Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding Human-Wildlife Conflict
- III. The Role of Research in Understanding Human-Wildlife Interaction
- IV. Impacts of Human-Wildlife Interaction
- V. Strategies for Mitigating Human-Wildlife Conflict
- VI. The Role of Technology in Understanding Human-Wildlife Interaction
- VII. Best Practices for Coexistence with Wildlife
- VIII. Case Studies of Human-Wildlife Coexistence
- IX. The Importance of Public Engagement in Research and Conservation
- A. Citizen science initiatives
- B. Public participation in decision-making processes
- C. Advocacy and outreach programs
- 1. How can I prevent wildlife from entering my property?
- 2. What should I do if I encounter a dangerous wild animal?
- 3. How can I support conservation efforts for endangered species?
- 4. Are there any legal protections for wildlife?
- 5. How does climate change affect human-wildlife interaction?
- 6. What are the most effective methods for reducing human-wildlife conflict?
- 7. Can human-wildlife conflict be completely eliminated?
- 8. How can I report wildlife sightings or incidents?
- 9. What are the ethical considerations in wildlife research?
- 10. How can I get involved in research on human-wildlife interaction?
I. Introduction

Welcome to the world of human-wildlife interaction! This fascinating field of study explores the complex relationship between humans and the wildlife that surrounds us. From the majestic elephants of Africa to the playful dolphins of the ocean, our interactions with these creatures have a profound impact on both their lives and ours.
In this article, we will delve into the importance of research in understanding human-wildlife interaction. By examining the various aspects of this relationship, we can gain valuable insights into how to coexist harmoniously with the natural world.
Humans have been interacting with wildlife for centuries, but it is only in recent years that we have begun to truly appreciate the significance of these interactions. Research plays a crucial role in shedding light on the complexities of this relationship, helping us to understand the ecological, social, and economic implications.
Through research, we can gain a deeper understanding of the behaviors, habitats, and needs of wildlife species. This knowledge allows us to develop effective conservation strategies, mitigate conflicts, and promote sustainable practices.
Furthermore, research helps us to assess the impact of human activities on wildlife populations. By studying the effects of habitat loss, pollution, climate change, and other factors, we can identify the threats facing wildlife and take appropriate measures to protect them.
In the following sections of this article, we will explore the different dimensions of human-wildlife interaction and discuss the importance of research in each area. From understanding animal behavior to managing conflicts, research is the key to fostering a harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife.
II. Understanding Human-Wildlife Conflict

Human-wildlife conflict refers to the negative interactions between humans and wildlife that arise when their interests and needs overlap. This conflict can occur in various forms, from property damage and livestock predation to threats to human safety and the conservation of wildlife populations. To gain a deeper understanding of this complex issue, it is crucial to explore its definition, examples, factors contributing to its occurrence, and real-life case studies.
A. Definition and examples of human-wildlife conflict
Human-wildlife conflict encompasses a wide range of situations where the interests of humans and wildlife clash. It occurs when wildlife’s natural behaviors or habitat requirements come into conflict with human activities or needs. This conflict can manifest in different ways, such as:
- Crop raiding: Wildlife, such as elephants, monkeys, or wild boars, damaging agricultural crops, leading to economic losses for farmers.
- Livestock predation: Predatory animals, including wolves, lions, or coyotes, attacking and killing livestock, impacting the livelihoods of farmers and herders.
- Human injuries or fatalities: Wildlife, such as bears or snakes, posing a threat to human safety, resulting in injuries or even loss of life.
- Conflicts over resources: Competition between humans and wildlife for limited resources, such as water, food, or space, leading to conflicts and negative impacts on both parties.
These are just a few examples of the diverse scenarios that fall under the umbrella of human-wildlife conflict. Each situation is unique and requires careful analysis to develop effective strategies for mitigation and coexistence.
B. Factors contributing to human-wildlife conflict
Several factors contribute to the occurrence and escalation of human-wildlife conflict. Understanding these factors is crucial for devising sustainable solutions. The following are key factors that play a significant role:
1. Habitat loss and fragmentation
As human populations expand and urbanization encroaches upon natural habitats, wildlife face shrinking and fragmented spaces. This loss and fragmentation of habitat force wildlife to seek resources in human-dominated landscapes, increasing the likelihood of conflict. The destruction of natural habitats also disrupts ecological balance, leading to changes in wildlife behavior and movement patterns.
2. Competition for resources
Competition for limited resources, such as water, food, and shelter, can intensify human-wildlife conflict. As human activities alter landscapes and deplete resources, wildlife may venture into human settlements in search of sustenance. This competition for resources can result in damage to property, agricultural crops, and livestock, leading to economic losses for humans and retaliatory actions against wildlife.
3. Human activities and behavior
Human activities and behavior can significantly influence the occurrence of human-wildlife conflict. Factors such as improper waste management, habitat encroachment, and the illegal wildlife trade can disrupt ecosystems and attract wildlife to human settlements. Additionally, human behavior, such as feeding or approaching wildlife, can habituate animals to human presence, increasing the risk of conflict.
C. Case studies of human-wildlife conflict
Examining real-life case studies provides valuable insights into the complexities of human-wildlife conflict and the diverse approaches taken to address it. Let’s explore a few notable examples:
1. Human-elephant conflict in India
In India, the conflict between humans and elephants has been a long-standing issue. As elephants’ natural habitats shrink due to deforestation and land conversion, they increasingly come into contact with human settlements. This conflict has resulted in crop damage, economic losses for farmers, and occasional human casualties. Conservation organizations and local communities have implemented measures such as elephant-proof trenches, early warning systems, and community-based conservation initiatives to mitigate this conflict.
2. Predation on livestock by wolves in North America
The predation of livestock by wolves in North America has been a contentious issue. Ranchers and farmers often suffer financial losses due to wolf attacks on their livestock. To address this conflict, various strategies have been employed, including the use of non-lethal deterrents, compensation programs for livestock losses, and collaborative efforts between stakeholders to promote coexistence and minimize the negative impacts on both wolves and livestock.
3. Human-carnivore conflict in Africa
Africa is home to numerous large carnivores, such as lions, leopards, and hyenas, which often come into conflict with local communities. Livestock predation and threats to human safety are common issues in areas where humans and carnivores share landscapes. Conservation organizations and governments have implemented measures such as predator-proof enclosures, community-based conservation programs, and education initiatives to reduce conflict and promote harmonious coexistence.
These case studies highlight the complexity of human-wildlife conflict and the importance of context-specific solutions. By studying and learning from these examples, we can develop effective strategies to mitigate conflict, protect wildlife, and ensure the well-being of both humans and animals.
III. The Role of Research in Understanding Human-Wildlife Interaction
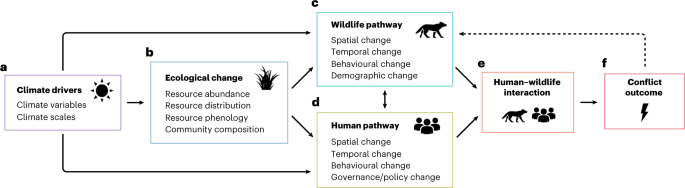
Research plays a crucial role in understanding human-wildlife interaction. By conducting scientific studies and collecting data, researchers can gain valuable insights into the dynamics of this relationship. This section will explore the importance of scientific studies and data collection, as well as the methods used in researching human-wildlife interaction. Additionally, we will delve into some examples of research projects that have shed light on this fascinating field.
A. Importance of scientific studies and data collection
Scientific studies and data collection are essential for understanding human-wildlife interaction. These studies provide a systematic and evidence-based approach to studying the complex dynamics between humans and wildlife. By collecting data, researchers can analyze patterns, trends, and behaviors, allowing them to make informed decisions and recommendations for conservation efforts.
One of the key benefits of scientific studies is that they provide a standardized framework for data collection and analysis. This ensures that the findings are reliable and can be replicated by other researchers. Moreover, scientific studies often involve rigorous methodologies and statistical analyses, further enhancing the credibility of the research.
Furthermore, data collection allows researchers to identify the factors that influence human-wildlife interaction. By understanding these factors, conservationists and policymakers can develop strategies to mitigate conflicts and promote coexistence between humans and wildlife.
B. Methods used in researching human-wildlife interaction
Researchers employ various methods to study human-wildlife interaction. These methods allow them to gather data on the behavior, ecology, and impact of wildlife on human populations. Some commonly used methods include:
- Surveys and questionnaires: Surveys and questionnaires are valuable tools for gathering information about human perceptions, attitudes, and experiences with wildlife. They can provide insights into the level of tolerance, conflicts, and interactions between humans and wildlife.
- Camera trapping and tracking: Camera trapping involves setting up motion-activated cameras in wildlife habitats to capture images and videos of animals. This method helps researchers study wildlife behavior, population dynamics, and movement patterns. Tracking, on the other hand, involves attaching GPS collars or tags to animals to monitor their movements and understand their interactions with human settlements.
- Genetic analysis: Genetic analysis involves collecting samples, such as hair, feathers, or scat, from wildlife and analyzing their DNA. This method helps researchers determine population structure, genetic diversity, and relatedness among individuals. It also aids in identifying the source of conflicts and understanding the impact of human activities on wildlife populations.
- Remote sensing and GIS: Remote sensing uses satellite imagery and aerial photography to study changes in land cover, habitat fragmentation, and human encroachment on wildlife habitats. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) allow researchers to analyze and visualize spatial data, helping them identify areas of high human-wildlife interaction and prioritize conservation efforts.
C. Examples of research projects on human-wildlife interaction
Several research projects have significantly contributed to our understanding of human-wildlife interaction. One such project is the Yellowstone Wolf Project, which aimed to study the reintroduction of wolves into Yellowstone National Park. Researchers collected data on the wolves’ impact on the ecosystem, their interactions with other wildlife, and their influence on visitor experiences. The project’s findings highlighted the crucial role of predators in maintaining ecosystem balance and provided insights into the complex relationships between predators, prey, and humans.
Another notable research project is the Human-Elephant Conflict Mitigation Project in Asia. This project focused on understanding the factors contributing to conflicts between humans and elephants and developing effective mitigation strategies. Through surveys, camera trapping, and GIS analysis, researchers identified key areas of conflict, implemented early warning systems, and promoted community-based conservation initiatives. The project’s success in reducing human-elephant conflicts serves as a model for other regions facing similar challenges.
IV. Impacts of Human-Wildlife Interaction

Human-wildlife interaction has wide-ranging impacts on various aspects of our society and the environment. In this section, we will explore the ecological, economic, and social impacts of such interactions.
A. Ecological impacts
1. Disruption of natural ecosystems
Human-wildlife interaction often leads to the disruption of natural ecosystems. As human activities encroach upon wildlife habitats, it can result in habitat loss and fragmentation. This can have detrimental effects on the biodiversity and overall health of ecosystems. When natural habitats are destroyed or altered, it can disrupt the delicate balance of species interactions and ecological processes.
2. Changes in species distribution and abundance
Human-wildlife interaction can also cause changes in the distribution and abundance of species. As human populations expand and encroach upon wildlife habitats, it can force animals to adapt or relocate. This can lead to shifts in the distribution of species, as well as changes in their population sizes. Some species may thrive in human-altered environments, while others may struggle to survive.
B. Economic impacts
1. Crop and livestock damage
Human-wildlife interaction can have significant economic impacts, particularly in agricultural areas. Wildlife, such as deer, rabbits, and birds, can cause extensive damage to crops and livestock. This can result in financial losses for farmers and impact food production. Farmers often have to implement various measures to deter wildlife from their fields, such as installing fences or using scare tactics.
2. Tourism and conservation revenue
On the other hand, human-wildlife interaction can also have positive economic impacts. Many regions around the world rely on wildlife tourism as a major source of revenue. People are drawn to areas with diverse wildlife populations, such as national parks and wildlife reserves. This creates opportunities for tourism-related businesses, such as hotels, restaurants, and tour operators. Additionally, conservation efforts aimed at protecting wildlife can also generate revenue through donations and grants.
C. Social impacts
1. Threats to human safety
Human-wildlife interaction can pose risks to human safety. Encounters with certain wildlife species, such as large predators or venomous snakes, can be dangerous and even fatal. In areas where human settlements overlap with wildlife habitats, conflicts can arise. Measures are often taken to minimize these risks, such as implementing wildlife management strategies and educating the public about coexisting safely with wildlife.
2. Cultural and psychological effects
Human-wildlife interaction is not only about the physical impacts but also has cultural and psychological effects. Wildlife plays a significant role in many cultures and traditions around the world. The loss of certain species or the degradation of their habitats can have profound cultural implications. Additionally, wildlife can provide psychological benefits to people, such as a sense of connection with nature and opportunities for recreation and relaxation.
V. Strategies for Mitigating Human-Wildlife Conflict
Human-wildlife conflict is a pressing issue that requires effective strategies to minimize negative interactions between humans and wildlife. In this section, we will explore various approaches to mitigate human-wildlife conflict, including habitat management and restoration, non-lethal deterrents and exclusion methods, community-based conservation initiatives, policy and legislation, and case studies of successful conflict mitigation efforts.
A. Habitat management and restoration
Habitat management and restoration play a crucial role in mitigating human-wildlife conflict. By enhancing and protecting natural habitats, we can provide wildlife with suitable environments, reducing the likelihood of them encroaching into human settlements in search of resources.
One effective strategy is the creation of wildlife corridors, which are strips of land that connect fragmented habitats. These corridors enable animals to move freely between different areas, reducing the chances of conflicts with humans. Additionally, restoring degraded habitats and implementing sustainable land-use practices can help maintain a balance between human needs and wildlife conservation.
B. Non-lethal deterrents and exclusion methods
Non-lethal deterrents and exclusion methods are essential tools for preventing human-wildlife conflicts. These strategies aim to discourage wildlife from entering human settlements or agricultural areas without causing harm to the animals.
One commonly used method is the installation of electric fences around vulnerable areas. These fences emit a mild electric shock when touched, creating a deterrent for wildlife. Other non-lethal deterrents include noise devices, such as sirens or ultrasonic devices, which can startle and repel animals.
Exclusion methods involve the use of physical barriers to prevent wildlife access to certain areas. For example, constructing fences around crops or using netting to protect livestock can effectively reduce conflicts. It is important to ensure that these methods are well-maintained and regularly assessed to remain effective.
C. Community-based conservation initiatives
Community-based conservation initiatives empower local communities to actively participate in wildlife conservation efforts. By involving communities in decision-making processes and providing them with incentives for conservation, these initiatives can help reduce human-wildlife conflicts.
One approach is to establish community conservancies, where local communities manage and benefit from wildlife resources. This not only fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility but also provides economic opportunities through ecotourism and sustainable resource utilization.
Education and awareness programs are also crucial components of community-based conservation. By educating communities about the importance of wildlife and providing them with tools to coexist peacefully, we can foster a culture of tolerance and understanding.
D. Policy and legislation
Effective policies and legislation are vital for addressing human-wildlife conflict at a broader scale. Governments and regulatory bodies play a key role in developing and implementing regulations that protect both humans and wildlife.
These policies can include measures such as zoning regulations, which designate specific areas for human settlements and wildlife habitats. By separating these areas, conflicts can be minimized. Additionally, regulations can be put in place to control the hunting or poaching of wildlife, ensuring their populations remain stable.
Collaboration between different stakeholders, including government agencies, conservation organizations, and local communities, is essential for the successful implementation of policies and legislation.
E. Case studies of successful conflict mitigation efforts
Examining case studies of successful conflict mitigation efforts can provide valuable insights and inspiration for addressing human-wildlife conflict in different contexts. These case studies highlight innovative strategies and best practices that have effectively reduced conflicts and promoted coexistence.
For example, in Kenya’s Maasai Mara National Reserve, the establishment of predator-proof bomas (livestock enclosures) has significantly reduced livestock predation by carnivores. Similarly, in India’s Kaziranga National Park, the implementation of anti-poaching measures, community engagement, and habitat restoration efforts have resulted in a remarkable recovery of the one-horned rhinoceros population.
By studying these successful initiatives, we can learn from their experiences and adapt their approaches to other regions facing similar challenges.
VI. The Role of Technology in Understanding Human-Wildlife Interaction
Technology has revolutionized the way we study and understand human-wildlife interaction. With the advancements in various tools and devices, researchers are now able to gather more accurate and detailed data, leading to a deeper understanding of this complex relationship.
A. Use of drones and aerial surveys
Drones have become an invaluable tool in studying human-wildlife interaction. These unmanned aerial vehicles provide researchers with a bird’s-eye view of wildlife habitats, allowing them to monitor animal behavior and movement patterns. By capturing high-resolution images and videos, drones enable scientists to study wildlife populations, habitat changes, and the impact of human activities on these ecosystems.
For example, in a recent research project conducted in a national park, drones were used to monitor the behavior of elephants and their interactions with tourists. The aerial footage provided valuable insights into the stress levels of elephants and helped identify areas where human-wildlife conflict was more likely to occur. This information was then used to develop strategies to mitigate such conflicts and ensure the safety of both humans and wildlife.
B. Advancements in tracking and monitoring devices
Tracking and monitoring devices have come a long way in recent years, allowing researchers to collect real-time data on animal movements and behavior. These devices, such as GPS collars and tags, provide valuable information about the habitat preferences, migration patterns, and social interactions of wildlife species.
By tracking individual animals, researchers can gain insights into their daily routines, feeding habits, and breeding behaviors. This information is crucial for understanding the impact of human activities on wildlife populations and developing effective conservation strategies.
For instance, in a study on the impact of urbanization on bird populations, researchers used GPS tags to track the movements of different bird species in urban and rural areas. The data collected revealed significant differences in habitat use and behavior between the two environments, highlighting the need for targeted conservation efforts in urban settings.
C. Data analysis and modeling tools
Data analysis and modeling tools have become essential in interpreting the vast amount of data collected through various technological advancements. By using advanced statistical techniques and modeling algorithms, researchers can uncover patterns and relationships that were previously hidden.
These tools allow scientists to analyze complex datasets and identify key factors influencing human-wildlife interaction. For example, researchers can use data on human population density, land use, and wildlife distribution to model the potential areas of conflict and develop strategies to minimize such interactions.
In a recent study on the impact of climate change on polar bear populations, researchers used data analysis and modeling tools to predict the future distribution of polar bears based on different climate scenarios. This information is crucial for developing conservation plans and policies to protect this endangered species.
D. Examples of technology-driven research projects
There have been numerous research projects that have successfully utilized technology to gain a better understanding of human-wildlife interaction. These projects have provided valuable insights into the behavior, ecology, and conservation needs of various wildlife species.
One such project focused on the use of camera traps to study the behavior of elusive carnivores in a protected area. The camera traps, equipped with motion sensors, captured images and videos of these animals in their natural habitat, providing researchers with valuable data on their feeding habits, social interactions, and population dynamics.
Another notable research project used acoustic monitoring devices to study the vocalizations of marine mammals. By analyzing the sounds produced by these animals, researchers were able to identify different species, track their movements, and assess the impact of human activities, such as underwater noise pollution, on their behavior and communication.
These examples highlight the power of technology in advancing our understanding of human-wildlife interaction. By harnessing the capabilities of drones, tracking devices, data analysis tools, and other technological advancements, researchers are able to gather accurate and detailed information that is crucial for effective conservation and management of wildlife populations.
VII. Best Practices for Coexistence with Wildlife
In order to promote harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife, it is crucial to adopt certain best practices. These practices aim to educate individuals, encourage responsible behavior, and create environments that are conducive to wildlife conservation. By implementing these practices, we can minimize negative interactions and ensure the long-term survival of both humans and wildlife.
A. Education and awareness programs
Education and awareness programs play a vital role in fostering understanding and appreciation for wildlife. By educating the public about the importance of conservation and the ecological significance of wildlife, we can inspire individuals to take action and make informed decisions. These programs can be conducted through various mediums such as schools, community centers, and online platforms. They should focus on topics like biodiversity, habitat preservation, and the impact of human activities on wildlife populations.
Furthermore, it is essential to raise awareness about specific species that may be at risk or require special attention. By highlighting the unique characteristics and challenges faced by these species, we can encourage individuals to actively participate in their conservation efforts. Education and awareness programs should also emphasize the importance of ethical wildlife interactions and the potential consequences of irresponsible behavior.
B. Responsible wildlife viewing and photography
Wildlife viewing and photography can be incredibly rewarding experiences, allowing individuals to connect with nature and appreciate the beauty of wildlife. However, it is crucial to approach these activities responsibly to minimize disturbance and stress to the animals. When observing wildlife, it is important to maintain a safe distance and avoid encroaching on their natural habitats.
Responsible wildlife photographers should prioritize the welfare of the animals over capturing the perfect shot. This means avoiding actions that may cause stress or alter the natural behavior of the animals. It is essential to familiarize oneself with local guidelines and regulations regarding wildlife photography and adhere to them strictly.
Additionally, it is important to respect the privacy of wildlife and refrain from using flash photography, especially in sensitive environments or during nocturnal activities. By practicing responsible wildlife viewing and photography, we can ensure that these activities remain sustainable and do not negatively impact the well-being of the animals.
C. Proper waste management and food storage
Proper waste management is crucial in minimizing human-wildlife conflicts. Wildlife is often attracted to human settlements due to the availability of food waste. To prevent wildlife from becoming dependent on human sources of food, it is essential to dispose of waste properly and secure it in wildlife-proof containers.
Residents living in areas with a high potential for wildlife encounters should be educated on the importance of proper waste management. This includes storing garbage in secure containers, using bear-resistant bins where necessary, and avoiding leaving food scraps or leftovers in open areas. By eliminating these attractants, we can reduce the likelihood of wildlife entering human settlements in search of food.
D. Creating wildlife-friendly landscapes
Creating wildlife-friendly landscapes involves designing and managing outdoor spaces in a way that supports the needs of wildlife. This can include planting native vegetation, providing water sources, and creating sheltered areas. By incorporating these elements, we can attract a variety of wildlife species and provide them with suitable habitats.
Residents can contribute to creating wildlife-friendly landscapes by planting native species in their gardens, installing bird feeders and bird baths, and providing nesting boxes for birds and bats. These small actions can have a significant impact on local wildlife populations and contribute to the overall biodiversity of the area.
E. Collaboration between stakeholders
Effective wildlife conservation requires collaboration between various stakeholders, including government agencies, non-profit organizations, local communities, and individuals. By working together, these stakeholders can pool their resources, expertise, and knowledge to develop and implement effective conservation strategies.
Collaboration can take various forms, including joint research projects, community-based conservation initiatives, and the establishment of protected areas. By involving local communities in decision-making processes and empowering them to take an active role in wildlife conservation, we can ensure the long-term success of these efforts.
VIII. Case Studies of Human-Wildlife Coexistence
A. Successful examples of coexistence in different regions
Throughout the world, there have been numerous successful examples of human-wildlife coexistence in different regions. These case studies highlight the importance of understanding and managing the interactions between humans and wildlife to ensure the survival of both.
One such example is the case of the African elephant population in Botswana. In recent years, Botswana has implemented innovative conservation strategies that have allowed elephants and humans to coexist harmoniously. By establishing protected areas and implementing community-based conservation initiatives, Botswana has been able to reduce human-elephant conflicts and promote peaceful coexistence.
Another successful case study comes from the Sundarbans region in Bangladesh and India, where the Royal Bengal tiger and local communities have found a way to live side by side. The Sundarbans is the largest mangrove forest in the world and is home to a significant population of tigers. Through the establishment of protected areas, community-based conservation programs, and sustainable livelihood initiatives, the local communities have learned to coexist with these majestic creatures.
In North America, the Yellowstone National Park in the United States serves as an excellent example of successful human-wildlife coexistence. The reintroduction of gray wolves into the park has had a profound impact on the ecosystem, leading to a more balanced and healthy environment. Despite initial concerns and conflicts, the local communities have come to appreciate the importance of these predators in maintaining the park’s biodiversity.
These case studies demonstrate that with proper management and conservation efforts, humans and wildlife can coexist successfully. By implementing measures such as protected areas, community involvement, and sustainable practices, we can ensure the long-term survival of both humans and wildlife.
B. Lessons learned from these case studies
The successful case studies of human-wildlife coexistence provide valuable lessons that can guide future conservation efforts. These lessons can help us develop effective strategies to mitigate conflicts and promote peaceful coexistence between humans and wildlife.
Firstly, community involvement is crucial for the success of any conservation program. In all the case studies mentioned, local communities played a significant role in implementing and sustaining conservation initiatives. By actively involving the communities in decision-making processes and providing them with incentives for conservation, we can create a sense of ownership and responsibility towards wildlife.
Secondly, protected areas are essential for preserving wildlife habitats and minimizing human-wildlife conflicts. The establishment of protected areas, as seen in the case of Botswana and the Sundarbans, provides a safe haven for wildlife while allowing humans to coexist with them. These protected areas should be carefully planned, taking into consideration the needs of both wildlife and local communities.
Furthermore, education and awareness are vital in promoting coexistence. The case studies demonstrate the importance of educating local communities about the value of wildlife and the benefits of conservation. By raising awareness and providing information about wildlife behavior, conflict prevention strategies, and sustainable practices, we can foster a culture of coexistence.
Lastly, sustainable livelihood initiatives can help alleviate conflicts and provide economic incentives for conservation. The case studies highlight the success of programs that provide alternative livelihood options for communities living in close proximity to wildlife. By offering sustainable income-generating activities such as ecotourism, handicraft production, and sustainable agriculture, we can reduce the dependence on natural resources and minimize conflicts.
IX. The Importance of Public Engagement in Research and Conservation
In today’s world, research and conservation efforts are no longer limited to the scientific community. Public engagement plays a crucial role in understanding and addressing the complex issues surrounding human-wildlife interaction. This section explores the various ways in which public involvement can contribute to research and conservation, including citizen science initiatives, public participation in decision-making processes, and advocacy and outreach programs.
A. Citizen science initiatives
Citizen science initiatives have gained significant momentum in recent years, allowing individuals from all walks of life to actively participate in scientific research. These initiatives involve the general public in data collection, analysis, and interpretation, providing valuable insights into various aspects of wildlife behavior, ecology, and conservation.
One example of a successful citizen science initiative is the Great Backyard Bird Count. Each year, bird enthusiasts from around the world come together to observe and record bird sightings in their local areas. By contributing their observations to a global database, participants help researchers monitor bird populations, migration patterns, and the impact of environmental changes.
Engaging the public in such initiatives not only enhances data collection but also fosters a sense of ownership and connection to the natural world. It empowers individuals to contribute to scientific knowledge and conservation efforts, ultimately leading to more informed decision-making and effective management strategies.
B. Public participation in decision-making processes
Public participation in decision-making processes is essential for ensuring that diverse perspectives and values are considered when developing policies and management plans. When it comes to human-wildlife interaction, decisions regarding wildlife conservation, land use, and resource management can have significant social, economic, and environmental implications.
By involving the public in these processes, stakeholders have the opportunity to voice their concerns, share their knowledge and experiences, and contribute to the development of more inclusive and sustainable solutions. Public participation can take various forms, including public hearings, workshops, surveys, and collaborative planning processes.
For example, in the case of a proposed wildlife corridor project, public participation would allow local communities, indigenous groups, landowners, and other stakeholders to provide input on the project’s design, potential impacts, and mitigation measures. This collaborative approach ensures that decisions are informed by a wide range of perspectives and expertise, leading to more socially acceptable and ecologically sound outcomes.
C. Advocacy and outreach programs
Advocacy and outreach programs play a vital role in raising awareness, promoting understanding, and mobilizing public support for wildlife conservation. These programs aim to educate and engage individuals, communities, and decision-makers, fostering a sense of responsibility and stewardship towards the natural world.
One example of an effective advocacy and outreach program is the “Save Our Seas” campaign, which focuses on marine conservation. Through a combination of educational initiatives, public events, and media campaigns, the program highlights the importance of protecting marine ecosystems and the need for sustainable fishing practices.
By effectively communicating scientific findings, conservation challenges, and potential solutions, advocacy and outreach programs can inspire individuals to take action, make informed choices, and support conservation efforts. They can also facilitate dialogue between scientists, policymakers, and the public, promoting collaboration and shared responsibility for the well-being of both wildlife and human communities.
1. How can I prevent wildlife from entering my property?
Preventing wildlife from entering your property requires a combination of proactive measures and deterrents. Here are some tips to help you keep wildlife away:
- Secure garbage cans and compost bins with tight-fitting lids.
- Remove potential food sources, such as fallen fruits and bird feeders.
- Seal any openings or gaps in your home’s exterior, including cracks, crevices, and holes.
- Install fencing around your property, making sure it extends underground to prevent burrowing animals from digging under.
- Keep your yard well-maintained and free of debris that can attract wildlife.
2. What should I do if I encounter a dangerous wild animal?
Encountering a dangerous wild animal can be a frightening experience, but it’s important to stay calm and take the following steps:
- Do not approach or try to feed the animal.
- Back away slowly and maintain a safe distance.
- If the animal approaches you, make yourself appear larger by raising your arms and speaking loudly.
- If necessary, use noise-making devices or throw objects to scare the animal away.
- Report the encounter to local wildlife authorities or animal control.
3. How can I support conservation efforts for endangered species?
Supporting conservation efforts for endangered species is crucial to their survival. Here are some ways you can help:
- Donate to reputable conservation organizations that focus on protecting endangered species.
- Get involved in local conservation projects or volunteer at wildlife rehabilitation centers.
- Advocate for stronger wildlife protection laws and regulations.
- Spread awareness about endangered species and the importance of conservation through social media and other platforms.
- Make sustainable choices in your daily life to reduce your impact on the environment.
4. Are there any legal protections for wildlife?
Yes, there are legal protections in place to safeguard wildlife. These protections vary by country and region, but common measures include:
- Designating protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife reserves.
- Enforcing hunting and fishing regulations to prevent overexploitation of wildlife.
- Implementing laws against wildlife trafficking and illegal trade.
- Establishing conservation programs and initiatives to promote the recovery of endangered species.
5. How does climate change affect human-wildlife interaction?
Climate change has significant impacts on human-wildlife interaction. Here are some ways it affects the relationship between humans and wildlife:
- Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can alter the availability of food and water sources for wildlife, leading to shifts in their behavior and habitat use.
- Rising sea levels and coastal erosion can threaten the nesting grounds of marine species, such as sea turtles.
- Extreme weather events, such as hurricanes and droughts, can disrupt ecosystems and cause population declines in certain species.
- Climate change can also contribute to the spread of diseases among wildlife, which can have cascading effects on ecosystems.
6. What are the most effective methods for reducing human-wildlife conflict?
Reducing human-wildlife conflict requires a combination of strategies. Here are some effective methods:
- Implementing non-lethal deterrents, such as fencing, motion-activated lights, and sound devices, to keep wildlife away from human-populated areas.
- Providing alternative food sources for wildlife to reduce their reliance on human-provided resources.
- Developing and implementing land-use plans that consider wildlife habitat needs and minimize conflicts.
- Educating communities about coexistence with wildlife and providing guidelines for responsible behavior.
- Supporting research and innovation to develop new technologies and approaches for reducing human-wildlife conflict.
7. Can human-wildlife conflict be completely eliminated?
While it may not be possible to completely eliminate human-wildlife conflict, proactive measures can significantly reduce its occurrence. By implementing effective management strategies and promoting coexistence, we can minimize conflicts and create a more harmonious relationship with wildlife.
8. How can I report wildlife sightings or incidents?
If you have witnessed wildlife sightings or incidents, it is important to report them to the appropriate authorities. Here are some steps you can take:
- Contact your local wildlife agency or animal control to report the sighting or incident.
- Provide detailed information about the location, date, and description of the wildlife involved.
- Follow any instructions or guidelines provided by the authorities.
- Keep a safe distance from the wildlife and avoid interfering with their natural behavior.
9. What are the ethical considerations in wildlife research?
Wildlife research raises important ethical considerations. Researchers must prioritize the welfare of the animals involved and ensure that their studies are conducted ethically. Some key ethical considerations in wildlife research include:
- Minimizing harm and stress to the animals during capture, handling, and data collection.
- Obtaining necessary permits and approvals from relevant authorities before conducting research.
- Respecting the natural behavior and habitat of the animals.
- Sharing research findings in a transparent and responsible manner.
- Contributing to the conservation and protection of wildlife through research outcomes.
10. How can I get involved in research on human-wildlife interaction?
If you are interested in contributing to research on human-wildlife interaction, there are several ways to get involved:
- Join local research organizations or universities that conduct studies on wildlife and human-wildlife interaction.
- Volunteer for field research projects or citizen science initiatives.
- Participate in data collection efforts, such as wildlife monitoring programs or surveys.
- Support research financially by donating to organizations that fund wildlife research.
- Stay informed about current research and conservation efforts through scientific publications and conferences.

