Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding Substance Abuse
- III. Impact of Substance Abuse on Physical Health
- IV. Impact of Substance Abuse on Mental Health
- V. Social and Economic Consequences of Substance Abuse
- VI. Treatment Options for Substance Abuse and Addiction
- VII. Support Systems for Recovery
- VIII. Prevention Strategies for Substance Abuse
- IX. Overcoming Stigma and Seeking Help
- A. Addressing societal attitudes towards substance abuse
- B. Encouraging individuals to seek help and treatment
- C. Resources for finding treatment and support
- 1. What is the difference between substance abuse and addiction?
- 2. How can I recognize if someone is struggling with substance abuse?
- 3. What are the most commonly abused substances?
- 4. Are there any physical health risks associated with substance abuse?
- 5. Can substance abuse lead to mental health disorders?
- 6. What treatment options are available for substance abuse?
- 7. How can I support a loved one in their recovery journey?
- 8. What are some effective prevention strategies for substance abuse?
- 9. How can I overcome the stigma associated with substance abuse?
- 10. Where can I find resources for help and support?
I. Introduction
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the dangers of substance abuse and addiction. In this article, we will explore the various aspects of substance abuse, its impact on individuals and society, and the importance of seeking help for addiction.
Substance abuse refers to the harmful use of drugs or alcohol that can lead to physical and psychological dependence. It is a widespread issue that affects people of all ages, genders, and backgrounds. The consequences of substance abuse can be devastating, not only for the individuals involved but also for their families and communities.
Throughout this article, we will delve into the reasons why people turn to substances, the risk factors associated with addiction, and the physical and mental health implications. We will also discuss the importance of early intervention and treatment options available for those struggling with addiction.
Our aim is to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of substance abuse and addiction, as well as the resources and support available to help individuals overcome these challenges. By shedding light on this topic, we hope to raise awareness and encourage open conversations about addiction.
So, let’s dive in and explore the complex world of substance abuse and addiction, and discover how we can work together to combat this growing issue.
II. Understanding Substance Abuse

In order to effectively address the dangers of substance abuse and addiction, it is crucial to have a clear understanding of what substance abuse entails. Substance abuse refers to the harmful or excessive use of substances such as alcohol, drugs, or prescription medications. It is important to note that substance abuse can affect individuals of all ages, genders, and backgrounds.
A. Definition and types of substances commonly abused
Substance abuse can involve a wide range of substances, each with its own unique effects and risks. Some of the most commonly abused substances include:
- Alcohol: Alcohol abuse is a prevalent issue worldwide, with detrimental effects on physical and mental health. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to liver damage, addiction, and impaired judgment.
- Illegal drugs: Drugs such as cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, and marijuana are frequently abused substances. These drugs can have severe health consequences and can lead to addiction, overdose, and even death.
- Prescription medications: While prescription medications can be beneficial when used as directed by a healthcare professional, they can also be misused or abused. Opioids, benzodiazepines, and stimulants are among the most commonly abused prescription drugs.
It is important to note that substance abuse can extend beyond these categories, as individuals may abuse other substances such as inhalants, hallucinogens, or synthetic drugs.
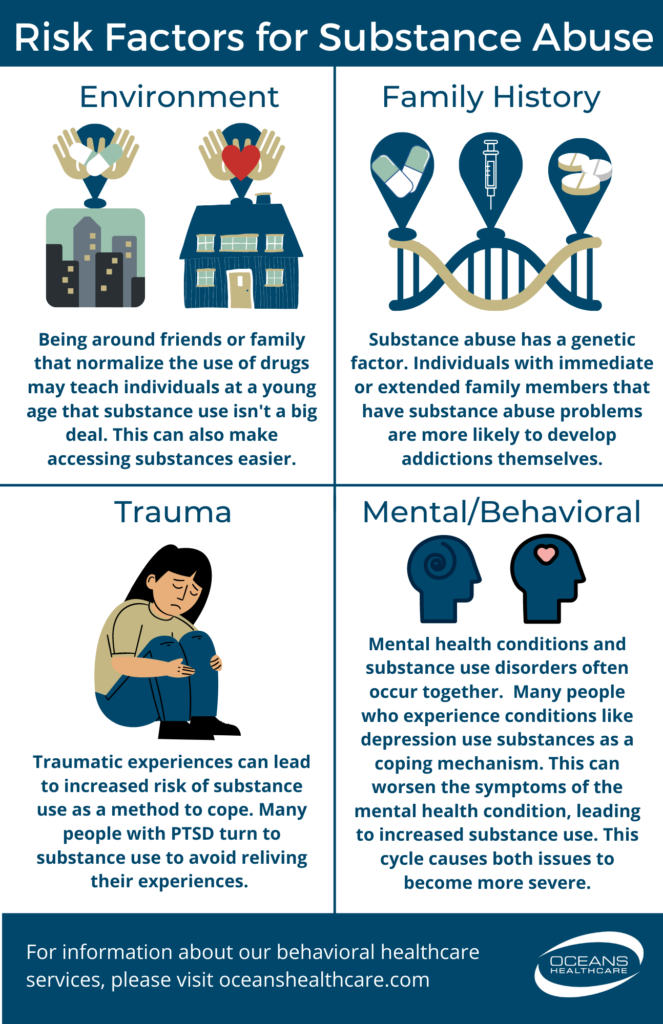
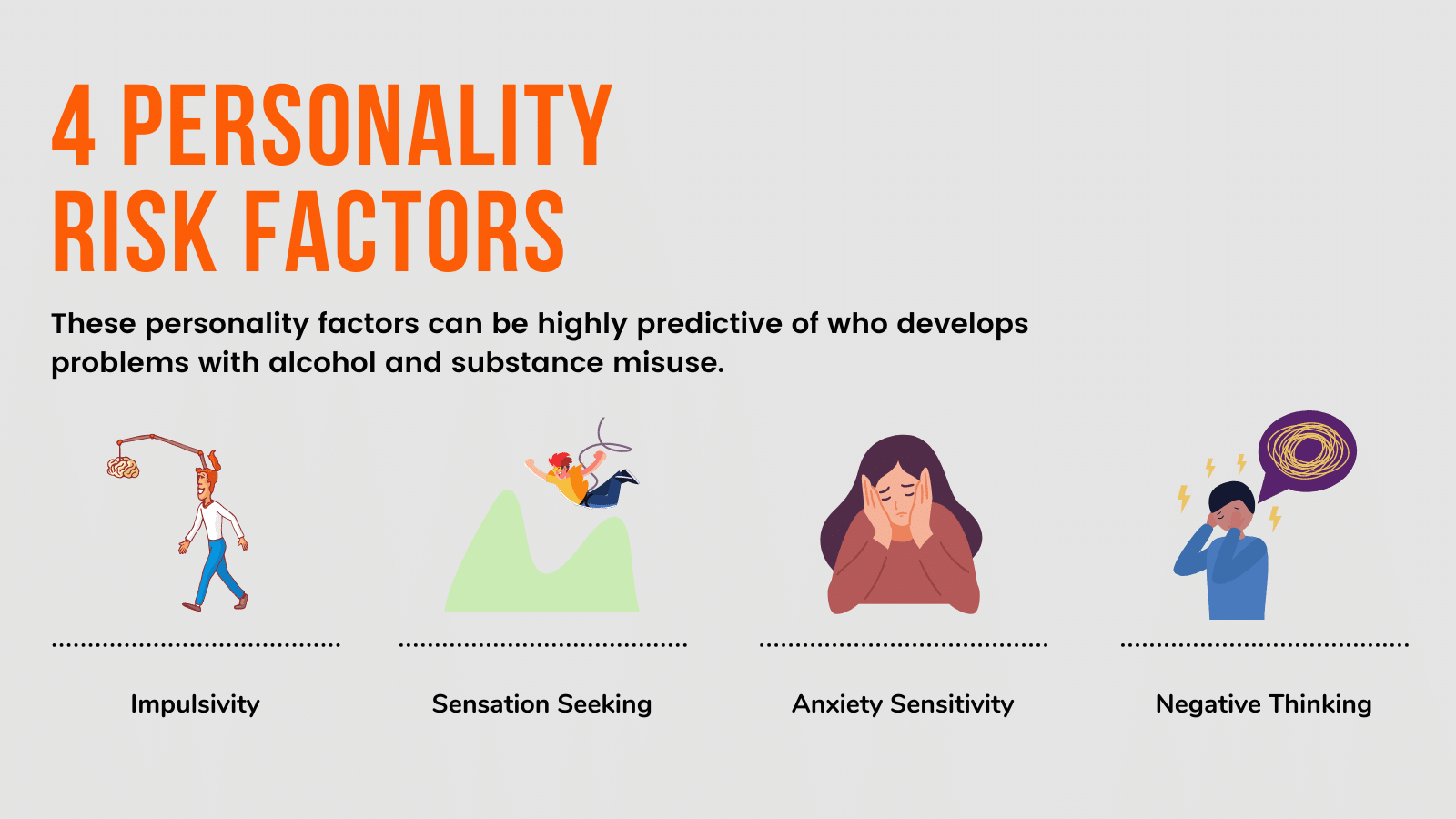
B. Risk factors for substance abuse
Substance abuse does not occur in a vacuum; it is influenced by various risk factors that can increase an individual’s susceptibility to developing an addiction. Some common risk factors for substance abuse include:
- Genetic predisposition: Certain individuals may have a genetic predisposition to substance abuse, making them more vulnerable to developing an addiction.
- Environmental factors: The environment in which an individual grows up or lives can play a significant role in their likelihood of engaging in substance abuse. Factors such as peer pressure, availability of substances, and exposure to trauma or stress can contribute to the development of substance abuse.
- Mental health conditions: Individuals with mental health disorders, such as depression, anxiety, or post-traumatic stress disorder, may turn to substances as a means of self-medication or coping with their symptoms.
- Family history: Growing up in a family where substance abuse is prevalent can increase the risk of developing substance abuse issues later in life.
- Early exposure: Early initiation of substance use, especially during adolescence, can significantly increase the likelihood of developing an addiction.
It is important to recognize these risk factors and address them proactively in order to prevent or intervene in cases of substance abuse.
C. Signs and symptoms of substance abuse
Identifying the signs and symptoms of substance abuse is crucial for early intervention and treatment. While the specific signs may vary depending on the substance being abused, some common indicators include:
- Physical changes: Individuals may experience changes in appetite, weight loss or gain, bloodshot eyes, dilated or constricted pupils, or unexplained bruises or marks on their body.
- Behavioral changes: Substance abuse can lead to noticeable changes in behavior, such as increased secrecy, withdrawal from social activities, sudden mood swings, irritability, or aggression.
- Neglecting responsibilities: Individuals struggling with substance abuse may neglect their responsibilities at work, school, or home. This can manifest as a decline in performance, frequent absences, or a lack of interest in previously enjoyed activities.
- Financial difficulties: Substance abuse can be financially burdensome, leading individuals to experience financial difficulties, such as unpaid bills, borrowing money, or selling personal belongings.
- Relationship problems: Substance abuse can strain relationships with family, friends, and romantic partners. Individuals may become increasingly isolated or engage in conflicts and arguments.
It is important to approach individuals showing signs of substance abuse with empathy and support, encouraging them to seek professional help. Early intervention can significantly improve the chances of successful recovery.
III. Impact of Substance Abuse on Physical Health
Substance abuse can have detrimental effects on a person’s physical health, both in the short-term and long-term. The specific health risks associated with different substances can vary, but it is important to understand the potential harm that substance abuse can cause to the body.
A. Short-term effects on the body
When a person engages in substance abuse, they may experience immediate and short-term effects on their physical health. These effects can vary depending on the substance being abused.
1. Stimulants: Stimulant drugs, such as cocaine or amphetamines, can have a significant impact on the body. They can increase heart rate and blood pressure, leading to a higher risk of heart attack or stroke. Additionally, stimulants can cause irregular heart rhythms and chest pain.
2. Depressants: Depressant substances, such as alcohol or opioids, can slow down the body’s functions. They can cause drowsiness, confusion, and impaired coordination. In higher doses, depressants can lead to respiratory depression, coma, or even death.
3. Hallucinogens: Hallucinogenic substances, like LSD or psilocybin mushrooms, can alter a person’s perception of reality. They can cause hallucinations, distorted thinking, and impaired judgment. In some cases, hallucinogens can lead to panic attacks or psychosis.
4. Inhalants: Inhalant abuse involves the inhalation of chemical vapors from household products or other substances. This can lead to immediate effects such as dizziness, nausea, and impaired coordination. Inhalants can also cause damage to the brain, liver, kidneys, and other organs.
5. Cannabis: The short-term effects of cannabis use include impaired memory, difficulty concentrating, and altered perception of time. It can also cause increased heart rate and blood pressure. Additionally, cannabis use can impair coordination and judgment, increasing the risk of accidents.
B. Long-term effects on the body
Continued substance abuse can have long-term effects on a person’s physical health. These effects can be severe and may persist even after the individual stops using the substance.
1. Cardiovascular system: Substance abuse, particularly the use of stimulants, can have a detrimental impact on the cardiovascular system. Prolonged use can lead to high blood pressure, heart disease, and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
2. Liver damage: Alcohol abuse can cause liver damage, leading to conditions such as alcoholic hepatitis, cirrhosis, and liver cancer. Chronic use of certain drugs, such as opioids, can also result in liver damage or failure.
3. Respiratory system: Inhalation of substances like tobacco or illicit drugs can cause significant damage to the respiratory system. Chronic smoking can lead to lung diseases such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. Inhalation of chemicals from illicit drugs can cause lung damage and respiratory distress.
4. Brain function: Substance abuse can have long-lasting effects on brain function. It can impair cognitive abilities, memory, and decision-making skills. Prolonged substance abuse can also lead to mental health disorders such as anxiety, depression, or psychosis.
5. Immune system: Substance abuse weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections and diseases. It can also hinder the body’s ability to heal and recover from illnesses or injuries.
C. Specific health risks associated with different substances
Each substance of abuse carries its own set of specific health risks. It is essential to understand these risks to fully comprehend the potential harm caused by substance abuse.
1. Alcohol: Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to liver damage, pancreatitis, cardiovascular diseases, and an increased risk of certain cancers. It can also cause neurological disorders, such as Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome, which affects memory and cognitive function.
2. Opioids: Prolonged use of opioids can result in respiratory depression, constipation, hormonal imbalances, and increased sensitivity to pain. It can also lead to opioid addiction, which can be challenging to overcome.
3. Cocaine: Cocaine abuse can cause heart problems, including heart attacks and arrhythmias. It can also lead to seizures, strokes, and respiratory issues. Prolonged use can result in severe damage to the nasal tissues and septum.
4. Methamphetamine: Methamphetamine abuse can have devastating effects on the body, including cardiovascular damage, dental problems (known as “meth mouth”), and neurological damage. It can also lead to psychosis and cognitive impairments.
5. Tobacco: Smoking tobacco increases the risk of various health conditions, including lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), heart disease, and stroke. It can also cause oral and throat cancers.
It is crucial to recognize the impact of substance abuse on physical health and take steps to prevent and address these issues. Seeking professional help and support is essential for individuals struggling with substance abuse and addiction.
IV. Impact of Substance Abuse on Mental Health

Substance abuse can have a significant impact on an individual’s mental health. The relationship between substance abuse and mental health disorders is complex and often intertwined. Many individuals who struggle with substance abuse also experience mental health issues, and vice versa. It is important to understand the common mental health issues that can result from substance abuse and the concept of dual diagnosis, which involves co-occurring substance abuse and mental health disorders.
A. Relationship between substance abuse and mental health disorders
Substance abuse and mental health disorders often go hand in hand. The misuse of drugs or alcohol can exacerbate existing mental health conditions or even trigger the onset of new ones. For example, individuals with depression may turn to substances as a way to self-medicate and alleviate their symptoms temporarily. However, this can lead to a vicious cycle of substance abuse and worsening mental health.
Similarly, substance abuse can increase the risk of developing mental health disorders such as anxiety, bipolar disorder, or psychosis. The effects of substances on the brain can disrupt the delicate balance of neurotransmitters and alter brain chemistry, contributing to the development of mental health issues.
Furthermore, substance abuse can also impair judgment, increase impulsivity, and lower inhibitions, making individuals more vulnerable to engaging in risky behaviors that can further impact their mental health.
B. Common mental health issues resulting from substance abuse
Substance abuse can lead to a wide range of mental health issues. Some of the most common mental health disorders resulting from substance abuse include:
- Depression: Substance abuse can contribute to the development of depression, and individuals with depression may be more prone to substance abuse as a form of self-medication.
- Anxiety disorders: Substance abuse can trigger or worsen anxiety disorders, leading to heightened feelings of fear, worry, and panic.
- Bipolar disorder: Substance abuse can complicate the management of bipolar disorder, making it more challenging to stabilize mood swings and manage symptoms effectively.
- Psychosis: Certain substances, such as hallucinogens or stimulants, can induce psychotic symptoms, including hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
- Personality disorders: Substance abuse can contribute to the development or exacerbation of personality disorders, such as borderline personality disorder or antisocial personality disorder.
It is important to note that the relationship between substance abuse and mental health disorders is complex and multifaceted. The specific impact of substance abuse on mental health can vary depending on factors such as the type of substance used, the frequency and duration of use, and individual susceptibility.
C. Dual diagnosis: Substance abuse and co-occurring mental health disorders
Dual diagnosis refers to the presence of both substance abuse and co-occurring mental health disorders in an individual. It is common for individuals with substance abuse issues to also have underlying mental health conditions. Dual diagnosis requires a comprehensive and integrated approach to treatment, as both the substance abuse and mental health disorders need to be addressed simultaneously for effective recovery.
When someone has a dual diagnosis, it is essential to identify and treat both the substance abuse and the mental health disorder concurrently. Treating one without addressing the other can lead to incomplete recovery and an increased risk of relapse.
Integrated treatment approaches that combine therapy, medication management, and support groups are often recommended for individuals with dual diagnosis. These approaches aim to address the underlying causes of substance abuse and mental health disorders, promote relapse prevention, and improve overall well-being.
V. Social and Economic Consequences of Substance Abuse
Substance abuse has far-reaching social and economic consequences that can impact various aspects of an individual’s life. From relationships and family dynamics to academic and work performance, substance abuse can have severe implications. Additionally, the financial burden of substance abuse can be overwhelming for individuals and society as a whole.
A. Effects on relationships and family dynamics
Substance abuse can strain relationships and disrupt family dynamics. The effects of substance abuse on relationships can be devastating, leading to conflicts, mistrust, and breakdowns in communication. Substance abuse often causes individuals to prioritize their addiction over their loved ones, resulting in neglect and emotional distance.
Family members of individuals struggling with substance abuse may experience a range of emotions, including anger, frustration, and sadness. They may also face challenges in providing support and care for their loved ones. The constant worry and stress can take a toll on their own mental and emotional well-being.
Children growing up in households affected by substance abuse are particularly vulnerable. They may experience neglect, instability, and a lack of proper care. This can have long-term effects on their emotional, cognitive, and social development.
B. Impact on academic and work performance
Substance abuse can significantly impact academic and work performance. Individuals struggling with addiction may find it difficult to concentrate, remember information, and complete tasks effectively. This can result in poor academic performance, missed deadlines, and decreased productivity in the workplace.
For students, substance abuse can lead to absenteeism, lower grades, and a higher risk of dropping out of school. The cognitive impairments caused by substance abuse can hinder learning and hinder the ability to retain information.
In the workplace, substance abuse can lead to decreased job performance, increased absenteeism, and a higher likelihood of accidents or errors. It can also strain relationships with colleagues and supervisors, leading to disciplinary actions or even job loss.
C. Financial implications of substance abuse
The financial implications of substance abuse can be significant for individuals and society as a whole. Substance abuse often leads to increased healthcare costs, including medical treatments, therapy, and rehabilitation programs. The expenses associated with managing the physical and mental health consequences of substance abuse can quickly accumulate.
Individuals struggling with addiction may also experience financial difficulties due to job loss, decreased earning potential, and legal issues. The need to fund their addiction can lead to financial strain, resulting in debt, bankruptcy, and loss of assets.
Furthermore, substance abuse places a burden on society through increased healthcare costs, law enforcement efforts, and social welfare programs. The economic impact of substance abuse extends beyond the individual, affecting communities and the overall economy.
VI. Treatment Options for Substance Abuse and Addiction
When it comes to addressing substance abuse and addiction, there are several treatment options available to individuals seeking help. These options range from detoxification and withdrawal management to inpatient rehabilitation programs and outpatient treatment and counseling services. Each option offers its own unique benefits and considerations, and the choice of treatment will depend on the individual’s specific needs and circumstances.
A. Detoxification and Withdrawal Management
Detoxification, also known as detox, is often the first step in treating substance abuse and addiction. This process involves removing the toxic substances from the body and managing the accompanying withdrawal symptoms. Detoxification can be done in a variety of settings, including hospitals, specialized detox centers, or even at home under medical supervision.
During detox, individuals may experience a range of withdrawal symptoms, which can vary depending on the substance abused. These symptoms can be both physical and psychological, and may include nausea, sweating, anxiety, depression, and cravings. Detoxification programs typically provide medical supervision and support to help individuals manage these symptoms safely and comfortably.
It’s important to note that detoxification alone is not sufficient to address substance abuse and addiction in the long term. It is often followed by additional treatment options to address the underlying causes and provide ongoing support for recovery.
B. Inpatient Rehabilitation Programs
Inpatient rehabilitation programs, also known as residential treatment programs, offer a structured and intensive approach to treating substance abuse and addiction. These programs provide individuals with a supportive and therapeutic environment where they can focus on their recovery without the distractions and triggers of the outside world.
During an inpatient rehabilitation program, individuals reside at the treatment facility for a specified period of time, which can range from a few weeks to several months. The length of stay will depend on the individual’s needs and progress in treatment. Inpatient programs typically offer a combination of individual therapy, group therapy, educational sessions, and other therapeutic activities to address the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of addiction.
One of the key advantages of inpatient rehabilitation programs is the 24/7 support and supervision provided by trained professionals. This level of care can be particularly beneficial for individuals with severe addiction or those who require a structured and controlled environment to overcome their substance abuse.
C. Outpatient Treatment and Counseling Services
Outpatient treatment and counseling services offer a more flexible approach to addressing substance abuse and addiction. These programs allow individuals to receive treatment while continuing to live at home and maintain their daily responsibilities, such as work or school.
Outpatient treatment typically involves regular counseling sessions, either individually or in a group setting. These sessions focus on addressing the underlying causes of addiction, developing coping skills, and providing support for recovery. Outpatient programs may also include educational sessions, relapse prevention strategies, and access to community resources.
Outpatient treatment is often recommended for individuals with mild to moderate addiction or those who have completed an inpatient rehabilitation program and require ongoing support. It can also be a suitable option for individuals who have strong social support systems and a stable living environment.
It’s important to note that while outpatient treatment offers flexibility, it may not provide the same level of intensity and supervision as inpatient programs. Individuals in outpatient treatment must have a strong commitment to their recovery and actively participate in the treatment process to achieve positive outcomes.
VII. Support Systems for Recovery
Support systems play a crucial role in the recovery process for individuals struggling with substance abuse and addiction. These systems provide the necessary support, guidance, and resources to help individuals overcome their challenges and maintain long-term sobriety. In this section, we will explore the role of support groups and 12-step programs, the importance of family and community support, and various therapeutic interventions and alternative approaches that can aid in the recovery journey.
A. Role of Support Groups and 12-Step Programs
Support groups and 12-step programs have proven to be invaluable resources for individuals seeking recovery from substance abuse and addiction. These groups provide a safe and non-judgmental environment where individuals can share their experiences, receive support, and learn from others who have faced similar challenges.
One of the most well-known support groups is Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), which follows a 12-step program that focuses on admitting powerlessness over alcohol and surrendering to a higher power. AA meetings provide a platform for individuals to connect with others who understand their struggles and offer guidance and encouragement.
Similarly, Narcotics Anonymous (NA) is a support group that follows the same 12-step model but is specifically tailored to individuals recovering from drug addiction. These groups emphasize the importance of accountability, self-reflection, and spiritual growth in the recovery process.
Support groups and 12-step programs offer a sense of community and fellowship, which can be incredibly beneficial for individuals in recovery. They provide a platform for individuals to share their stories, gain insights, and build meaningful relationships with others who are on the same journey.
B. Importance of Family and Community Support
Family and community support are vital components of the recovery process. The encouragement and understanding of loved ones can make a significant difference in an individual’s ability to overcome addiction and maintain sobriety.
Family members can play a crucial role in supporting their loved ones through their recovery journey. By educating themselves about addiction, attending family therapy sessions, and participating in support groups such as Al-Anon or Nar-Anon, family members can gain a better understanding of the challenges their loved ones face and learn how to provide the necessary support.
Community support is also essential in the recovery process. Local organizations, religious institutions, and community centers often offer resources and programs specifically designed to support individuals in recovery. These resources may include counseling services, vocational training, and sober living environments.
By fostering a supportive and understanding community, individuals in recovery can feel a sense of belonging and find the encouragement they need to stay on track.
C. Therapeutic Interventions and Alternative Approaches
In addition to support groups and family/community support, various therapeutic interventions and alternative approaches can complement the recovery journey and enhance the chances of long-term success.
One such approach is cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with substance abuse. CBT equips individuals with coping mechanisms, stress management techniques, and relapse prevention strategies.
Another effective therapeutic intervention is motivational interviewing (MI), which aims to enhance an individual’s motivation and commitment to change. MI helps individuals explore their ambivalence towards recovery, identify their personal values and goals, and develop a plan for positive change.
Alternative approaches such as mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and holistic therapies like yoga, meditation, and acupuncture can also be beneficial in promoting overall well-being and reducing stress levels, which are often triggers for substance abuse.
It is important to note that the recovery journey is highly individualized, and what works for one person may not work for another. Therefore, it is essential to explore different therapeutic interventions and alternative approaches to find the combination that best suits an individual’s needs and preferences.
VIII. Prevention Strategies for Substance Abuse
Substance abuse and addiction are significant public health issues that require comprehensive prevention strategies. By implementing effective prevention measures, we can reduce the prevalence of substance abuse and its associated consequences. In this section, we will explore three key prevention strategies that have shown promising results:
A. Education and awareness programs
Education and awareness programs play a crucial role in preventing substance abuse. By providing accurate information about the risks and consequences of substance abuse, these programs aim to empower individuals to make informed decisions and resist peer pressure. These programs should be tailored to different age groups and populations, taking into account their specific needs and vulnerabilities.
One effective approach is to incorporate substance abuse prevention into school curricula. By integrating prevention education into subjects like health and science, students can develop a better understanding of the dangers associated with substance abuse. Additionally, schools can invite guest speakers, such as recovering addicts or healthcare professionals, to share their personal experiences and insights.
Furthermore, community-based awareness campaigns can reach a wider audience and create a supportive environment that discourages substance abuse. These campaigns can utilize various mediums, including social media, posters, and public service announcements, to disseminate information and promote healthy behaviors.
B. Early intervention and screening
Early intervention and screening are crucial in identifying individuals at risk of developing substance abuse problems. By detecting and addressing substance abuse at an early stage, we can prevent the progression to addiction and mitigate its negative consequences.
Healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, can play a key role in early intervention. Routine screenings for substance abuse can be incorporated into regular medical check-ups, allowing healthcare professionals to identify potential issues and provide appropriate interventions. Additionally, healthcare providers can offer counseling and support services to individuals who exhibit early signs of substance abuse.
It is also important to implement screening programs in schools, colleges, and workplaces. These programs can identify students or employees who may be engaging in substance abuse and provide them with the necessary support and resources. By intervening early, we can prevent substance abuse from becoming a chronic and debilitating problem.
C. Policy and legislation to reduce availability and accessibility
Policy and legislation play a crucial role in reducing the availability and accessibility of substances that are commonly abused. By implementing stricter regulations and enforcement measures, we can create barriers that discourage substance abuse and protect vulnerable populations.
One effective policy approach is to regulate the sale and distribution of substances with a high potential for abuse, such as alcohol and tobacco. This can include age restrictions, licensing requirements, and taxation measures. By making these substances less accessible, especially to underage individuals, we can reduce the likelihood of initiation and subsequent abuse.
Furthermore, policies can be implemented to limit the marketing and advertising of substances that are commonly abused. This includes restrictions on the promotion of alcohol and tobacco products, particularly targeting youth-oriented platforms and events. By reducing the exposure to these substances, we can minimize the influence of advertising on substance abuse behaviors.
Additionally, policies can focus on promoting responsible prescribing practices for medications with abuse potential, such as opioids. By implementing prescription drug monitoring programs and educating healthcare providers about the risks of overprescribing, we can prevent the misuse and diversion of these medications.
IX. Overcoming Stigma and Seeking Help
Substance abuse and addiction are complex issues that not only affect individuals physically and mentally but also carry a significant social stigma. Addressing societal attitudes towards substance abuse is crucial in creating an environment where individuals feel comfortable seeking help and treatment.
A. Addressing societal attitudes towards substance abuse
One of the biggest barriers to seeking help for substance abuse is the stigma associated with it. Society often views addiction as a moral failing or a lack of willpower, rather than recognizing it as a chronic disease that requires medical intervention. This stigma can prevent individuals from reaching out for help and can lead to feelings of shame and isolation.
As an author with first-hand experience in the field of substance abuse, I understand the importance of challenging these societal attitudes. By educating the public about the nature of addiction and its underlying causes, we can help break down the stereotypes and misconceptions surrounding substance abuse.
It is essential to emphasize that addiction is not a choice but a result of various factors, including genetic predisposition, trauma, and environmental influences. By highlighting the scientific evidence supporting addiction as a disease, we can shift the narrative away from blame and towards empathy and understanding.
Sharing personal anecdotes and experiences can also be a powerful tool in challenging societal attitudes. By humanizing the issue and showing the real-life impact of addiction, we can foster empathy and encourage others to reevaluate their preconceived notions.
B. Encouraging individuals to seek help and treatment
Overcoming the stigma associated with substance abuse is only the first step. We must also actively encourage individuals to seek help and treatment. Many people struggling with addiction may feel ashamed or afraid to reach out, fearing judgment or repercussions.
As an author with expertise in the field, I can provide valuable insights into the treatment options available and the benefits of seeking help. It is crucial to emphasize that recovery is possible and that seeking treatment is a courageous and empowering decision.
Highlighting success stories and showcasing individuals who have overcome addiction can inspire hope and motivate others to take that first step towards recovery. By sharing stories of resilience and highlighting the positive outcomes of treatment, we can counteract the fear and uncertainty that often accompany the decision to seek help.
Additionally, providing practical information on how to access treatment and support resources is essential. This can include listing helpline numbers, treatment centers, and online support groups. By making this information readily available, we can remove some of the barriers that individuals may face when seeking help.
C. Resources for finding treatment and support
When it comes to finding treatment and support for substance abuse, having access to reliable resources is crucial. As an author with affiliations and positions in the field, I can provide valuable recommendations and insights into the best resources available.
One effective way to help individuals find treatment is by listing specific well-known treatment centers and programs. By providing detailed information about these resources, including their approach, success rates, and specialized services, we can guide individuals towards the most suitable options for their needs.
In addition to treatment centers, there are various support groups and organizations that offer assistance to individuals struggling with substance abuse. These groups provide a sense of community, understanding, and guidance throughout the recovery journey.
As an author with first-hand experience, I can share my knowledge of these support groups and organizations, including their mission, services, and how individuals can access their support. By providing this information, we can connect individuals with the resources they need to navigate their recovery successfully.
1. What is the difference between substance abuse and addiction?
Substance abuse and addiction are often used interchangeably, but they have distinct differences. Substance abuse refers to the misuse or excessive use of drugs or alcohol, which can lead to negative consequences in various areas of life. It is characterized by a pattern of harmful use despite the negative effects it has on physical, mental, and social well-being.
On the other hand, addiction is a chronic brain disease that is characterized by compulsive drug seeking and use, despite the harmful consequences. It is a more severe form of substance abuse and is often accompanied by physical and psychological dependence on the substance.
2. How can I recognize if someone is struggling with substance abuse?
Recognizing substance abuse in someone can be challenging, as individuals may try to hide their behavior. However, there are some common signs and symptoms to look out for:
- Changes in behavior or personality
- Physical signs such as bloodshot eyes, dilated pupils, or sudden weight loss
- Neglecting responsibilities at work, school, or home
- Withdrawal from social activities or hobbies
- Financial problems or sudden need for money
- Mood swings or irritability
- Secretive behavior or lying
If you suspect someone is struggling with substance abuse, it is important to approach them with empathy and encourage them to seek help from a healthcare professional or addiction specialist.
3. What are the most commonly abused substances?
There are several substances that are commonly abused, including:
- Alcohol
- Tobacco
- Marijuana
- Prescription drugs (such as opioids, benzodiazepines, and stimulants)
- Cocaine
- Methamphetamine
- Heroin
- Ecstasy
It is important to note that the prevalence of substance abuse can vary depending on factors such as geographical location and cultural influences.
4. Are there any physical health risks associated with substance abuse?
Yes, substance abuse can have serious physical health risks. The specific risks depend on the substance being abused. For example:
- Alcohol abuse can lead to liver damage, cardiovascular problems, and an increased risk of certain cancers.
- Smoking tobacco can cause lung cancer, heart disease, and respiratory problems.
- Drug abuse, such as heroin or cocaine, can lead to organ damage, infectious diseases, and overdose.
It is important to seek medical attention if you or someone you know is struggling with substance abuse to address and manage any potential physical health complications.
5. Can substance abuse lead to mental health disorders?
Yes, substance abuse can contribute to the development of mental health disorders. Substance abuse can disrupt the brain’s normal functioning and lead to changes in mood, behavior, and cognitive abilities. It can also exacerbate existing mental health conditions or trigger the onset of new ones.
Common mental health disorders associated with substance abuse include:
- Depression
- Anxiety disorders
- Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
- Psychosis
It is important to seek professional help to address both substance abuse and any co-occurring mental health disorders for effective treatment and recovery.
6. What treatment options are available for substance abuse?
There are various treatment options available for substance abuse, and the most appropriate approach depends on the individual’s specific needs and circumstances. Some common treatment options include:
- Detoxification: This is the process of removing the substance from the body under medical supervision.
- Inpatient rehabilitation: This involves staying at a residential facility where individuals receive intensive therapy and support.
- Outpatient programs: These programs allow individuals to receive treatment while living at home and attending therapy sessions and support groups.
- Medication-assisted treatment: This involves the use of medications, such as methadone or buprenorphine, to help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings.
- Therapy: Individual and group therapy sessions can help individuals address the underlying causes of substance abuse and develop coping mechanisms.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or addiction specialist to determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
7. How can I support a loved one in their recovery journey?
Supporting a loved one in their recovery journey is crucial for their success. Here are some ways you can provide support:
- Educate yourself about addiction and recovery to better understand what your loved one is going through.
- Offer emotional support and encouragement without judgment.
- Encourage them to seek professional help and attend therapy or support group meetings.
- Help create a supportive and substance-free environment.
- Be patient and understanding, as recovery is a lifelong process.
Remember to take care of yourself as well and seek support from others who understand the challenges of supporting someone in recovery.
8. What are some effective prevention strategies for substance abuse?
Prevention is key in reducing the risk of substance abuse. Some effective prevention strategies include:
- Educating individuals about the risks and consequences of substance abuse.
- Promoting healthy coping mechanisms and stress management techniques.
- Encouraging open communication within families and communities.
- Implementing policies and regulations to restrict access to substances.
- Providing support and resources for individuals at risk, such as counseling services or after-school programs.
Prevention efforts should start early, targeting children and adolescents, and continue throughout adulthood.
9. How can I overcome the stigma associated with substance abuse?
Overcoming the stigma associated with substance abuse can be challenging, but it is essential for individuals seeking help and support. Here are some strategies to combat stigma:
- Educate yourself and others about the nature of addiction as a disease rather than a moral failing.
- Share personal stories and experiences to humanize the issue and challenge stereotypes.
- Advocate for policy changes that promote access to treatment and support services.
- Support organizations and initiatives that aim to reduce stigma and promote understanding.
- Encourage open and non-judgmental conversations about substance abuse.
By challenging stigma, we can create a more supportive and compassionate society for individuals in recovery.
10. Where can I find resources for help and support?
There are various resources available for help and support for substance abuse:
- Local addiction treatment centers or clinics
- Support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) or Narcotics Anonymous (NA)
- National helplines or hotlines
- Online forums and communities
- Therapists or counselors specializing in addiction
It is important to reach out to these resources to get the help and support needed for recovery.
