Contents
I. Introduction

Welcome to the world of protected areas, where humans and wildlife coexist in harmony. Managing human-wildlife interaction in these areas is crucial to ensure the preservation of both the natural environment and the safety of visitors. In this article, we will explore effective strategies and best practices for managing human-wildlife interaction in protected areas.
Protected areas play a vital role in conserving biodiversity and providing habitats for a wide range of wildlife species. However, the increasing number of visitors to these areas has led to a rise in human-wildlife conflicts. It is essential to strike a balance between allowing visitors to experience the wonders of nature and ensuring the well-being of the wildlife that call these areas home.
Throughout this article, we will delve into various aspects of managing human-wildlife interaction. We will discuss the importance of educating visitors about wildlife behavior and safety precautions, as well as implementing effective monitoring and mitigation measures. By following these guidelines, protected area managers can create a safe environment for both humans and wildlife.
Furthermore, we will explore the significance of community involvement in managing human-wildlife interaction. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts not only fosters a sense of ownership but also provides valuable insights and traditional knowledge that can contribute to successful management strategies.
Join us on this journey as we uncover the secrets to managing human-wildlife interaction in protected areas. Whether you are a protected area manager, a wildlife enthusiast, or a curious visitor, this article will equip you with the knowledge and tools to ensure a harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife.
II. Understanding Human-Wildlife Interaction

In order to effectively manage human-wildlife interaction in protected areas, it is crucial to have a thorough understanding of the types of interactions that occur and the factors that influence them. This knowledge can help inform conservation strategies and mitigate potential conflicts between humans and wildlife.
A. Types of human-wildlife interaction
1. Direct interactions:
Direct interactions refer to situations where humans and wildlife come into direct contact with each other. This can include encounters such as wildlife viewing, wildlife photography, or even incidents of wildlife aggression towards humans. These interactions can be both positive and negative, depending on the context and the behavior of the wildlife involved.
2. Indirect interactions:
Indirect interactions occur when humans and wildlife interact indirectly through their impact on the environment. This can include activities such as habitat modification, land use changes, or the introduction of invasive species. Indirect interactions can have significant consequences for wildlife populations and their habitats, and can often lead to conflicts between humans and wildlife.
B. Factors influencing human-wildlife interaction
1. Habitat fragmentation:
Habitat fragmentation, which is the division of large habitats into smaller, isolated fragments, is a major factor influencing human-wildlife interaction. As human activities continue to encroach upon natural habitats, wildlife populations become increasingly fragmented and isolated. This can disrupt their natural behavior patterns and increase the likelihood of negative interactions with humans.
2. Human activities:
Human activities, such as agriculture, urban development, and infrastructure construction, can have a significant impact on wildlife populations and their habitats. These activities can lead to habitat destruction, pollution, and the loss of food sources for wildlife. As a result, wildlife may be forced to seek alternative resources, often bringing them into closer proximity with humans and increasing the likelihood of conflicts.
3. Wildlife behavior:
The behavior of wildlife species also plays a crucial role in human-wildlife interaction. Some species may be more tolerant of human presence, while others may be more aggressive or territorial. Understanding the behavior patterns of different wildlife species can help predict and manage potential conflicts with humans. It is important to consider the natural behavior and needs of wildlife when implementing conservation measures and managing human activities in protected areas.
III. Impacts of Human-Wildlife Interaction

Human-wildlife interaction can have both negative impacts on wildlife and humans. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which this interaction can affect both parties.
A. Negative impacts on wildlife
1. Habitat loss and degradation
As human populations continue to expand, natural habitats are being destroyed or fragmented to make way for agriculture, infrastructure, and urban development. This loss of habitat can have severe consequences for wildlife, leading to a decline in population numbers and reduced biodiversity. Animals are forced to compete for limited resources, and some may even face the risk of extinction.
2. Disruption of natural behaviors
Human activities such as hunting, poaching, and deforestation can disrupt the natural behaviors of wildlife. Animals may be forced to alter their feeding, mating, and migration patterns, which can have long-term consequences for their survival and reproductive success. For example, noise pollution from human activities can interfere with the communication signals of animals, making it difficult for them to find mates or warn of potential dangers.
3. Increased stress and mortality
Human-wildlife interaction can cause increased stress levels in animals, leading to higher mortality rates. Encounters with humans can trigger the release of stress hormones, which can negatively impact the immune system and reproductive health of wildlife. Additionally, human activities such as hunting and poaching can directly result in the death of animals, further contributing to population declines.
B. Negative impacts on humans
1. Crop and livestock damage
Human-wildlife conflict often arises when wildlife encroaches on agricultural lands, causing damage to crops and livestock. This can result in significant economic losses for farmers and communities who depend on agriculture for their livelihoods. In some cases, farmers may resort to using lethal methods to protect their crops, leading to the killing of wildlife.
2. Threats to human safety
Certain wildlife species can pose a threat to human safety, especially when they come into close proximity with human settlements. Predatory animals such as lions, tigers, and bears can attack humans, leading to injuries or even fatalities. This can create fear and tension within communities, affecting their overall well-being and quality of life.
3. Economic losses
Human-wildlife conflict can result in significant economic losses for communities that rely on tourism as a source of income. When wildlife populations decline due to negative interactions with humans, it can impact the tourism industry, leading to a loss of revenue and job opportunities. This can have long-term implications for the socio-economic development of affected regions.
IV. Strategies for Managing Human-Wildlife Interaction
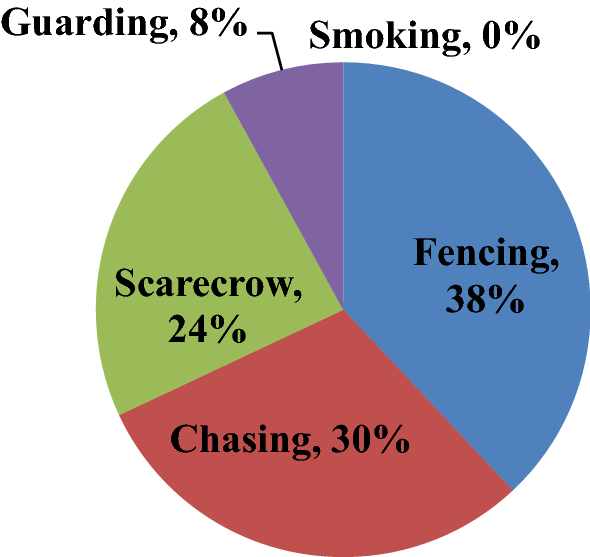
Managing human-wildlife interaction in protected areas is crucial to ensure the conservation of both wildlife and the well-being of local communities. By implementing effective strategies, we can mitigate conflicts and create a harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife. In this section, we will explore some key strategies for managing human-wildlife interaction.
A. Habitat management
Habitat management plays a vital role in minimizing human-wildlife conflicts. By creating buffer zones and restoring and enhancing habitat connectivity, we can provide wildlife with suitable habitats while reducing the likelihood of encounters with humans.
1. Creating buffer zones:
Buffer zones act as a protective barrier between human settlements and wildlife habitats. These areas are designed to minimize the negative impacts of human activities on wildlife and vice versa. By establishing buffer zones, we can reduce the chances of human-wildlife conflicts, such as crop raiding or predation on livestock.
2. Restoring and enhancing habitat connectivity:
Fragmentation of habitats due to human activities can isolate wildlife populations, leading to reduced genetic diversity and increased vulnerability to extinction. By restoring and enhancing habitat connectivity, we can create corridors that allow animals to move freely between different areas, promoting gene flow and ensuring the long-term survival of species.
B. Wildlife management
Effective wildlife management strategies are essential for minimizing conflicts and ensuring the well-being of both wildlife and humans. By monitoring and controlling populations and using deterrents and repellents, we can reduce the negative impacts of wildlife on human activities.
1. Population monitoring and control:
Regular monitoring of wildlife populations helps us understand their dynamics and make informed management decisions. By implementing population control measures, such as regulated hunting or contraception, we can maintain balanced population sizes that are sustainable and compatible with human activities.
2. Use of deterrents and repellents:
Deterrents and repellents can be effective tools for reducing human-wildlife conflicts. For example, electric fences can deter elephants from raiding crops, while scent repellents can discourage animals from approaching human settlements. By using these non-lethal methods, we can protect both wildlife and human interests.
C. Education and awareness
Education and awareness programs are crucial for fostering a culture of responsible behavior towards wildlife and promoting coexistence between humans and animals.
1. Community outreach programs:
Engaging local communities through outreach programs can help raise awareness about the importance of wildlife conservation and the potential impacts of human activities on wildlife. These programs can include workshops, training sessions, and interactive activities that encourage community participation and empower individuals to take action.
2. Promoting responsible behavior:
Encouraging responsible behavior among visitors to protected areas is essential for minimizing disturbances to wildlife. This can be achieved through clear signage, interpretive materials, and guidelines that educate visitors about appropriate behavior, such as maintaining a safe distance from animals, not feeding them, and disposing of waste properly.
By implementing these strategies for managing human-wildlife interaction, we can ensure the long-term conservation of protected areas while promoting the well-being of both wildlife and local communities.
V. Best Practices for Visitors in Protected Areas
When visiting protected areas, it is important to be mindful of the wildlife and their habitat, follow park regulations and guidelines, practice proper waste management, and report any wildlife sightings or incidents. By respecting these best practices, we can ensure a positive and sustainable human-wildlife interaction in protected areas.
A. Respecting wildlife and their habitat
One of the most important aspects of visiting protected areas is to respect the wildlife and their natural habitat. It is crucial to remember that we are guests in their home, and it is our responsibility to minimize our impact and disturbance. Here are some best practices to follow:
- Observe wildlife from a safe distance: It is essential to maintain a safe distance from wildlife to avoid causing stress or harm to them. Use binoculars or a zoom lens to get a closer look without intruding on their space.
- Do not feed the wildlife: Feeding wildlife can disrupt their natural behavior and diet. It can also lead to dependency on human food, which can be harmful to their health.
- Stay on designated trails: Stick to established trails and paths to avoid trampling on sensitive vegetation or disturbing wildlife habitats.
- Do not touch or approach wildlife: It is important to remember that wild animals are just that – wild. Approaching or touching them can be dangerous for both you and the animal.
B. Following park regulations and guidelines
Protected areas have specific regulations and guidelines in place to ensure the conservation and preservation of the natural environment. By following these rules, we can help maintain the integrity of the protected areas. Here are some key regulations and guidelines to keep in mind:
- Observe speed limits: Many protected areas have speed limits in place to protect wildlife and reduce the risk of accidents. Adhering to these limits not only ensures your safety but also the safety of the wildlife.
- Respect quiet zones: Some protected areas may have designated quiet zones to minimize noise pollution and provide a peaceful environment for wildlife and other visitors. Be mindful of these areas and keep noise to a minimum.
- Observe camping restrictions: If camping is allowed in the protected area, make sure to follow the designated camping areas and any restrictions on campfires or waste disposal.
- Respect closures and restricted areas: Some areas within protected areas may be temporarily closed or restricted to protect sensitive habitats or nesting grounds. Always obey these closures and respect the boundaries.
C. Proper waste management
Proper waste management is crucial in protected areas to prevent pollution and maintain the natural beauty of the environment. Here are some tips for responsible waste management:
- Carry out what you carry in: Make sure to bring a trash bag and pack out all your waste, including food wrappers, bottles, and any other items.
- Dispose of waste properly: Use designated trash bins or recycling facilities within the protected area. If there are no facilities available, carry your waste out with you and dispose of it in appropriate bins outside the protected area.
- Avoid littering: Never leave any trash or litter behind. Even small items like cigarette butts can have a significant impact on the environment and wildlife.
- Reduce waste: Minimize waste by opting for reusable containers and bottles instead of single-use plastics. Choose eco-friendly products whenever possible.
D. Reporting wildlife sightings and incidents
Reporting wildlife sightings and incidents is not only beneficial for researchers and conservationists but also helps ensure the safety of both visitors and wildlife. Here’s why reporting is important:
- Contribute to research and conservation efforts: By reporting wildlife sightings, you provide valuable data that can help researchers monitor populations, track migration patterns, and better understand the behavior of different species.
- Assist in wildlife management: Reporting incidents such as aggressive behavior or injured animals can help park authorities take appropriate action to ensure the safety of visitors and the well-being of the wildlife.
- Help protect endangered species: If you come across a rare or endangered species, reporting the sighting can aid in their protection and conservation.
- Stay informed about potential risks: Reporting incidents like animal encounters or sightings of dangerous wildlife can help other visitors stay informed and take necessary precautions.
By following these best practices for visitors in protected areas, we can contribute to the conservation and preservation of these natural treasures. Let’s enjoy the beauty of wildlife and their habitats while ensuring their long-term survival for future generations to appreciate and enjoy.
