Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Health Risks of a Sedentary Lifestyle
- III. Understanding the Impact of Prolonged Sitting
- IV. Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
- V. Incorporating Physical Activity into Daily Routine
- VI. Tips for Staying Active at Work
- VII. Active Lifestyle for Different Age Groups
- VIII. The Role of Nutrition in Supporting an Active Lifestyle
- IX. Overcoming Barriers to Physical Activity
- A. Lack of time and busy schedules
- B. Overcoming physical limitations and disabilities
- C. Addressing motivation and staying consistent
- D. Overcoming environmental barriers
- 1. How much physical activity is recommended for adults?
- 2. Can sedentary behavior be reversed?
- 3. What are some low-impact exercises for individuals with joint pain?
- 4. Is it necessary to engage in high-intensity workouts to stay active?
- 5. How can I stay active while working from home?
- 6. Can physical activity help with weight loss?
- 7. What are some fun outdoor activities for families?
- 8. Are there any health risks associated with excessive physical activity?
- 9. How long does it take to see the benefits of regular exercise?
- 10. Can physical activity improve cognitive function?
I. Introduction

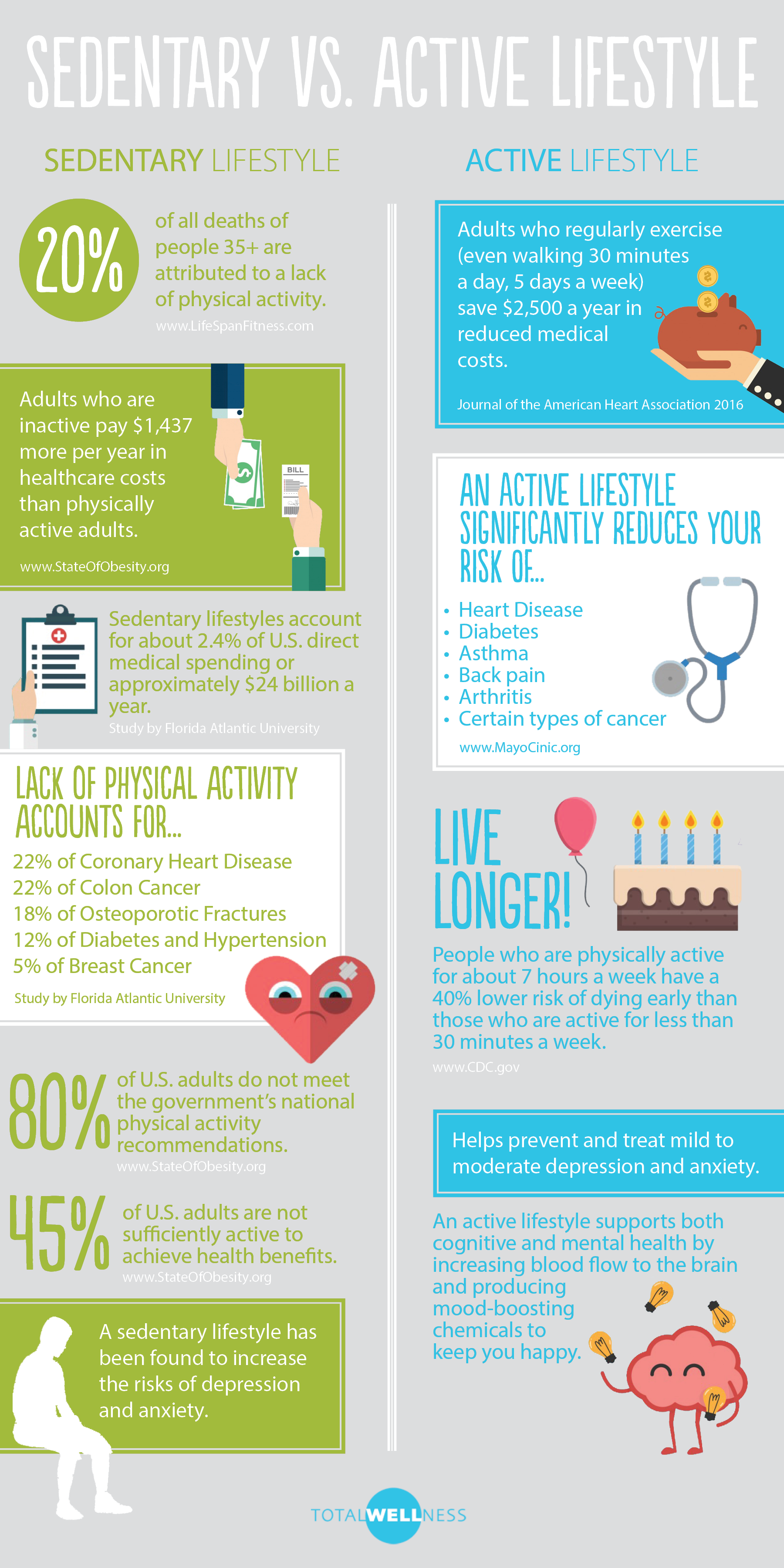
Welcome to the world of sedentary lifestyle and its associated risks. In today’s fast-paced world, it’s easy to fall into the trap of sitting for long hours, whether it’s at work, during commute, or while relaxing at home. However, this seemingly harmless habit can have serious consequences on our health and well-being.
The risks of a sedentary lifestyle are numerous and can affect both our physical and mental health. Prolonged sitting has been linked to increased risk of obesity, heart disease, diabetes, and even certain types of cancer. It can also lead to poor posture, muscle imbalances, and chronic pain.
But don’t worry, there are ways to combat the sedentary lifestyle and stay active. In this article, we will explore the various risks associated with a sedentary lifestyle and provide practical tips on how to incorporate more physical activity into your daily routine.
We will delve into the importance of regular exercise, the benefits of standing desks, and the role of movement breaks in combating the negative effects of prolonged sitting. We will also discuss the psychological impact of a sedentary lifestyle and how staying active can improve our mood and overall well-being.
So, if you’re ready to take charge of your health and break free from the sedentary lifestyle, join us on this journey to discover the risks of sedentary living and learn how to stay active in a world that encourages sitting.
II. Health Risks of a Sedentary Lifestyle

A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by prolonged periods of sitting or physical inactivity, can have detrimental effects on both physical and mental health. In this section, we will explore the various health risks associated with a sedentary lifestyle.
A. Increased risk of obesity and weight gain
One of the most significant health risks of a sedentary lifestyle is the increased risk of obesity and weight gain. When we spend long hours sitting or engaging in minimal physical activity, our bodies burn fewer calories. This can lead to weight gain over time, as the excess calories are stored as fat.
Furthermore, a sedentary lifestyle often goes hand in hand with poor dietary choices, such as consuming processed foods and sugary drinks. These unhealthy eating habits, combined with a lack of physical activity, can contribute to weight gain and obesity.
To combat this risk, it is crucial to incorporate regular exercise and movement into our daily routines. Engaging in activities such as walking, jogging, or participating in sports can help burn calories and maintain a healthy weight.
B. Higher chances of developing cardiovascular diseases
Sitting for long periods without movement can have detrimental effects on our cardiovascular health. Research has shown that a sedentary lifestyle increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease and stroke.
When we sit for extended periods, our blood flow slows down, and our muscles burn less fat, leading to higher levels of triglycerides in the bloodstream. This can contribute to the buildup of plaque in the arteries, increasing the risk of heart disease.
To mitigate this risk, it is essential to incorporate regular physical activity into our daily lives. Engaging in aerobic exercises, such as swimming or cycling, can help improve cardiovascular health and reduce the risk of developing heart disease.
C. Impact on mental health and increased risk of depression
A sedentary lifestyle not only affects our physical health but also has a significant impact on our mental well-being. Studies have shown a link between sedentary behavior and an increased risk of depression and other mental health disorders.
When we lead a sedentary lifestyle, we often miss out on the mood-boosting benefits of physical activity. Exercise releases endorphins, which are natural mood enhancers that help reduce stress and anxiety. Without regular exercise, our bodies may not produce enough endorphins, leading to a higher risk of depression.
To improve mental health and reduce the risk of depression, it is crucial to incorporate physical activity into our daily routines. Engaging in activities such as yoga, dancing, or even taking a brisk walk can have a positive impact on our mental well-being.
D. Link between sedentary behavior and certain types of cancer
Research has also found a link between sedentary behavior and an increased risk of certain types of cancer, including colon, breast, and lung cancer. Prolonged sitting or physical inactivity can contribute to the development of cancer cells in the body.
One possible explanation for this link is that sitting for long periods can lead to weight gain and obesity, which are known risk factors for various types of cancer. Additionally, a sedentary lifestyle may disrupt hormone levels in the body, potentially increasing the risk of hormone-related cancers.
To reduce the risk of cancer, it is important to incorporate regular physical activity into our daily lives. Engaging in moderate-intensity exercises, such as jogging or cycling, can help maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of cancer.
E. Negative effects on musculoskeletal health
A sedentary lifestyle can have negative effects on our musculoskeletal health, leading to issues such as muscle stiffness, joint pain, and decreased flexibility. When we sit for prolonged periods, our muscles and joints become inactive, leading to muscle imbalances and reduced range of motion.
Additionally, sitting in a poor posture, such as slouching or hunching over a desk, can further exacerbate musculoskeletal issues. This can lead to conditions such as back pain, neck pain, and even chronic conditions like osteoarthritis.
To improve musculoskeletal health, it is important to incorporate regular movement and exercise into our daily routines. Stretching exercises, strength training, and maintaining good posture can help alleviate musculoskeletal issues and improve overall physical well-being.
III. Understanding the Impact of Prolonged Sitting
In today’s modern society, many individuals find themselves spending a significant amount of time sitting. Whether it be at a desk job, during long commutes, or while engaging in leisure activities, prolonged sitting has become a common part of our daily lives. However, what many people fail to realize is the detrimental impact that this sedentary behavior can have on our overall health and well-being. In this section, we will explore the various effects of prolonged sitting and shed light on the importance of staying active.
A. Effects on posture and back pain
One of the most noticeable effects of prolonged sitting is its impact on posture and back pain. When we sit for extended periods, our muscles become inactive, leading to muscle imbalances and weakened core strength. This can result in poor posture, as our bodies adapt to the seated position. Over time, this can lead to chronic back pain and discomfort.
Furthermore, sitting for long hours can also put excessive pressure on the intervertebral discs in our spine. This can cause them to compress, leading to conditions such as herniated discs or sciatica. It is crucial to maintain good posture and take regular breaks from sitting to alleviate these issues.
B. Increased risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes
Another concerning effect of prolonged sitting is its association with an increased risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. When we sit for extended periods, our muscles are not engaged, leading to decreased insulin sensitivity. This can result in elevated blood sugar levels and insulin resistance, increasing the risk of developing metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes.
Studies have shown that individuals who sit for more than eight hours a day have a significantly higher risk of developing these conditions compared to those who are more active. Therefore, it is crucial to incorporate regular physical activity and breaks from sitting throughout the day to mitigate these risks.
C. Impact on blood circulation and deep vein thrombosis
Prolonged sitting can also have a detrimental impact on blood circulation, increasing the risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT). When we sit for long periods, blood flow becomes sluggish, especially in the lower extremities. This can lead to the formation of blood clots in the deep veins, which can be potentially life-threatening if they travel to the lungs.
Individuals who frequently engage in long-haul flights or spend extended periods sitting without movement are particularly susceptible to DVT. To prevent this condition, it is essential to take regular breaks from sitting, perform leg exercises, and stay hydrated to promote healthy blood circulation.
D. Relationship between sedentary behavior and poor sleep quality
Lastly, prolonged sitting has been found to have a negative impact on sleep quality. Research has shown that individuals who engage in sedentary behavior throughout the day, especially close to bedtime, experience difficulties falling asleep and maintaining a restful sleep throughout the night.
This can be attributed to various factors, including decreased physical activity, increased stress levels, and disrupted circadian rhythms. To improve sleep quality, it is recommended to incorporate regular exercise, avoid prolonged sitting before bedtime, and establish a consistent sleep routine.
IV. Benefits of Regular Physical Activity
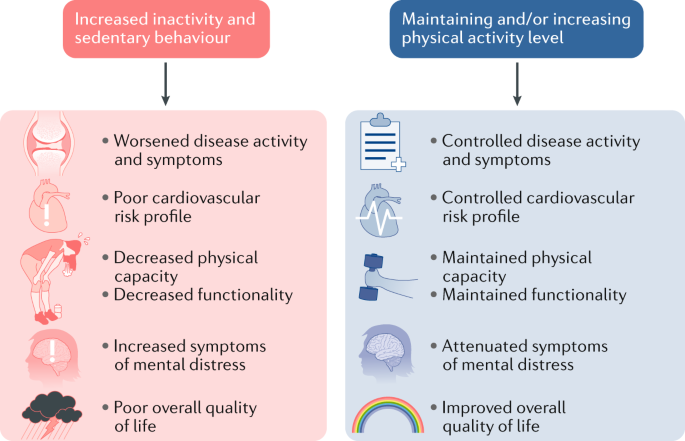
Regular physical activity offers numerous benefits to both the body and mind. Incorporating exercise into your daily routine can have a positive impact on various aspects of your health and well-being. Let’s explore some of the key benefits of regular physical activity:
A. Weight management and increased calorie burn
One of the most obvious benefits of regular physical activity is its role in weight management. Engaging in physical activities such as cardio exercises, strength training, and sports can help burn calories and maintain a healthy weight. When you engage in physical activity, your body utilizes energy, which in turn helps you shed excess pounds and maintain a healthy body mass index (BMI).
Additionally, regular exercise can boost your metabolism, leading to increased calorie burn even when you’re at rest. This means that you continue to burn calories even after you’ve finished your workout, making it easier to achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
B. Improved cardiovascular health and reduced risk of heart diseases
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in improving cardiovascular health and reducing the risk of heart diseases. Engaging in aerobic exercises, such as brisk walking, running, cycling, or swimming, helps strengthen the heart muscle, improve blood circulation, and lower blood pressure.
By engaging in regular physical activity, you can reduce the risk of developing conditions such as high blood pressure, heart disease, and stroke. Exercise helps to keep your heart strong and healthy, ensuring that it can efficiently pump blood throughout your body.
C. Positive effects on mental well-being and reduced stress levels
Physical activity is not only beneficial for the body but also for the mind. Regular exercise has been shown to have positive effects on mental well-being and can help reduce stress levels. When you engage in physical activity, your body releases endorphins, also known as “feel-good” hormones, which can improve your mood and reduce feelings of stress and anxiety.
In addition to endorphins, exercise also promotes the release of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that plays a role in regulating mood. By incorporating regular physical activity into your routine, you can experience improved mental well-being, reduced symptoms of depression, and increased overall happiness.
D. Enhanced muscle strength and flexibility
Engaging in regular physical activity can help enhance muscle strength and flexibility. Activities such as weightlifting, resistance training, and yoga can help build and tone muscles, improving overall strength and endurance.
Strength training exercises target specific muscle groups, helping to increase muscle mass and improve overall body composition. This can lead to improved posture, increased bone density, and reduced risk of age-related muscle loss.
Furthermore, regular physical activity can also enhance flexibility and joint mobility. Stretching exercises, such as yoga or Pilates, can help improve flexibility, making everyday movements easier and reducing the risk of injuries.
E. Improved sleep quality and duration
Regular physical activity can have a positive impact on sleep quality and duration. Engaging in exercise during the day can help regulate your sleep-wake cycle, making it easier to fall asleep at night and wake up feeling refreshed in the morning.
Exercise has been shown to improve sleep quality by reducing the time it takes to fall asleep and increasing the amount of deep sleep experienced throughout the night. Additionally, physical activity can help alleviate symptoms of sleep disorders such as insomnia and sleep apnea.
By incorporating regular physical activity into your routine, you can enjoy a more restful and rejuvenating sleep, leading to improved overall health and well-being.
V. Incorporating Physical Activity into Daily Routine
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/sedentary-lifestyle-2000-a3b919589cc94ba2b95da99749e640f9.jpg)
Living a sedentary lifestyle can have detrimental effects on both physical and mental health. However, finding ways to incorporate physical activity into your daily routine can help combat the risks associated with a sedentary lifestyle. Here are some practical tips to help you set realistic goals, find enjoyable activities, make use of technology, and integrate physical activity into your daily tasks and chores.
A. Setting realistic goals and creating a workout plan
When it comes to incorporating physical activity into your daily routine, it’s important to start with realistic goals. Setting unattainable goals can lead to frustration and demotivation. Instead, focus on small, achievable steps that you can build upon over time. For example, aim to take a 10-minute walk during your lunch break or do a short workout routine before starting your day.
To stay consistent with your physical activity, it can be helpful to create a workout plan. This plan should include specific activities, durations, and frequencies. By scheduling your workouts in advance, you are more likely to follow through and make physical activity a regular part of your routine.
B. Finding enjoyable activities and hobbies that involve movement
One of the keys to incorporating physical activity into your daily routine is to find activities that you genuinely enjoy. Engaging in activities that you find fun and interesting will make it easier to stay motivated and committed. Consider trying out different sports, dance classes, or outdoor activities to discover what you enjoy the most.
Additionally, incorporating physical activity into your hobbies can be a great way to make it a seamless part of your daily routine. For example, if you enjoy gardening, spend extra time tending to your plants or create a mini workout routine while doing household chores. By combining physical activity with activities you already enjoy, you’ll be more likely to stick with it.
C. Making use of technology and fitness apps
In today’s digital age, technology can be a valuable tool for incorporating physical activity into your daily routine. There are numerous fitness apps available that can help you track your progress, provide workout routines, and offer motivation and guidance. These apps can be particularly helpful if you prefer working out at home or need some extra support and structure.
Additionally, wearable fitness trackers can also be a useful tool for monitoring your daily activity levels. These devices can provide insights into your steps, heart rate, and calories burned, helping you stay accountable and motivated to reach your physical activity goals.
D. Incorporating physical activity into daily tasks and chores
Another effective way to incorporate physical activity into your daily routine is by finding opportunities to be active during your daily tasks and chores. For example, instead of taking the elevator, opt for the stairs. If you need to run errands, consider walking or biking instead of driving. These small changes can add up and contribute to your overall physical activity levels.
When doing household chores, such as cleaning or gardening, try to make them more physically demanding. For instance, increase the intensity of your cleaning by adding squats or lunges while vacuuming or mopping. Gardening can also be a great way to engage in physical activity, as it involves bending, lifting, and stretching.
By incorporating physical activity into your daily tasks and chores, you can make the most of your time and ensure that you’re getting regular exercise, even on busy days.
VI. Tips for Staying Active at Work
As someone who has spent years working in a sedentary job, I understand the challenges of staying active while being confined to a desk for long hours. However, I have discovered several effective strategies to incorporate physical activity into my work routine. In this section, I will share some tips that have helped me stay active and maintain my health despite the demands of a sedentary job.
A. Utilizing standing desks and ergonomic chairs
One of the most significant changes I made to my work environment was investing in a standing desk and an ergonomic chair. These ergonomic solutions have been designed to promote better posture and reduce the strain on the body caused by prolonged sitting. By alternating between sitting and standing throughout the day, I have noticed a significant improvement in my energy levels and overall well-being.
Standing desks allow me to work in a more upright position, engaging my core muscles and promoting better blood circulation. Additionally, ergonomic chairs provide proper support to my back, reducing the risk of developing back pain or other musculoskeletal issues. I highly recommend investing in these ergonomic solutions to create a more active and comfortable work environment.
B. Taking regular breaks and stretching exercises
Another effective strategy for staying active at work is to take regular breaks and incorporate stretching exercises into your routine. Sitting for prolonged periods can lead to muscle stiffness and decreased flexibility. By taking short breaks every hour or so, I give myself an opportunity to stretch my muscles and get my blood flowing.
During these breaks, I perform simple stretching exercises that target different muscle groups. These exercises include neck rolls, shoulder stretches, wrist rotations, and leg stretches. Not only do these exercises help prevent muscle tension and stiffness, but they also provide a mental break, allowing me to refocus and improve my productivity.
C. Incorporating walking meetings and active breaks
One of the most innovative ways I have found to stay active at work is by incorporating walking meetings and active breaks. Instead of sitting in a conference room, I suggest taking meetings outside and walking while discussing important matters. Not only does this promote physical activity, but it also enhances creativity and collaboration.
Additionally, I make it a point to take active breaks throughout the day. Instead of scrolling through social media or checking emails during my breaks, I engage in physical activities such as walking, jogging, or doing a quick workout. These active breaks not only help me stay fit but also provide a much-needed mental break, allowing me to return to work with renewed focus and energy.
D. Using fitness trackers and reminder apps
To stay accountable and motivated in my journey towards a more active lifestyle, I rely on fitness trackers and reminder apps. Fitness trackers, such as smartwatches or fitness bands, help me track my daily steps, calories burned, and overall activity level. By setting goals and monitoring my progress, I am motivated to achieve my daily activity targets.
In addition to fitness trackers, I also use reminder apps on my phone or computer to prompt me to take regular breaks and engage in physical activity. These apps send notifications at predetermined intervals, reminding me to get up, stretch, or go for a short walk. By incorporating these technological tools into my work routine, I have successfully integrated physical activity into my daily life.
By implementing these tips, I have been able to combat the negative effects of a sedentary job and maintain an active and healthy lifestyle. Utilizing standing desks and ergonomic chairs, taking regular breaks and performing stretching exercises, incorporating walking meetings and active breaks, and using fitness trackers and reminder apps have all contributed to my overall well-being. I encourage you to try these strategies and discover the positive impact they can have on your health and productivity.
VII. Active Lifestyle for Different Age Groups
Leading an active lifestyle is crucial for individuals of all age groups. Regular physical activity not only promotes physical health but also contributes to mental well-being. In this section, we will explore the importance of staying active during childhood and adolescence, maintaining physical activity in adulthood, and the significance of exercise for seniors and older adults.
A. Staying active during childhood and adolescence
Childhood and adolescence are critical stages for physical development and establishing healthy habits. Engaging in regular physical activity during these years sets the foundation for a lifetime of well-being. It is recommended that children and adolescents engage in at least 60 minutes of moderate to vigorous physical activity every day.
Physical activity during childhood and adolescence offers numerous benefits. It helps in maintaining a healthy weight, building strong bones and muscles, improving cardiovascular fitness, and promoting overall physical and mental health. Additionally, regular exercise enhances cognitive function, concentration, and academic performance.
Encouraging children and adolescents to participate in a variety of physical activities, such as team sports, swimming, cycling, dancing, and martial arts, can make exercise enjoyable and help them develop a lifelong love for being active. It is also important to limit sedentary activities, such as excessive screen time, and promote outdoor play and recreational activities.
B. Maintaining physical activity in adulthood
As individuals transition into adulthood, maintaining an active lifestyle becomes increasingly important. Regular exercise in adulthood helps in preventing chronic diseases, managing weight, improving cardiovascular health, and enhancing mental well-being.
Engaging in a combination of aerobic activities, such as jogging, swimming, or cycling, and strength training exercises, like weightlifting or yoga, is recommended for adults. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days.
It is crucial to find physical activities that align with personal interests and preferences to ensure long-term adherence. Joining fitness classes, participating in recreational sports leagues, or incorporating physical activity into daily routines, such as walking or cycling to work, can make exercise more enjoyable and sustainable.
C. Importance of exercise for seniors and older adults
Regular exercise is equally important for seniors and older adults to maintain physical function, independence, and overall quality of life. Engaging in appropriate physical activities can help prevent age-related declines in muscle mass, strength, flexibility, and balance.
For older adults, it is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week, along with muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days. Activities such as brisk walking, swimming, water aerobics, tai chi, and yoga are excellent options for older adults.
Exercise can help manage chronic conditions, such as arthritis, osteoporosis, and heart disease, and reduce the risk of falls and injuries. It also promotes cognitive function, improves mood, and enhances social connections, as many physical activities can be done in group settings.
It is important for older adults to consult with healthcare professionals or certified exercise specialists to determine the most suitable activities and exercise modifications based on individual health conditions and physical abilities.
VIII. The Role of Nutrition in Supporting an Active Lifestyle
As an avid fitness enthusiast and certified nutritionist, I understand the importance of maintaining a balanced diet to support an active lifestyle. Proper nutrition not only provides the necessary energy for physical activities but also aids in muscle recovery and overall performance. In this section, we will explore the significance of a balanced diet for energy levels, discuss nutritional considerations for pre and post-workout meals, and delve into the impact of hydration on physical performance.
A. Importance of a Balanced Diet for Energy Levels
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in providing the energy needed to fuel our bodies during physical activities. It consists of a combination of macronutrients, including carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, as well as micronutrients such as vitamins and minerals. Each of these components contributes to the overall energy production and maintenance of bodily functions.
Carbohydrates, in the form of complex carbohydrates found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, are the primary source of energy for our muscles. They are broken down into glucose, which is then utilized by our cells to produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP), the energy currency of our bodies. Including an adequate amount of carbohydrates in our diet ensures that we have enough energy to perform physical activities and prevents fatigue.
Proteins, on the other hand, are essential for muscle repair and growth. During exercise, our muscles undergo microtears, and protein consumption helps in their recovery and rebuilding. Including lean sources of protein, such as chicken, fish, tofu, and legumes, in our diet is crucial for maintaining muscle mass and supporting an active lifestyle.
Fats, although often demonized, are an important part of a balanced diet. They provide a concentrated source of energy and help in the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins. Including healthy fats, such as avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, in our diet can provide sustained energy and support overall health.
In addition to macronutrients, micronutrients also play a vital role in energy production. B vitamins, for example, are involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, and their deficiency can lead to decreased energy levels. Including a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in our diet ensures an adequate intake of these essential micronutrients.
B. Nutritional Considerations for Pre and Post-Workout Meals
What we eat before and after a workout can significantly impact our performance and recovery. Pre-workout meals should provide a combination of carbohydrates and proteins to fuel our muscles and enhance endurance. Consuming a meal or snack that is easily digestible and low in fat is ideal to prevent discomfort during exercise.
Some examples of pre-workout meals include a banana with a tablespoon of peanut butter, a Greek yogurt with berries, or a whole grain toast with avocado and eggs. These options provide a good balance of carbohydrates and proteins to sustain energy levels and support muscle function.
Post-workout meals, on the other hand, should focus on replenishing glycogen stores and aiding in muscle recovery. Including a combination of carbohydrates and proteins within 30 minutes to an hour after exercise is crucial for optimal recovery. This timing allows for efficient nutrient absorption and utilization by the muscles.
Some post-workout meal ideas include a protein shake with a banana, grilled chicken with sweet potatoes and vegetables, or a quinoa salad with mixed greens and grilled salmon. These options provide the necessary nutrients to repair and rebuild muscles, as well as replenish energy stores.
C. Hydration and Its Impact on Physical Performance
Staying hydrated is essential for maintaining optimal physical performance. Water is involved in various bodily functions, including temperature regulation, nutrient transport, and joint lubrication. During exercise, we lose water through sweat, and it is crucial to replenish these losses to prevent dehydration.
Dehydration can lead to decreased endurance, muscle cramps, and impaired cognitive function. It is recommended to drink water before, during, and after exercise to maintain proper hydration levels. The exact amount of water needed varies depending on factors such as intensity and duration of exercise, as well as individual sweat rates.
In addition to water, electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium are also lost through sweat and need to be replenished. Including electrolyte-rich foods and beverages, such as coconut water, sports drinks, and fruits and vegetables, can help maintain electrolyte balance and enhance hydration.
It is important to listen to our bodies and drink when thirsty, as thirst is a signal of dehydration. By staying properly hydrated, we can optimize our physical performance, prevent fatigue, and support overall health.
IX. Overcoming Barriers to Physical Activity
Physical activity plays a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. However, many individuals face various barriers that hinder their ability to engage in regular exercise. In this section, we will explore some common barriers to physical activity and discuss strategies to overcome them.
A. Lack of time and busy schedules
One of the most common barriers to physical activity is a lack of time and busy schedules. Many individuals find it challenging to fit exercise into their daily routines due to work, family commitments, and other responsibilities. However, with some planning and prioritization, it is possible to overcome this barrier.
Firstly, it is essential to assess your daily schedule and identify pockets of time that can be dedicated to physical activity. This could include waking up earlier in the morning, utilizing lunch breaks, or setting aside specific time slots in the evening. By incorporating exercise into your daily routine, you can make it a non-negotiable part of your day.
Additionally, consider incorporating physical activity into your daily activities. For example, instead of driving to work, you could opt to walk or cycle if feasible. Similarly, you can take the stairs instead of the elevator or park your car farther away from your destination to increase your daily steps.
Moreover, it can be helpful to prioritize physical activity by treating it as an important appointment. Just as you would schedule a meeting or a doctor’s appointment, block off time for exercise in your calendar. By treating it as a non-negotiable commitment, you are more likely to follow through and make it a regular habit.
B. Overcoming physical limitations and disabilities
Physical limitations and disabilities can pose significant barriers to engaging in physical activity. However, it is essential to remember that physical activity can be adapted to suit individual needs and abilities. There are various options available for individuals with physical limitations or disabilities to stay active.
Firstly, consult with a healthcare professional or a certified exercise specialist who can provide guidance on suitable exercises and modifications. They can help design a personalized exercise program that takes into account your specific limitations and goals.
Furthermore, consider exploring adaptive sports and activities that cater to individuals with disabilities. These activities are designed to accommodate different abilities and provide opportunities for individuals to engage in physical activity. Examples include wheelchair basketball, seated yoga, and adaptive swimming.
Additionally, technology can be a valuable tool in overcoming physical limitations. There are numerous assistive devices and equipment available that can aid in physical activity. For example, individuals with mobility impairments can use adaptive equipment such as hand cycles or recumbent bikes to engage in cardiovascular exercise.
C. Addressing motivation and staying consistent
Motivation and consistency are key factors in maintaining an active lifestyle. However, many individuals struggle with staying motivated and consistent with their exercise routines. Here are some strategies to address motivation and enhance consistency:
1. Set realistic goals: Start by setting achievable and realistic goals that align with your interests and abilities. Break down larger goals into smaller milestones to track progress and stay motivated.
2. Find activities you enjoy: Engage in physical activities that you genuinely enjoy. Whether it’s dancing, hiking, or playing a sport, finding activities that bring you joy will make it easier to stay motivated and consistent.
3. Mix it up: Avoid monotony by incorporating a variety of activities into your routine. Trying new exercises or participating in different classes can keep things interesting and prevent boredom.
4. Buddy up: Find a workout buddy or join a group exercise class. Exercising with others can provide accountability, social support, and make the experience more enjoyable.
5. Track progress: Keep track of your progress to stay motivated. Whether it’s through a fitness app, a journal, or a wearable device, monitoring your achievements can boost motivation and provide a sense of accomplishment.
D. Overcoming environmental barriers
Environmental barriers can significantly impact an individual’s ability to engage in physical activity. These barriers can include lack of access to safe and convenient exercise facilities, limited green spaces, or unfavorable weather conditions. However, there are ways to overcome these environmental barriers:
1. Explore alternative exercise options: If access to a gym or fitness center is limited, consider alternative exercise options that can be done at home or in your local community. These can include bodyweight exercises, yoga, or outdoor activities such as walking or running.
2. Utilize online resources: Take advantage of online workout videos, fitness apps, and virtual classes. These resources provide a wide range of exercise options that can be done from the comfort of your own home.
3. Make use of public spaces: Look for parks, trails, or community centers in your area that offer free or low-cost exercise facilities. Many cities have outdoor fitness equipment or designated exercise areas that can be utilized for physical activity.
4. Dress for the weather: Don’t let unfavorable weather conditions deter you from being active. Invest in appropriate gear and clothing that allows you to exercise comfortably in different weather conditions.
5. Advocate for change: If you identify specific environmental barriers in your community, consider advocating for change. This could involve collaborating with local authorities, community organizations, or neighborhood groups to improve access to safe and convenient exercise facilities.
By addressing these common barriers to physical activity, individuals can overcome challenges and lead a more active and healthy lifestyle. Remember, every small step towards incorporating physical activity into your routine is a step towards better health and well-being.
1. How much physical activity is recommended for adults?
For adults, it is recommended to engage in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic activity per week. This can be spread out over several days and can include activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Additionally, adults should also incorporate muscle-strengthening activities that work all major muscle groups on two or more days a week.
2. Can sedentary behavior be reversed?
Yes, sedentary behavior can be reversed. Making small changes to your daily routine can help reduce sedentary time and increase physical activity. Taking short breaks to stand up and stretch, using a standing desk, or incorporating regular movement breaks throughout the day can all help combat the negative effects of prolonged sitting.
3. What are some low-impact exercises for individuals with joint pain?
Low-impact exercises are gentle on the joints and can be beneficial for individuals with joint pain. Some examples include swimming, water aerobics, cycling, using an elliptical machine, or practicing yoga. These activities help improve cardiovascular fitness, strengthen muscles, and increase flexibility without putting excessive strain on the joints.
4. Is it necessary to engage in high-intensity workouts to stay active?
No, it is not necessary to engage in high-intensity workouts to stay active. While high-intensity workouts can provide additional benefits, such as improved cardiovascular fitness and increased calorie burn, moderate-intensity activities can still contribute to overall health and well-being. It’s important to choose activities that you enjoy and that align with your fitness level and goals.
5. How can I stay active while working from home?
Staying active while working from home can be challenging, but there are several strategies you can try. Set regular breaks to stretch and move around, incorporate short exercise sessions during your breaks, use a standing desk or adjustable workstation, take walking meetings, or try online workout classes or fitness apps that can be done from home. Finding ways to incorporate physical activity into your daily routine is key.
6. Can physical activity help with weight loss?
Yes, physical activity can be an important component of weight loss. Regular exercise helps burn calories, increase metabolism, and build lean muscle mass, all of which can contribute to weight loss. However, it’s important to combine physical activity with a balanced diet and overall healthy lifestyle for optimal weight management.
7. What are some fun outdoor activities for families?
There are plenty of fun outdoor activities that families can enjoy together. Some ideas include hiking, biking, picnicking in the park, playing sports like soccer or frisbee, going for nature walks, or visiting local playgrounds. These activities not only promote physical fitness but also provide opportunities for quality family time and connection with nature.
8. Are there any health risks associated with excessive physical activity?
While regular physical activity is generally beneficial for health, excessive or intense exercise without proper rest and recovery can increase the risk of injury and overtraining. It’s important to listen to your body, gradually increase the intensity and duration of your workouts, and incorporate rest days into your routine. If you have any underlying health conditions or concerns, it’s always a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new exercise program.
9. How long does it take to see the benefits of regular exercise?
The timeline for experiencing the benefits of regular exercise can vary depending on factors such as individual fitness level, the type and intensity of exercise, and consistency. However, in general, you may start noticing some improvements in cardiovascular fitness, energy levels, and mood within a few weeks of starting a regular exercise routine. Long-term benefits, such as improved muscle strength, weight management, and reduced risk of chronic diseases, can take several months or more of consistent effort.
10. Can physical activity improve cognitive function?
Yes, physical activity has been shown to have positive effects on cognitive function. Regular exercise can improve memory, attention, and executive function, as well as reduce the risk of cognitive decline and age-related cognitive disorders. Engaging in aerobic activities that increase heart rate and blood flow to the brain, such as brisk walking or cycling, may be particularly beneficial for cognitive health.
