combat trafficking effectively.
4. Lack of awareness and education:
A lack of awareness and education about the dangers of human trafficking contributes to its perpetuation. Many individuals, especially in marginalized communities, are unaware of the tactics used by traffickers and the rights they are entitled to. Education and awareness programs are crucial in preventing trafficking and empowering individuals to protect themselves and others.
III. Global Human Trafficking Statistics
![]()
Human trafficking is a global issue that affects millions of people worldwide. In this section, we will delve into the global human trafficking statistics, providing an overview of the problem, regional variations, and trends and patterns in human trafficking.
A. Overview of Global Human Trafficking Statistics
Human trafficking is a grave violation of human rights and a lucrative criminal enterprise. According to the International Labour Organization (ILO), an estimated 40.3 million people were victims of modern slavery in 2016. This includes forced labor, forced marriage, and sexual exploitation.
It is important to note that these statistics are just the tip of the iceberg, as human trafficking is a clandestine crime, making it difficult to obtain accurate data. Many victims remain hidden and unidentified, and cases often go unreported.
Furthermore, human trafficking is not limited to any particular region or country. It is a transnational crime that affects every corner of the globe. No country is immune to this heinous crime, whether as a source, transit, or destination country.
Victims of human trafficking come from diverse backgrounds, including men, women, and children. They can be subjected to various forms of exploitation, such as forced labor in industries like agriculture, construction, manufacturing, and domestic work. Additionally, many are forced into the commercial sex industry, including prostitution, pornography, and sex tourism.
B. Regional Variations in Human Trafficking
1. Asia
Asia is a region that experiences high levels of human trafficking. It is both a source and destination for victims, with internal trafficking being prevalent in many countries. The region is known for its large-scale labor migration, which often leads to vulnerable individuals falling prey to traffickers.
Countries like India, China, Thailand, and the Philippines have been identified as major source countries for human trafficking. These countries have large populations and significant economic disparities, making their citizens vulnerable to exploitation.
Moreover, Southeast Asia is a hotspot for sex trafficking, with countries like Thailand, Cambodia, and Vietnam being notorious for their thriving sex trade. The demand for cheap labor and sexual services fuels the trafficking industry in this region.
2. Europe
Europe is a diverse region with varying levels of human trafficking. It serves as both a source and destination for victims, with trafficking networks operating across borders. The European Union (EU) has implemented measures to combat human trafficking, but the problem persists.
Eastern European countries, such as Albania, Moldova, and Ukraine, are known as major source countries for human trafficking. Economic instability, political conflicts, and social vulnerabilities contribute to the high number of victims from these regions.
Western European countries, including Germany, the Netherlands, and the United Kingdom, are often destinations for trafficked individuals. These countries have robust economies and high demand for cheap labor, making them attractive to traffickers.
3. Americas
The Americas, comprising North, Central, and South America, are affected by human trafficking to varying degrees. The region is a source, transit, and destination for victims, with different countries facing distinct challenges.
In North America, the United States and Canada are significant destinations for trafficked individuals. The proximity to Mexico and Central America makes these countries vulnerable to cross-border trafficking. Many victims are forced into labor exploitation, particularly in industries such as agriculture, construction, and hospitality.
In Central and South America, countries like Brazil, Mexico, and Colombia are known for their high levels of human trafficking. Factors such as poverty, political instability, and organized crime contribute to the prevalence of trafficking in these regions.
4. Africa
Africa faces significant challenges in combating human trafficking. The continent is a source, transit, and destination for victims, with internal trafficking being a major concern. Poverty, armed conflicts, and weak governance contribute to the vulnerability of individuals in many African countries.
Countries in West Africa, such as Nigeria, Benin, and Ghana, are known as major source countries for human trafficking. Many victims from these regions are trafficked for forced labor, including domestic servitude, agricultural work, and mining.
Eastern and Southern African countries, including Kenya, Tanzania, and South Africa, also experience high levels of human trafficking. Factors such as high unemployment rates, political instability, and the demand for cheap labor contribute to the problem.
C. Trends and Patterns in Human Trafficking
Human trafficking is a dynamic and evolving crime, with trends and patterns constantly changing. Understanding these trends is crucial for effective prevention and intervention efforts.
One emerging trend is the use of technology in human trafficking. Traffickers exploit the internet and social media platforms to recruit and exploit victims. Online platforms provide anonymity and facilitate the trafficking of individuals for sexual exploitation and forced labor.
Another trend is the increasing involvement of organized criminal networks in human trafficking. These networks operate across borders, making it difficult for law enforcement agencies to dismantle them. They often have sophisticated methods of recruitment, transportation, and exploitation.
Furthermore, there is a growing recognition of the intersectionality of human trafficking with other forms of organized crime, such as drug trafficking and arms smuggling. These criminal activities often overlap, with traffickers diversifying their operations to maximize profits.
It is also important to note the gender dimension of human trafficking. While both men and women can be victims, women and girls are disproportionately affected. They are often trafficked for sexual exploitation, forced marriage, and domestic servitude.
IV. The Impact of Human Trafficking

Human trafficking is a heinous crime that affects millions of people worldwide. Its impact is far-reaching, causing physical and psychological harm to its victims and leading to social and economic consequences that disrupt families and communities. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which human trafficking leaves a lasting impact on individuals and society as a whole.
A. Physical and Psychological Impact on Victims
1. Physical Abuse and Violence
Victims of human trafficking often endure physical abuse and violence at the hands of their traffickers. They are subjected to beatings, sexual assault, and other forms of physical harm. The physical injuries sustained during trafficking can range from bruises and broken bones to more severe injuries that require medical attention.
These acts of violence not only cause immediate physical pain but also leave lasting scars, both physically and emotionally. Victims may suffer from chronic pain, disabilities, and long-term health issues as a result of the abuse they have endured.
2. Emotional Trauma and Mental Health Issues
The emotional trauma inflicted upon victims of human trafficking is profound. They are stripped of their freedom, dignity, and basic human rights, leading to feelings of fear, helplessness, and despair. The constant threat of violence and the loss of control over their own lives can have severe psychological consequences.
Many survivors of human trafficking experience post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), depression, anxiety, and other mental health disorders. The trauma they have endured can have a long-lasting impact on their ability to trust others, form healthy relationships, and reintegrate into society.
B. Social and Economic Consequences
1. Disruption of Families and Communities
Human trafficking tears families apart and disrupts entire communities. When a person is trafficked, their loved ones are left behind, often unaware of their whereabouts or well-being. This separation causes immense emotional distress and can lead to a breakdown in family structures.
Children who are trafficked may be separated from their parents or caregivers, leaving them vulnerable to further exploitation and abuse. The loss of familial support and stability can have long-term effects on their development and well-being.
Communities that are plagued by human trafficking also suffer. The presence of trafficking networks can create an environment of fear and mistrust, eroding the social fabric of the community. This can hinder community development and make it difficult for individuals to seek help or report instances of trafficking.
2. Economic Exploitation and Loss of Income
Human trafficking is driven by profit, and victims are often subjected to economic exploitation. They may be forced to work in exploitative conditions, such as sweatshops, farms, or brothels, with little or no pay. This loss of income not only affects the individual victim but also has broader economic implications.
Furthermore, the economic impact of human trafficking extends beyond the immediate victims. Trafficking undermines legitimate businesses, distorts labor markets, and perpetuates a cycle of poverty and inequality. It hinders economic growth and development, making it a pressing issue that requires comprehensive solutions.
V. Factors Facilitating Human Trafficking

In this section, we will explore the various factors that facilitate human trafficking. It is important to understand these factors in order to effectively combat this heinous crime and protect vulnerable individuals from falling victim to it.
A. Demand for cheap labor and sexual services
One of the key factors that facilitates human trafficking is the demand for cheap labor and sexual services. Traffickers exploit this demand by recruiting and exploiting individuals who are desperate for work or who are forced into the sex trade against their will.
The demand for cheap labor is often driven by industries that prioritize profit over the well-being of workers. These industries may include agriculture, construction, manufacturing, and domestic work. Traffickers take advantage of vulnerable individuals who are seeking employment opportunities and subject them to exploitative working conditions, including long hours, low wages, and physical abuse.
Similarly, the demand for sexual services fuels the trafficking of individuals, particularly women and children, into the sex trade. Traffickers prey on individuals who are vulnerable, such as those living in poverty, those who have experienced abuse or neglect, or those who are seeking better economic opportunities. These victims are coerced, manipulated, and forced into prostitution, often enduring physical and psychological abuse.
B. Corruption and complicity
Corruption and complicity within law enforcement agencies, government officials, and other authorities play a significant role in facilitating human trafficking. Traffickers often bribe or coerce officials to turn a blind eye to their criminal activities or to provide them with protection.
Corrupt officials may intentionally fail to investigate or prosecute cases of human trafficking, allowing traffickers to operate with impunity. This lack of accountability enables traffickers to continue exploiting vulnerable individuals and perpetuating the cycle of trafficking.
Furthermore, complicity among individuals within communities can also facilitate human trafficking. In some cases, community members may be aware of trafficking activities but choose to remain silent out of fear, indifference, or even complicity. This silence allows traffickers to operate discreetly and continue victimizing others.
C. Inadequate legal frameworks and law enforcement
The presence of inadequate legal frameworks and weak law enforcement contributes to the facilitation of human trafficking. Without robust legislation and effective enforcement mechanisms, traffickers can operate with little fear of being apprehended or punished.
Many countries lack comprehensive anti-trafficking laws or have laws that are not effectively implemented. This creates loopholes that traffickers exploit to evade prosecution. In addition, limited resources allocated to law enforcement agencies hinder their ability to effectively investigate and combat human trafficking.
Furthermore, the transnational nature of human trafficking poses additional challenges for law enforcement. Traffickers often operate across borders, making it difficult to coordinate efforts and apprehend them. This lack of international cooperation and coordination further facilitates the trafficking of individuals.
D. Lack of victim support and rehabilitation services
The lack of adequate victim support and rehabilitation services is another factor that facilitates human trafficking. Survivors of trafficking often face numerous challenges, including physical and psychological trauma, social stigma, and limited access to essential services.
Many survivors struggle to reintegrate into society due to the lack of specialized support and rehabilitation programs. These programs should address the unique needs of survivors, including medical and mental health care, education and vocational training, safe housing, and legal assistance.
Without proper support systems in place, survivors are at a higher risk of re-victimization and may find it difficult to break free from the cycle of trafficking. It is crucial to invest in comprehensive and survivor-centered support services to ensure the recovery and empowerment of survivors.
VI. The Role of Technology in Human Trafficking
Technology has played a significant role in the proliferation of human trafficking, both in terms of recruitment and facilitating trafficking activities. The internet and social media platforms have become powerful tools for traffickers to target vulnerable individuals and carry out their illicit activities. However, technology also presents opportunities for combating human trafficking and raising awareness about this heinous crime.
The internet and social media platforms have revolutionized the way people connect and communicate, but they have also provided traffickers with new avenues for recruitment. These platforms allow traffickers to easily reach a large audience and exploit individuals who may be seeking better opportunities or are in vulnerable situations.
Through deceptive tactics, traffickers lure their victims by promising them jobs, education, or a better life. They create fake profiles and use persuasive techniques to gain the trust of potential victims. By leveraging the anonymity and reach of the internet, traffickers can target individuals from different geographical locations and exploit their vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, social media platforms provide traffickers with an opportunity to showcase their victims and attract clients. They may post misleading advertisements or use coded language to advertise individuals for sexual exploitation or forced labor. The ease of sharing information and connecting with potential clients makes it difficult for law enforcement agencies to track and apprehend these criminals.
B. Online platforms facilitating trafficking activities
While the internet and social media platforms have become recruitment tools for traffickers, there are also online platforms specifically designed to facilitate trafficking activities. These platforms provide a marketplace for buying and selling individuals, making it easier for traffickers to operate discreetly.
One such example is the dark web, a hidden part of the internet that requires specific software to access. The dark web provides a platform for illegal activities, including human trafficking. Here, traffickers can communicate anonymously, exchange information, and even conduct financial transactions without leaving a digital trace.
Additionally, online classified ad websites have been misused by traffickers to advertise individuals for sexual exploitation or forced labor. These websites, which were originally created to facilitate legitimate transactions, have become a breeding ground for human trafficking. Despite efforts to regulate and monitor these platforms, traffickers find ways to circumvent the rules and continue their illicit activities.
C. Challenges and opportunities for combating human trafficking online
The rise of technology has presented both challenges and opportunities for combating human trafficking. On one hand, the fast-paced nature of the internet and the ever-evolving tactics used by traffickers make it difficult for law enforcement agencies to keep up. The anonymity provided by the internet also poses challenges in identifying and apprehending traffickers.
However, technology also provides opportunities for raising awareness, detecting trafficking activities, and supporting survivors. Social media platforms can be used to educate the public about the signs of human trafficking and provide resources for reporting suspicious activities. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and law enforcement agencies can leverage technology to monitor online platforms and identify potential traffickers.
Furthermore, advancements in artificial intelligence and data analytics can be utilized to detect patterns and identify potential victims. By analyzing online data, law enforcement agencies can identify common recruitment tactics and target their efforts accordingly. Technology can also be used to provide support to survivors, through online counseling services and platforms that connect them with resources and assistance.
VII. International Efforts to Combat Human Trafficking
In the fight against human trafficking, international cooperation is crucial. Various organizations and initiatives have been established to address this global issue. This section will explore the efforts made by the United Nations (UN), regional and bilateral cooperation, and the role of non-governmental organizations (NGOs).
A. United Nations initiatives and conventions
The United Nations has been at the forefront of combating human trafficking through various initiatives and conventions. One of the key initiatives is the United Nations Global Plan of Action to Combat Trafficking in Persons. This plan provides a comprehensive framework for member states to prevent trafficking, protect victims, and prosecute traffickers.
Additionally, the UN has established the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) to coordinate global efforts against human trafficking. The UNODC works closely with member states to strengthen legal frameworks, enhance law enforcement capacity, and provide support to victims.
Furthermore, the UN has adopted several conventions to address different aspects of human trafficking. The Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children, also known as the Palermo Protocol, is one of the most significant international legal instruments in this field. It provides a comprehensive definition of human trafficking and sets out measures to prevent and combat it.
The UN also monitors the implementation of these initiatives and conventions through the United Nations Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR). The OHCHR works to ensure that member states fulfill their obligations and take effective measures to combat human trafficking.
B. Regional and bilateral cooperation
In addition to the UN’s efforts, regional and bilateral cooperation plays a crucial role in combating human trafficking. Countries often collaborate with their neighbors and international partners to share information, coordinate law enforcement efforts, and provide mutual assistance.
Regional organizations, such as the European Union (EU), the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), and the Organization of American States (OAS), have developed frameworks and action plans to address human trafficking within their respective regions.
Bilateral agreements between countries also facilitate cooperation in combating human trafficking. These agreements can include provisions for joint investigations, extradition of traffickers, and mutual legal assistance.
Furthermore, countries may establish joint task forces or working groups to enhance collaboration and exchange best practices in combating human trafficking.
C. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and their role
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a vital role in the fight against human trafficking. They provide essential support to victims, raise awareness, advocate for policy changes, and collaborate with governments and international organizations.
NGOs often operate on the ground, providing direct assistance to survivors of trafficking. They offer shelter, medical care, legal aid, and rehabilitation services to help victims recover and reintegrate into society.
Moreover, NGOs engage in advocacy and lobbying efforts to raise awareness about human trafficking and push for stronger legislation and policies. They work closely with governments to ensure the protection of victims’ rights and the prosecution of traffickers.
NGOs also contribute to capacity building by providing training and technical assistance to law enforcement agencies, social workers, and other professionals involved in combating human trafficking.
VIII. Legal Frameworks and Law Enforcement
In the fight against human trafficking, it is crucial to have strong legal frameworks and effective law enforcement strategies in place. This section provides an overview of international and national laws related to human trafficking, highlights the challenges in enforcing anti-trafficking laws, and explores effective law enforcement strategies and best practices.
A. Overview of international and national laws
Human trafficking is a global issue that requires a coordinated international response. Various international conventions and protocols have been established to combat human trafficking and protect the rights of victims. One such example is the United Nations Protocol to Prevent, Suppress and Punish Trafficking in Persons, Especially Women and Children, also known as the Palermo Protocol.
The Palermo Protocol, adopted in 2000, defines human trafficking and sets out the obligations of states to prevent and combat this crime. It emphasizes the importance of international cooperation and provides a comprehensive framework for addressing the various aspects of human trafficking, including prevention, prosecution, and protection of victims.
In addition to international laws, many countries have enacted their own legislation to address human trafficking. These laws criminalize trafficking-related activities and provide legal remedies for victims. They also establish mechanisms for cooperation between law enforcement agencies, non-governmental organizations, and other stakeholders.
It is important for countries to have robust legal frameworks that are in line with international standards and adequately address the complexities of human trafficking. This includes defining trafficking offenses, providing for the protection and assistance of victims, and ensuring effective prosecution of traffickers.
B. Challenges in enforcing anti-trafficking laws
Enforcing anti-trafficking laws poses various challenges for law enforcement agencies. Human trafficking is a clandestine crime that often operates in the shadows, making it difficult to detect and investigate. Traffickers use sophisticated methods to exploit their victims and evade law enforcement authorities.
One of the major challenges is the lack of awareness and understanding of human trafficking among law enforcement personnel. Many officers may not be familiar with the signs of trafficking or may not prioritize it due to competing demands and limited resources. This can result in missed opportunities to identify and rescue victims.
Another challenge is the transnational nature of human trafficking. Traffickers often operate across borders, making it necessary for law enforcement agencies to collaborate and share information with their counterparts in other countries. This requires effective coordination and cooperation mechanisms, as well as the exchange of intelligence and evidence.
Furthermore, the fear and intimidation tactics used by traffickers can deter victims from coming forward and cooperating with law enforcement. This can make it challenging to gather evidence and build strong cases against traffickers.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that involves training and capacity building for law enforcement personnel, raising awareness among the general public, and strengthening international cooperation mechanisms.
C. Effective law enforcement strategies and best practices
Despite the challenges, there are several effective law enforcement strategies and best practices that have been proven to be successful in combating human trafficking.
First and foremost, proactive and victim-centered approaches are essential. This involves actively identifying and reaching out to potential victims, providing them with support and assistance, and ensuring their safety and well-being. Law enforcement agencies should prioritize the protection of victims and work closely with victim service providers to ensure their needs are met.
Collaboration and information sharing between law enforcement agencies, non-governmental organizations, and other stakeholders is also crucial. This includes establishing specialized units or task forces dedicated to combating human trafficking, as well as formalizing partnerships and cooperation agreements.
Training and capacity building for law enforcement personnel is another key element. This includes providing officers with the necessary knowledge and skills to identify and investigate trafficking cases, as well as sensitizing them to the needs and vulnerabilities of victims.
Technology can also play a significant role in enhancing law enforcement efforts. The use of advanced analytics, data sharing platforms, and digital tools can help identify patterns and trends, facilitate information exchange, and support investigations.
Lastly, public awareness campaigns and community engagement initiatives are important in preventing human trafficking and encouraging reporting. By educating the public about the signs of trafficking and the importance of reporting suspicions, law enforcement agencies can tap into a valuable source of information and increase their chances of identifying and apprehending traffickers.
IX. Prevention and Awareness
Human trafficking is a grave issue that affects millions of people worldwide. It is a violation of human rights and a form of modern-day slavery. In order to combat this heinous crime, prevention and awareness play a crucial role. In this section, we will explore the importance of prevention, education and awareness campaigns, and empowering vulnerable communities and individuals.
A. Importance of prevention in combating human trafficking
Prevention is the key to addressing human trafficking effectively. By taking proactive measures, we can reduce the vulnerability of individuals and communities to trafficking. Prevention efforts should focus on various aspects, including:
- Addressing root causes: Poverty, lack of education, unemployment, and social inequality are some of the underlying factors that make individuals susceptible to trafficking. By addressing these root causes, we can create a more resilient society.
- Legislation and law enforcement: Strong laws and effective law enforcement are essential in deterring traffickers and ensuring justice for victims. Governments should enact and enforce comprehensive anti-trafficking laws to create a deterrent effect.
- Border control and migration policies: Strengthening border control and implementing fair and humane migration policies can help prevent trafficking. By ensuring safe and legal migration channels, we can reduce the risk of exploitation.
- Collaboration and international cooperation: Human trafficking is a transnational crime that requires a coordinated response. Governments, civil society organizations, and international bodies should work together to share information, resources, and best practices.
By prioritizing prevention efforts, we can disrupt the operations of traffickers and protect potential victims from falling into their traps.
B. Education and awareness campaigns
Education and awareness campaigns play a crucial role in combating human trafficking. By raising public awareness, we can empower individuals to recognize the signs of trafficking and take action. Some key aspects of effective education and awareness campaigns include:
- Targeted outreach: Campaigns should be tailored to specific demographics and communities that are at higher risk of trafficking. This includes vulnerable groups such as migrants, children, and women.
- Information dissemination: Providing accurate and up-to-date information about human trafficking, its consequences, and available support services is essential. This can be done through various channels, including social media, community events, and educational institutions.
- Training and capacity building: Equipping frontline professionals, such as law enforcement officers, social workers, and healthcare providers, with the necessary knowledge and skills to identify and respond to trafficking cases is crucial.
- Partnerships with media: Collaboration with media outlets can help amplify the message and reach a wider audience. Media can play a vital role in exposing trafficking networks, sharing survivor stories, and advocating for policy changes.
Education and awareness campaigns should be ongoing and sustained to ensure a lasting impact. By empowering individuals with knowledge, we can create a society that is vigilant and actively involved in the fight against human trafficking.
C. Empowering vulnerable communities and individuals
Empowering vulnerable communities and individuals is a crucial aspect of combating human trafficking. By addressing the underlying factors that make individuals susceptible to trafficking, we can create a more resilient society. Some key strategies for empowerment include:
- Access to education and skills training: Providing quality education and skills training opportunities can empower individuals to secure better livelihoods and reduce their vulnerability to trafficking.
- Economic empowerment: Creating economic opportunities, such as microfinance programs and vocational training, can help individuals break free from the cycle of poverty and exploitation.
- Support for survivors: Ensuring comprehensive support services for survivors of trafficking, including shelter, healthcare, counseling, and legal assistance, is essential for their recovery and reintegration into society.
- Community engagement: Engaging with communities and involving them in anti-trafficking initiatives can foster a sense of ownership and collective responsibility. Community-led interventions are often more effective in addressing local challenges.
Empowerment should be holistic and multidimensional, addressing not only the immediate needs of individuals but also the structural barriers that perpetuate trafficking. By empowering vulnerable communities and individuals, we can create a society that is resilient and less susceptible to exploitation.

