Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Threats to endangered primates
- III. Conservation organizations working to protect endangered primates
- IV. Conservation strategies for protecting endangered primates
- V. Case studies of successful primate conservation projects
- VI. Role of research in primate conservation
- VII. Challenges and obstacles in primate conservation
- VIII. Collaboration and partnerships in primate conservation
- IX. Education and awareness in primate conservation
I. Introduction

Welcome to the world of conservation efforts to protect endangered primates. As human activities continue to encroach upon their natural habitats, many primate species are facing the threat of extinction. In this article, we will explore the various initiatives and strategies that are being implemented to safeguard these incredible creatures.
Primates, such as gorillas, orangutans, and lemurs, are highly intelligent and social animals. They play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems and are often considered keystone species. Unfortunately, due to factors like deforestation, illegal hunting, and the pet trade, their populations have been rapidly declining.
Conservation organizations and researchers around the world have recognized the urgent need to protect these endangered primates. Efforts are being made to establish protected areas, promote sustainable practices, and raise awareness about the importance of primate conservation.
One of the key strategies employed is the creation of protected areas or national parks specifically dedicated to primate conservation. These areas serve as safe havens for primates, allowing them to thrive without human interference. Additionally, they provide opportunities for researchers to study these animals and gather valuable data for conservation efforts.
Sustainable practices are also being promoted to mitigate the negative impact of human activities on primate habitats. This includes promoting responsible tourism, supporting local communities in adopting sustainable livelihoods, and implementing reforestation programs to restore degraded habitats.
Education and awareness play a vital role in primate conservation. By educating the public about the importance of these animals and the threats they face, we can foster a sense of responsibility and inspire action. Conservation organizations are actively engaging with local communities, schools, and governments to spread awareness and promote conservation practices.
II. Threats to endangered primates

Endangered primates face numerous threats that jeopardize their survival. These threats include habitat loss and fragmentation, illegal wildlife trade, and climate change. In this section, we will explore each of these threats in detail.
A. Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
Habitat loss and fragmentation are major threats to endangered primates. As human populations continue to expand, natural habitats are being destroyed to make way for agriculture, infrastructure development, and urbanization. This loss of habitat directly impacts primates, as it restricts their access to food sources, mating partners, and safe shelter.
Fragmentation occurs when large areas of continuous habitat are divided into smaller, isolated patches. This fragmentation disrupts the natural movement and gene flow of primates, leading to reduced genetic diversity and increased vulnerability to diseases. It also increases the risk of human-wildlife conflicts, as primates are forced to venture into human settlements in search of resources.
To address habitat loss and fragmentation, conservation organizations and governments need to prioritize the protection and restoration of primate habitats. This can be achieved through the establishment of protected areas, the implementation of sustainable land-use practices, and the promotion of community-based conservation initiatives.
B. Illegal Wildlife Trade
The illegal wildlife trade poses a significant threat to endangered primates. Primates are often targeted for their meat, body parts, and live specimens, which are highly valued in traditional medicine, exotic pet trade, and entertainment industries. This unsustainable demand drives the illegal hunting and capture of primates, pushing their populations further towards extinction.
Furthermore, the illegal wildlife trade is often linked to organized crime networks and corruption, making it a complex and challenging issue to tackle. Efforts to combat this trade require a multi-faceted approach, including strengthening law enforcement, raising public awareness, and promoting sustainable alternatives to the use of primate products.
Conservation organizations and governments play a crucial role in disrupting the illegal wildlife trade by supporting anti-poaching initiatives, improving legislation and enforcement, and collaborating with local communities to address the underlying drivers of this trade.
C. Climate Change
Climate change is a growing threat to endangered primates and their habitats. Rising temperatures, changing rainfall patterns, and extreme weather events can disrupt the delicate balance of ecosystems, affecting the availability of food, water, and suitable habitats for primates.
Primates, especially those living in tropical rainforests, are highly sensitive to changes in their environment. Climate change can lead to shifts in vegetation patterns, altering the distribution of food resources and disrupting the natural interactions between primates and their ecosystem.
Additionally, climate change can exacerbate other threats faced by primates, such as habitat loss and disease outbreaks. For example, deforestation driven by climate change can further fragment primate habitats, making them more vulnerable to human encroachment and reducing their resilience to diseases.
To mitigate the impacts of climate change on primates, it is essential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable practices. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, implementing reforestation and habitat restoration projects, and supporting local communities in adapting to the changing climate.
III. Conservation organizations working to protect endangered primates
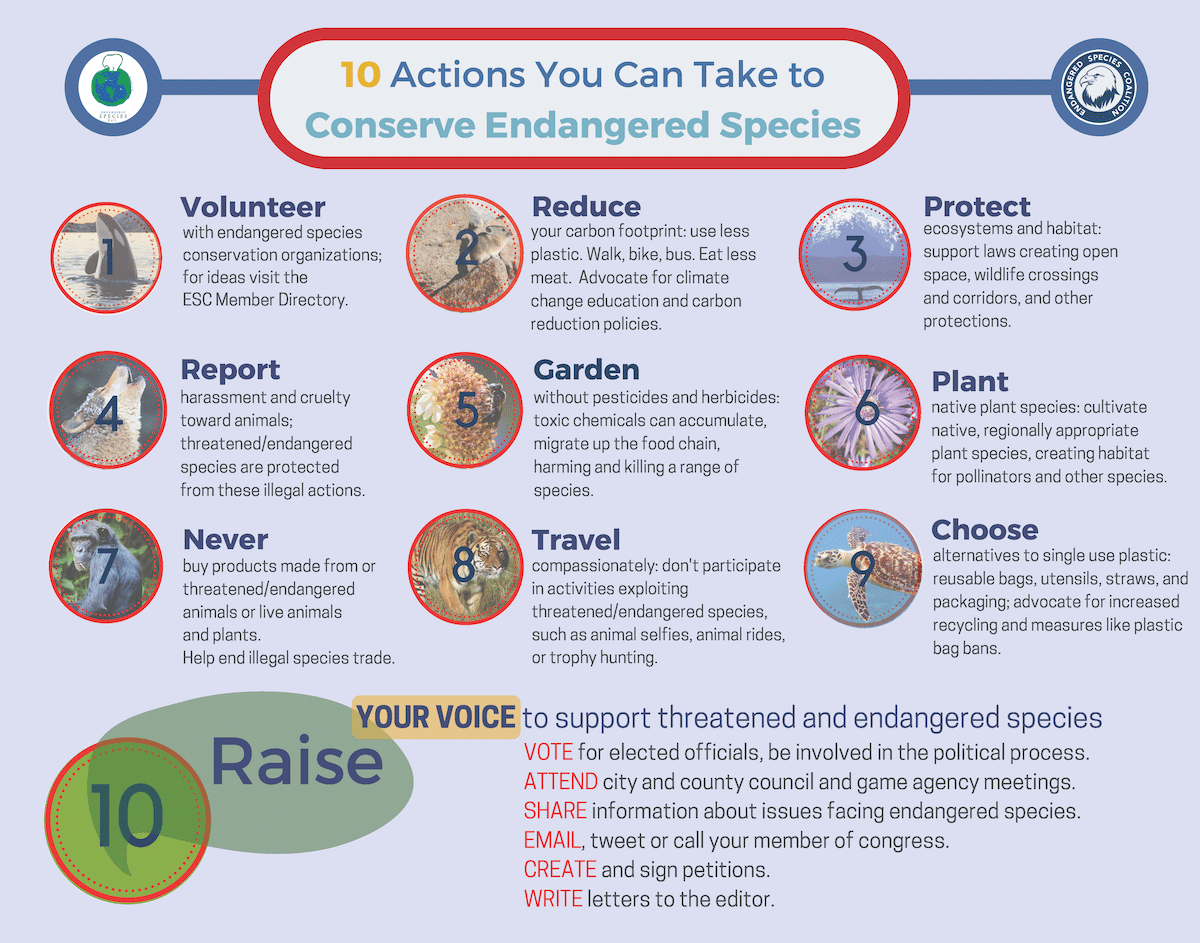
Conservation organizations play a crucial role in protecting endangered primates and their habitats. These organizations work tirelessly to raise awareness, conduct research, and implement conservation strategies to ensure the survival of these vulnerable species. In this section, we will explore three prominent conservation organizations that are actively involved in primate conservation efforts.
A. World Wildlife Fund (WWF)
The World Wildlife Fund (WWF) is a leading international conservation organization that has been working towards protecting endangered species and their habitats for over 60 years. With a strong focus on biodiversity conservation, the WWF has made significant contributions to primate conservation worldwide.
The WWF’s primate conservation initiatives involve a multi-faceted approach that includes habitat protection, community engagement, and policy advocacy. By collaborating with local communities, the WWF aims to promote sustainable livelihoods that are compatible with primate conservation. They also work closely with governments and policymakers to develop and implement effective conservation policies and laws.
One of the WWF’s notable primate conservation projects is the protection of the critically endangered mountain gorillas in Central Africa. Through partnerships with local organizations and governments, the WWF has been successful in increasing the population of mountain gorillas and improving their habitat.
The WWF also conducts research to better understand primate behavior, ecology, and threats they face. This knowledge is used to develop targeted conservation strategies and inform decision-making processes.
B. International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is a global authority on the status of the natural world and the measures needed to safeguard it. The IUCN’s mission is to influence, encourage, and assist societies throughout the world to conserve the integrity and diversity of nature and to ensure that any use of natural resources is equitable and ecologically sustainable.
The IUCN’s Primate Specialist Group focuses on primate conservation by providing scientific expertise and guidance to conservation efforts worldwide. The group assesses the conservation status of primate species, identifies threats, and develops action plans to address these challenges.
Through its Red List of Threatened Species, the IUCN assesses the extinction risk of various primate species and provides valuable information for conservation planning. The IUCN also supports field projects that aim to protect primate populations and their habitats.
Additionally, the IUCN collaborates with governments, NGOs, and local communities to develop conservation strategies, promote sustainable practices, and raise awareness about the importance of primate conservation.
C. Jane Goodall Institute
The Jane Goodall Institute (JGI) is a global organization founded by renowned primatologist Dr. Jane Goodall. The institute’s mission is to empower individuals to take action on behalf of all living things and the environment. With a specific focus on chimpanzees, the JGI has made significant contributions to primate conservation.
The JGI’s approach to primate conservation involves a combination of research, community-centered conservation, and education. Through their long-term research projects, the JGI collects valuable data on chimpanzee behavior, ecology, and conservation needs.
Community-centered conservation is a key aspect of the JGI’s work. By engaging with local communities, the JGI aims to address the root causes of habitat destruction and promote sustainable livelihoods. This approach not only benefits chimpanzees but also improves the well-being of local communities.
The JGI’s education programs focus on raising awareness about the importance of primate conservation and inspiring the next generation of conservationists. Through initiatives like Roots & Shoots, the JGI empowers young people to become environmental stewards and make a positive impact in their communities.
IV. Conservation strategies for protecting endangered primates

Conservation efforts play a crucial role in protecting endangered primates and ensuring their survival for future generations. Various strategies have been implemented to address the threats faced by these species, including the establishment of protected areas and national parks, habitat restoration and reforestation, and community-based conservation initiatives.
A. Protected areas and national parks
Protected areas and national parks serve as sanctuaries for endangered primates, providing them with a safe and secure habitat where they can thrive. These areas are carefully managed to ensure the preservation of biodiversity and the protection of critical ecosystems.
By designating specific regions as protected areas or national parks, governments and conservation organizations can regulate human activities and prevent habitat destruction, illegal hunting, and other threats to primate populations. These areas often have strict regulations in place to minimize human impact and promote the well-being of endangered species.
Furthermore, protected areas and national parks offer opportunities for research and monitoring, allowing scientists to gather valuable data on primate behavior, population dynamics, and ecological interactions. This information is crucial for developing effective conservation strategies and implementing targeted interventions to safeguard endangered primates.
B. Habitat restoration and reforestation
Habitat loss is one of the primary drivers of primate endangerment. To counteract this threat, conservationists focus on habitat restoration and reforestation efforts to create suitable environments for endangered primates to thrive.
Through habitat restoration, degraded areas are rehabilitated and transformed into functional ecosystems that can support diverse primate populations. This involves activities such as planting native tree species, removing invasive plants, and creating corridors to connect fragmented habitats.
Reforestation initiatives also play a crucial role in providing additional habitats for endangered primates. By planting trees in deforested areas, conservationists can recreate forest ecosystems and provide essential resources, such as food and shelter, for primate species.
Moreover, habitat restoration and reforestation efforts contribute to carbon sequestration, mitigating the effects of climate change and promoting overall ecosystem health. This multi-faceted approach not only benefits endangered primates but also helps to preserve the ecological balance of the surrounding environment.
C. Community-based conservation initiatives
Community-based conservation initiatives involve engaging local communities in the protection and conservation of endangered primates. These initiatives recognize the importance of collaboration and the active involvement of communities living in close proximity to primate habitats.
By working closely with local communities, conservation organizations can promote sustainable livelihoods that are compatible with primate conservation. This can include initiatives such as ecotourism, sustainable agriculture, and alternative income-generating activities that reduce the reliance on activities detrimental to primate populations.
Community-based conservation initiatives also prioritize education and awareness-raising programs to foster a sense of stewardship and responsibility towards endangered primates. By empowering local communities with knowledge about the importance of primate conservation, they become active participants in protecting these species.
Furthermore, these initiatives often involve capacity-building programs, providing training and resources to local communities to enable them to actively contribute to primate conservation efforts. This collaborative approach ensures the long-term sustainability of conservation initiatives and fosters a sense of ownership and pride among community members.
V. Case studies of successful primate conservation projects

In this section, we will explore three case studies of successful primate conservation projects from different parts of the world. These projects have made significant contributions to the protection and preservation of endangered primate species.
A. Orangutan conservation in Borneo
Borneo is home to one of the most iconic primate species, the orangutan. These magnificent creatures have faced numerous threats, including habitat loss, illegal hunting, and the illegal pet trade. However, thanks to the efforts of dedicated conservation organizations and local communities, significant progress has been made in protecting and conserving orangutans in Borneo.
One successful conservation project in Borneo is the Orangutan Foundation International (OFI). Founded by renowned primatologist Dr. Biruté Mary Galdikas, OFI has been working tirelessly to rehabilitate and release orangutans back into the wild, as well as to protect their natural habitat.
OFI’s approach involves rescuing orphaned and injured orangutans, providing them with medical care and rehabilitation, and eventually reintroducing them to protected forest areas. The organization also focuses on community engagement and education to raise awareness about the importance of orangutan conservation.
Through their efforts, OFI has successfully released numerous orangutans back into the wild, contributing to the overall population recovery of this critically endangered species. Their work has also led to the establishment of protected areas and the implementation of stricter regulations against illegal hunting and logging.
B. Mountain gorilla conservation in Rwanda
Rwanda is home to the endangered mountain gorillas, which face numerous threats, including habitat loss, poaching, and political instability. However, thanks to the collaborative efforts of the Rwandan government, conservation organizations, and local communities, mountain gorilla populations have shown remarkable recovery in recent years.
One of the most successful conservation projects in Rwanda is the Volcanoes National Park, which is home to a significant portion of the mountain gorilla population. The park has implemented strict protection measures, including anti-poaching patrols and community-based conservation initiatives.
Additionally, the Dian Fossey Gorilla Fund International has been instrumental in the conservation of mountain gorillas in Rwanda. The organization, founded by renowned primatologist Dian Fossey, focuses on research, education, and community development to ensure the long-term survival of these magnificent creatures.
The efforts of the Rwandan government and conservation organizations have led to a significant increase in the mountain gorilla population in recent years. This success story has not only contributed to the conservation of a critically endangered species but has also boosted eco-tourism in Rwanda, providing economic benefits to local communities.
C. Golden lion tamarin conservation in Brazil
The golden lion tamarin is a small primate species endemic to the Atlantic Forest in Brazil. Due to deforestation and habitat fragmentation, the population of golden lion tamarins declined rapidly, pushing them to the brink of extinction. However, thanks to the dedicated efforts of conservation organizations and government agencies, the golden lion tamarin population has shown signs of recovery.
One of the key players in golden lion tamarin conservation is the Golden Lion Tamarin Association (AMLD), which focuses on habitat restoration, captive breeding, and community engagement. Through their efforts, AMLD has successfully reintroduced captive-bred tamarins into protected forest areas, expanding their range and increasing their population.
In addition to AMLD, the Brazilian government has implemented strict regulations against deforestation and illegal wildlife trade, providing legal protection to the golden lion tamarin and its habitat. The government has also established protected areas and implemented conservation programs to ensure the long-term survival of this endangered primate species.
The combined efforts of conservation organizations, government agencies, and local communities have resulted in a significant increase in the golden lion tamarin population. This success story serves as an inspiration for primate conservation efforts worldwide and highlights the importance of collaborative conservation initiatives.
VI. Role of research in primate conservation
Research plays a crucial role in primate conservation efforts, providing valuable insights into primate populations, behavior, ecology, and genetics. By monitoring primate populations, studying their behavior and ecology, and conducting genetic research, scientists and conservationists can develop effective strategies to protect endangered primates and their habitats.
A. Monitoring primate populations
Monitoring primate populations is essential for understanding their distribution, abundance, and trends over time. This information helps identify areas of high conservation priority and guides the allocation of resources for primate conservation. Researchers employ various methods, including direct observations, camera traps, and acoustic monitoring, to collect data on primate populations.
Through monitoring, scientists can assess the impact of human activities, such as deforestation and hunting, on primate populations. This knowledge is crucial for implementing conservation measures and advocating for policies that protect primate habitats and regulate hunting practices.
B. Studying primate behavior and ecology
Studying primate behavior and ecology provides valuable insights into their social structure, feeding habits, mating systems, and habitat requirements. This knowledge helps researchers understand the ecological role of primates in their ecosystems and identify the factors that influence their survival and reproduction.
Researchers employ various methods, such as field observations, behavioral experiments, and GPS tracking, to study primate behavior and ecology. By studying primate social dynamics, researchers can identify the key individuals within a group and understand how social relationships impact their survival and reproductive success.
Additionally, studying primate feeding habits and dietary preferences helps identify the resources they rely on and the potential threats to their food sources. This information is crucial for designing conservation strategies that ensure the availability of suitable habitats and food resources for primates.
C. Genetic research for conservation purposes
Genetic research plays a vital role in primate conservation by providing insights into the genetic diversity, population structure, and evolutionary history of primate species. By analyzing DNA samples, researchers can identify genetically distinct populations, assess their vulnerability to extinction, and develop targeted conservation plans.
Genetic research also helps identify individuals with high genetic diversity, which is essential for the long-term survival of populations. By prioritizing the conservation of genetically diverse individuals, scientists can maintain the adaptive potential of primate populations and enhance their resilience to environmental changes.
Furthermore, genetic research aids in combating illegal wildlife trade and enforcing regulations on the international trade of primate species. DNA analysis can help identify the origin of confiscated primate specimens and provide evidence for prosecuting wildlife traffickers.
VII. Challenges and obstacles in primate conservation
Primate conservation is a crucial endeavor that aims to protect endangered primates and their habitats. However, there are several challenges and obstacles that conservationists face in their efforts to safeguard these species. In this section, we will explore three major challenges: lack of funding, political and social challenges, and human-wildlife conflict.
A. Lack of Funding
One of the biggest hurdles in primate conservation is the lack of adequate funding. Conservation projects require financial resources to carry out various activities such as research, habitat restoration, anti-poaching efforts, and community engagement. Unfortunately, funding for primate conservation is often limited and inconsistent.
Conservation organizations heavily rely on grants, donations, and sponsorships to fund their projects. However, securing these funds can be a daunting task. Many funding sources prioritize other causes or may not fully understand the importance of primate conservation. As a result, conservationists often struggle to obtain the necessary funds to implement their initiatives effectively.
To address this challenge, it is crucial to raise awareness about the value of primate conservation and its impact on the overall ecosystem. By educating the public and policymakers about the importance of protecting primates, we can advocate for increased funding and support for conservation efforts.
B. Political and Social Challenges
Primate conservation is not only a biological and ecological issue but also a political and social one. Political instability, corruption, and lack of governmental support can hinder conservation efforts. In some regions, conservation projects may face opposition from powerful interest groups or face challenges due to conflicting priorities.
Social challenges also arise in primate conservation. Local communities living near primate habitats may rely on natural resources for their livelihoods, leading to conflicts between human needs and conservation goals. Additionally, cultural beliefs and practices may pose challenges to conservation efforts, such as the use of primate body parts in traditional medicine or cultural ceremonies.
To overcome these challenges, it is essential to engage with local communities and stakeholders. Building strong relationships and partnerships can help foster mutual understanding and collaboration. By involving local communities in conservation initiatives and providing alternative livelihood options, we can address social and economic concerns while promoting primate conservation.
C. Human-Wildlife Conflict
Human-wildlife conflict is a significant obstacle in primate conservation. As human populations expand and encroach upon primate habitats, conflicts arise due to competition for resources. Primates may raid crops, leading to economic losses for farmers, who may retaliate by killing or capturing primates.
Furthermore, habitat fragmentation and degradation force primates to venture into human settlements in search of food and shelter. This proximity increases the likelihood of conflict and poses risks to both humans and primates.
To mitigate human-wildlife conflict, conservationists employ various strategies. These include implementing sustainable agriculture practices, such as crop diversification and the use of deterrents to protect crops from primate raids. Additionally, creating buffer zones around primate habitats and implementing effective waste management systems can help reduce the attraction of primates to human settlements.
Education and awareness programs are also vital in promoting coexistence between humans and primates. By educating communities about the ecological importance of primates and providing guidance on conflict resolution, we can foster tolerance and understanding.
VIII. Collaboration and partnerships in primate conservation
In the field of primate conservation, collaboration and partnerships play a crucial role in the efforts to protect endangered primates. Government agencies, non-governmental organizations (NGOs), international collaborations, and corporate partnerships all contribute to the conservation initiatives. These collaborations bring together diverse expertise, resources, and networks to address the complex challenges faced by primates and their habitats.
A. Government agencies and NGOs
Government agencies, such as wildlife departments and environmental ministries, are key players in primate conservation. They have the authority to enforce laws and regulations, protect natural habitats, and manage protected areas. These agencies work closely with NGOs, which are often at the forefront of primate conservation efforts.
NGOs, both local and international, bring specialized knowledge, experience, and passion to primate conservation. They engage in various activities, including research, habitat restoration, community outreach, and education. NGOs often collaborate with government agencies to develop and implement conservation strategies, advocate for policy changes, and raise public awareness about the importance of primate conservation.
One successful example of collaboration between government agencies and NGOs is the partnership between the Indonesian Ministry of Environment and Forestry and the Borneo Orangutan Survival Foundation (BOSF). Together, they have been working to protect the critically endangered Bornean orangutan and its habitat. This collaboration has resulted in the establishment of protected areas, rescue and rehabilitation centers, and community-based conservation programs.
B. International collaborations
Primate conservation is a global concern, as many primate species are found in multiple countries or have migratory patterns that cross borders. International collaborations are essential for sharing knowledge, coordinating efforts, and implementing conservation strategies on a larger scale.
International organizations, such as the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and the World Wildlife Fund (WWF), facilitate collaborations between governments, NGOs, and researchers from different countries. These collaborations involve joint research projects, capacity building initiatives, and policy advocacy at the international level.
For example, the Great Apes Survival Partnership (GRASP) is a collaboration between the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) and the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). GRASP brings together governments, NGOs, and experts to address the conservation challenges faced by great apes, including chimpanzees, gorillas, and orangutans. Through its collaborative efforts, GRASP aims to secure the long-term survival of great apes and their habitats.
C. Corporate partnerships
Corporate partnerships have the potential to make a significant impact on primate conservation. Companies can contribute financial resources, technical expertise, and innovative solutions to address conservation challenges. In return, these partnerships can enhance a company’s corporate social responsibility profile and contribute to sustainable development goals.
One notable example of a corporate partnership in primate conservation is the collaboration between the Jane Goodall Institute and the mobile technology company, Vodafone. Together, they have developed the “Instant Wild” app, which allows users to receive live images from camera traps placed in primate habitats. This partnership not only raises awareness about primate conservation but also provides valuable data for research and monitoring purposes.
Corporate partnerships can also involve collaborations between conservation organizations and businesses operating in or near primate habitats. These partnerships focus on sustainable practices, habitat restoration, and community development. By working together, conservation organizations and businesses can mitigate the negative impacts of economic activities on primate populations and their habitats.
IX. Education and awareness in primate conservation
Education and awareness play a crucial role in primate conservation efforts. By engaging the public, implementing outreach campaigns, and involving local communities, we can foster a sense of responsibility and promote sustainable practices that protect endangered primates and their habitats.
A. Public outreach and awareness campaigns
Public outreach campaigns are an effective way to raise awareness about the importance of primate conservation. These campaigns aim to educate the general public, including individuals, families, and communities, about the threats faced by endangered primates and the actions they can take to help protect them.
One successful example of a public outreach campaign is the “Save Our Primates” initiative. This campaign utilizes various media platforms, such as television, radio, and social media, to reach a wide audience. It features compelling stories, captivating visuals, and engaging content that highlights the beauty and significance of primates in our ecosystems.
Through this campaign, we aim to evoke empathy and inspire individuals to take action. We provide information on how to support primate conservation organizations, reduce consumption of products that contribute to deforestation, and participate in local conservation projects.
Additionally, we collaborate with schools, universities, and community centers to organize workshops, seminars, and interactive activities. These events provide opportunities for individuals to learn more about primates, their habitats, and the challenges they face. By fostering a sense of connection and understanding, we can encourage people to become advocates for primate conservation.
B. Environmental education programs
Environmental education programs are essential for instilling a sense of responsibility and stewardship towards our natural environment. These programs focus on educating children and young adults about the importance of primate conservation and the role they can play in protecting these endangered species.
One example of an environmental education program is the “Primate Guardians” initiative. This program is implemented in collaboration with local schools and aims to integrate primate conservation into the curriculum. Through interactive lessons, field trips, and hands-on activities, students learn about the ecological significance of primates and the threats they face.
The program also emphasizes the importance of sustainable practices, such as recycling, reducing waste, and conserving energy. By empowering young individuals with knowledge and skills, we can shape future generations of environmentally conscious citizens who actively contribute to primate conservation efforts.
C. Engaging local communities
Engaging local communities is crucial for the success of primate conservation initiatives. These communities often live in close proximity to primate habitats and can have a significant impact on their survival. By involving them in conservation efforts, we can ensure that their needs are met while also protecting the primates and their habitats.
One approach to engaging local communities is through the establishment of community-based conservation projects. These projects involve collaboration between conservation organizations, local governments, and community members to develop sustainable livelihood options that are compatible with primate conservation.
For example, in the village of XYZ, a community-based conservation project was implemented in partnership with the local community and XYZ Conservation Organization. The project focused on promoting sustainable agriculture practices that minimize deforestation and protect primate habitats.
Through training programs and capacity building, community members were equipped with the knowledge and skills to implement sustainable farming techniques. This not only helped protect the primates’ habitat but also improved the livelihoods of the community members by increasing crop yields and reducing dependency on unsustainable practices.
Engaging local communities also involves fostering a sense of ownership and pride in the conservation efforts. By involving community members in decision-making processes and recognizing their contributions, we can create a sense of shared responsibility and ensure the long-term success of primate conservation initiatives.
Primate conservation plays a crucial role in maintaining the balance and health of ecosystems worldwide. As keystone species, primates have significant ecological roles that contribute to the overall biodiversity and the provision of essential ecosystem services.
A. Keystone Species and Ecological Roles
Primates, such as monkeys and apes, are considered keystone species due to their vital role in maintaining the structure and functioning of ecosystems. These species have a disproportionate impact on their environment compared to their abundance. By influencing the distribution and abundance of other species, primates help regulate the ecosystem’s dynamics.
One of the key ecological roles of primates is seed dispersal. As they consume fruits and other plant parts, primates inadvertently transport seeds to different locations through their feces. This process promotes plant regeneration and contributes to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem. Without primates, many plant species would struggle to disperse their seeds effectively, leading to a decline in plant diversity.
Furthermore, primates also act as pollinators for certain plant species. As they move from flower to flower in search of nectar or food, they inadvertently transfer pollen, facilitating plant reproduction. This mutualistic relationship between primates and plants ensures the survival and genetic diversity of various plant species.
Additionally, primates play a crucial role in shaping forest structure. Through their feeding habits, primates influence the growth and distribution of vegetation. They selectively consume certain plant parts, which can influence the composition and density of plant species in an area. This, in turn, affects the availability of resources for other animals and contributes to the overall ecosystem dynamics.
B. Biodiversity Conservation
Primate conservation is closely linked to biodiversity conservation. As primates inhabit diverse habitats, their conservation efforts indirectly protect a wide range of plant and animal species that share their ecosystems. By safeguarding primate populations, we can help preserve the intricate web of life that exists in these habitats.
Primates serve as indicators of ecosystem health. Their presence or absence can reflect the overall condition of an ecosystem. Declines in primate populations often indicate environmental degradation, habitat loss, or the presence of other threats. Therefore, by focusing on primate conservation, we can address broader environmental issues and protect the biodiversity of entire ecosystems.
Furthermore, primates are often considered umbrella species. By conserving their habitats, we can protect a multitude of other species that rely on the same resources and share similar ecological requirements. This approach ensures the preservation of not only primates but also a wide range of flora and fauna that contribute to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
C. Ecosystem Services
Primate conservation also has significant implications for the provision of ecosystem services. Ecosystem services are the benefits that humans derive from nature, including the provision of food, clean water, climate regulation, and cultural and recreational opportunities.
One of the key ecosystem services provided by primates is seed dispersal, as mentioned earlier. By dispersing seeds, primates contribute to the regeneration and maintenance of forests, which in turn helps regulate local and regional climate patterns. Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Therefore, by preserving primate populations and their habitats, we can mitigate the impacts of climate change and ensure the provision of this vital ecosystem service.
Primates also contribute to the cultural and recreational value of ecosystems. They are often a source of inspiration for art, literature, and scientific research. Additionally, primates attract tourists and nature enthusiasts, generating economic benefits for local communities through ecotourism. By conserving primate populations, we can protect these cultural and recreational values and promote sustainable economic development.
