Contents
I. Introduction

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on the challenges and solutions for preventing pollution. In today’s world, pollution has become a pressing issue that affects not only the environment but also our health and well-being. From air and water pollution to plastic waste and chemical contamination, the impact of pollution is far-reaching and requires immediate attention.
In this article, we will delve into the various challenges associated with pollution and explore effective solutions to mitigate its harmful effects. Our goal is to provide you with a clear understanding of the causes and consequences of pollution, as well as practical steps that individuals, communities, and governments can take to combat this global problem.
Throughout this guide, we will address the needs and interests of a diverse audience, including concerned citizens, environmental activists, policymakers, and anyone seeking information on pollution prevention. By presenting the information in a conversational and engaging style, we aim to keep you informed and motivated to take action.
Before we dive into the specifics, it’s important to note that pollution is a complex issue with multiple dimensions. Therefore, our approach will be holistic, considering not only the environmental aspects but also the social, economic, and technological factors that contribute to pollution. By examining the problem from various angles, we can develop comprehensive solutions that address the root causes and promote sustainable practices.
So, let’s embark on this journey together and explore the challenges and solutions for preventing pollution. By the end of this guide, you will have the knowledge and tools to make a positive impact and contribute to a cleaner and healthier planet.
II. Understanding Pollution

A. Definition of Pollution
Pollution refers to the introduction of harmful substances or contaminants into the environment, resulting in adverse effects on living organisms and their surroundings. These contaminants can be in the form of solid, liquid, or gaseous pollutants that disrupt the natural balance of ecosystems and pose risks to human health.
Pollution can occur in various forms, including air pollution, water pollution, soil pollution, noise pollution, and light pollution. Each type of pollution has its own set of causes and impacts, but they are all interconnected and contribute to the overall degradation of the environment.
It is important to note that pollution can be caused by both natural and human activities. Natural sources of pollution include volcanic eruptions, forest fires, and dust storms, while human activities such as industrial processes, transportation, agriculture, and waste disposal are major contributors to pollution.
B. Different Types of Pollution
1. Air Pollution:
Air pollution refers to the presence of harmful substances in the air, such as gases, particulate matter, and toxic chemicals. It is primarily caused by the burning of fossil fuels, industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, and agricultural activities. Air pollution can have severe health effects, including respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and even premature death.
2. Water Pollution:
Water pollution occurs when contaminants are introduced into bodies of water, such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. It can be caused by industrial waste, sewage discharge, agricultural runoff, oil spills, and improper waste disposal. Water pollution not only affects aquatic life but also poses risks to human health, as contaminated water can lead to waterborne diseases.
3. Soil Pollution:
Soil pollution refers to the contamination of soil with toxic substances, such as heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals. It can result from improper waste disposal, agricultural practices, mining activities, and industrial pollution. Soil pollution can have detrimental effects on plant growth, soil fertility, and the overall ecosystem.
4. Noise Pollution:
Noise pollution is the excessive or disturbing noise that disrupts the natural environment and causes discomfort or harm to humans and animals. It can be caused by various sources, including traffic, construction activities, industrial machinery, and loud music. Prolonged exposure to noise pollution can lead to hearing loss, stress, and other health issues.
5. Light Pollution:
Light pollution refers to the excessive or misdirected artificial light that interferes with the natural darkness of the night sky. It is mainly caused by streetlights, outdoor advertising, and excessive indoor lighting. Light pollution can disrupt ecosystems, affect wildlife behavior, and have negative impacts on human sleep patterns and overall well-being.
It is crucial to address and mitigate the different types of pollution to protect the environment, preserve biodiversity, and ensure the well-being of present and future generations. Implementing sustainable practices, adopting cleaner technologies, and raising awareness about the importance of environmental conservation are essential steps towards preventing pollution and creating a healthier planet.
III. Environmental Impact of Pollution
A. Effects of pollution on air quality
Pollution has a detrimental effect on air quality, leading to a wide range of environmental and health issues. One of the most significant impacts is the deterioration of air quality due to the release of harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. These pollutants, such as carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides, are primarily emitted by industrial activities, vehicle emissions, and the burning of fossil fuels.
When these pollutants are released into the air, they can react with sunlight and other atmospheric components to form smog and ground-level ozone. These pollutants not only reduce visibility but also have severe health implications. Prolonged exposure to polluted air can lead to respiratory problems, cardiovascular diseases, and even premature death.
Furthermore, air pollution can also have a detrimental impact on ecosystems. Acid rain, for example, is a direct result of air pollution. When pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides combine with moisture in the atmosphere, they form acidic compounds that fall back to the ground as rain, snow, or fog. Acid rain can have devastating effects on forests, lakes, and aquatic life, leading to the decline of biodiversity and ecosystem imbalance.
B. Impact of pollution on water sources
Pollution poses a significant threat to water sources, including rivers, lakes, and groundwater. One of the primary causes of water pollution is the discharge of untreated or inadequately treated wastewater from industrial facilities and sewage systems. This wastewater often contains harmful chemicals, heavy metals, and pathogens that can contaminate water bodies and pose a risk to human health and aquatic life.
When pollutants enter water sources, they can disrupt the delicate balance of aquatic ecosystems. Excessive nutrient runoff, for example, can lead to eutrophication, a process in which an excess of nutrients, such as nitrogen and phosphorus, causes excessive algae and plant growth. This can deplete oxygen levels in the water, leading to the death of fish and other aquatic organisms.
Pollution can also have long-term consequences for human populations that rely on contaminated water sources for drinking and irrigation. Consuming polluted water can lead to waterborne diseases, such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid, which can have severe health implications, particularly in developing countries with limited access to clean water and sanitation facilities.
C. Consequences of pollution on land and soil
Pollution can have a significant impact on land and soil, affecting both the environment and human livelihoods. One of the most common forms of land pollution is the improper disposal of solid waste, including plastics, chemicals, and hazardous materials. These waste materials can contaminate soil, leaching harmful substances into the ground and potentially entering the food chain.
Contaminated soil can have detrimental effects on agriculture and food production. When crops are grown in polluted soil, they can absorb toxic substances, which can then be transferred to humans through the consumption of contaminated food. This poses a risk to human health and can lead to various diseases and disorders.
Pollution can also lead to soil erosion, particularly in areas where vegetation has been cleared for agriculture or urban development. When soil erosion occurs, fertile topsoil is washed away, degrading the quality of the remaining soil and reducing its ability to support plant growth. This can have severe implications for agricultural productivity and the sustainability of ecosystems.
IV. Major Sources of Pollution

When it comes to pollution, there are several major sources that contribute to the degradation of our environment. These sources include industrial pollution, agricultural practices, and household pollution. In this section, we will explore each of these sources in detail and discuss their causes.
A. Industrial pollution and its causes
Industrial pollution is one of the primary contributors to environmental pollution. Industries release various pollutants into the air, water, and soil, causing significant harm to ecosystems and human health. There are several causes of industrial pollution:
- Emissions from factories: Factories emit a wide range of pollutants, including greenhouse gases, toxic chemicals, and particulate matter. These emissions result from the burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, as well as the release of harmful chemicals used in industrial processes.
- Improper waste disposal: Many industries generate large amounts of waste, including hazardous materials. If not disposed of properly, these wastes can contaminate nearby water sources and soil, leading to pollution.
- Chemical spills and leaks: Accidental spills and leaks of chemicals are common in industrial settings. These incidents can have severe consequences, polluting nearby water bodies and soil, and posing a threat to human and animal life.
- Smokestack emissions: Smokestacks release a variety of pollutants, including sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These emissions contribute to air pollution and can lead to respiratory problems and other health issues.
It is crucial for industries to adopt sustainable practices and implement effective pollution control measures to minimize their environmental impact. This includes investing in cleaner technologies, improving waste management systems, and adhering to strict environmental regulations.
B. Agricultural practices contributing to pollution
Agriculture is another significant source of pollution, particularly due to the use of chemical fertilizers, pesticides, and herbicides. Here are some of the key agricultural practices that contribute to pollution:
- Chemical runoff: When farmers apply chemical fertilizers and pesticides to their crops, excess chemicals can wash off the fields and enter nearby water bodies. This runoff can lead to water pollution, harming aquatic life and affecting human health.
- Soil erosion: Intensive farming practices, such as monoculture and over-tilling, can result in soil erosion. When soil erodes, it can contaminate water sources with sediment and agricultural chemicals.
- Animal waste management: Livestock farming produces a significant amount of waste, including manure. If not managed properly, animal waste can contaminate water sources with excess nutrients and pathogens, causing water pollution.
- Deforestation: Clearing land for agriculture contributes to deforestation, which not only leads to the loss of biodiversity but also releases large amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, contributing to climate change.
To mitigate agricultural pollution, sustainable farming practices should be promoted. This includes organic farming methods, crop rotation, integrated pest management, and proper waste management systems for livestock farming.
C. Household pollution and its sources
Household pollution refers to pollution that originates from everyday activities within homes. While it may not be as prominent as industrial or agricultural pollution, household pollution can still have significant impacts on the environment and human health. Here are some common sources of household pollution:
- Indoor air pollution: Indoor activities such as cooking, heating, and using certain household products can release pollutants into the air. These pollutants include carbon monoxide, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter, which can cause respiratory problems and other health issues.
- Improper waste management: Improper disposal of household waste, including plastics, chemicals, and electronic waste, can lead to pollution of land and water sources. It is essential to practice proper waste segregation and recycling to minimize the environmental impact.
- Water pollution: Household activities such as using chemical-based cleaning products, improper disposal of pharmaceuticals, and excessive use of water can contribute to water pollution. These pollutants can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic ecosystems.
- Energy consumption: The energy used in households, particularly from non-renewable sources, contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change. Reducing energy consumption and transitioning to renewable energy sources can help mitigate this form of pollution.
By adopting sustainable practices at the household level, such as using eco-friendly products, conserving energy and water, and practicing proper waste management, individuals can contribute to reducing household pollution.
V. Challenges in Preventing Pollution
Preventing pollution is a complex task that requires addressing various challenges. In this section, we will explore three key challenges: lack of awareness and education, inadequate regulations and enforcement, and technological limitations in pollution prevention.
A. Lack of awareness and education
One of the major hurdles in preventing pollution is the lack of awareness and education among individuals and communities. Many people are unaware of the detrimental effects of pollution on the environment and human health. Without proper knowledge, they may not understand the importance of taking action to prevent pollution.
Addressing this challenge requires comprehensive education and awareness campaigns. Governments, non-profit organizations, and educational institutions play a crucial role in spreading awareness about the causes and consequences of pollution. By providing information and resources, they can empower individuals to make informed choices and take proactive measures to reduce pollution.
Furthermore, incorporating environmental education into school curricula can help instill a sense of responsibility and environmental stewardship in future generations. By teaching students about the impact of pollution and sustainable practices, we can foster a culture of environmental consciousness.
B. Inadequate regulations and enforcement
Another significant challenge in preventing pollution is the presence of inadequate regulations and enforcement mechanisms. Without proper regulations, industries and individuals may not be held accountable for their pollution-generating activities. This lack of accountability can lead to unchecked pollution and its detrimental effects on the environment.
To address this challenge, governments need to establish stringent regulations that set clear standards for pollution prevention. These regulations should cover various sectors, including industrial, agricultural, and residential activities. Additionally, governments must ensure effective enforcement of these regulations through regular inspections, monitoring, and penalties for non-compliance.
Collaboration between government agencies, environmental organizations, and industry stakeholders is crucial in developing and implementing effective pollution prevention strategies. By working together, we can create a regulatory framework that promotes sustainable practices and holds polluters accountable.
C. Technological limitations in pollution prevention
Technological limitations pose yet another challenge in preventing pollution. While advancements in technology have led to the development of various pollution control measures, there are still areas where technological solutions are limited or non-existent.
For instance, certain industries, such as heavy manufacturing or transportation, may rely on processes that inherently generate pollution. In such cases, finding alternative technologies or practices that minimize pollution can be challenging.
Addressing this challenge requires investment in research and development of innovative pollution prevention technologies. Governments, private companies, and research institutions should collaborate to explore and implement sustainable alternatives. By fostering innovation, we can overcome technological limitations and develop effective solutions for pollution prevention.
VI. Solutions for Preventing Pollution
In today’s world, pollution has become a pressing issue that affects the environment, human health, and the overall quality of life. However, there are various solutions available to combat pollution and create a cleaner and healthier planet. In this section, we will explore some of the key solutions for preventing pollution.
A. Government initiatives and policies
Government initiatives and policies play a crucial role in addressing pollution and promoting sustainable practices. Governments around the world have implemented a range of measures to reduce pollution levels and protect the environment. These initiatives include:
- Implementing stricter emission standards for industries and vehicles
- Investing in renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power
- Enforcing regulations on waste management and recycling
- Supporting research and development of clean technologies
- Creating protected areas and wildlife sanctuaries
By implementing these initiatives, governments can significantly reduce pollution levels and create a more sustainable future for generations to come.
B. Importance of individual actions in pollution prevention
While government initiatives are crucial, individual actions also play a significant role in preventing pollution. Each person can contribute to a cleaner environment by making small changes in their daily lives. Some important individual actions include:
- Reducing energy consumption by using energy-efficient appliances and turning off lights when not in use
- Conserving water by fixing leaks, using water-saving devices, and practicing responsible water usage
- Minimizing waste generation by practicing recycling, composting, and reducing the use of single-use plastics
- Using eco-friendly transportation options such as cycling, walking, or carpooling
- Supporting sustainable businesses and products
By adopting these individual actions, each person can contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment.
C. Role of technology in reducing pollution
Technology plays a crucial role in reducing pollution and creating sustainable solutions. Advancements in technology have led to the development of innovative solutions that can significantly reduce pollution levels. Some key technological advancements include:
- Renewable energy technologies such as solar panels and wind turbines
- Electric vehicles that produce zero emissions
- Advanced air and water pollution control systems
- Smart grid systems that optimize energy distribution and reduce wastage
- Waste-to-energy technologies that convert waste into usable energy
By harnessing the power of technology, we can reduce pollution levels and create a more sustainable future.
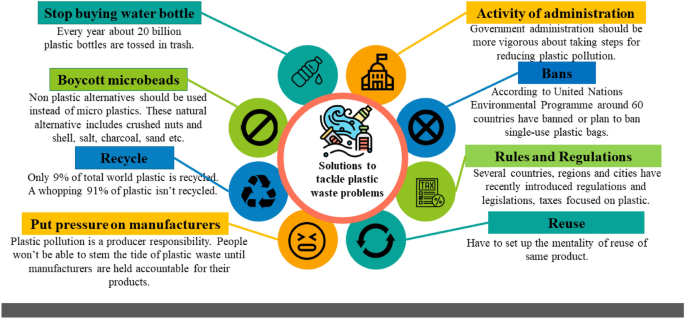
VII. Best Practices for Pollution Prevention
Pollution prevention is a critical aspect of environmental conservation and sustainability. By implementing effective strategies and adopting green technologies, we can minimize the negative impact of pollution on our planet. In this section, we will explore some of the best practices for pollution prevention, including sustainable waste management strategies, promoting renewable energy sources, and implementing green transportation systems.
A. Sustainable waste management strategies
Waste management plays a crucial role in preventing pollution and protecting the environment. Traditional waste disposal methods, such as landfilling and incineration, contribute to air and water pollution, as well as greenhouse gas emissions. To address this issue, adopting sustainable waste management strategies is essential.
One effective strategy is recycling. By separating recyclable materials from the waste stream, we can reduce the amount of waste sent to landfills and conserve valuable resources. Recycling not only helps prevent pollution but also promotes a circular economy where materials are reused and recycled, reducing the need for raw material extraction.
Composting is another sustainable waste management strategy. Organic waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, can be composted instead of being disposed of in landfills. Composting not only reduces methane emissions from decomposing organic waste but also produces nutrient-rich compost that can be used to enrich soil and support sustainable agriculture.
Furthermore, waste reduction initiatives, such as source reduction and product redesign, can significantly minimize the generation of waste. By encouraging manufacturers to produce goods with less packaging or promoting the use of reusable products, we can reduce the amount of waste generated at its source.
B. Promoting renewable energy sources
Transitioning from fossil fuels to renewable energy sources is vital for pollution prevention and combating climate change. Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, offer clean and sustainable alternatives to traditional energy sources that rely on fossil fuels.
Solar energy is one of the most abundant and readily available renewable energy sources. Installing solar panels on rooftops or in solar farms can harness the power of the sun to generate electricity without emitting harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases. Similarly, wind turbines can convert the kinetic energy of the wind into electricity, providing a clean and renewable source of power.
Hydropower, generated from flowing or falling water, is another renewable energy source that can contribute to pollution prevention. By harnessing the power of rivers and tides, hydropower plants can generate electricity without burning fossil fuels or releasing harmful emissions.
Promoting the use of renewable energy sources requires investment in infrastructure and policy support. Governments and organizations can incentivize the adoption of renewable energy technologies through subsidies, tax credits, and feed-in tariffs. Additionally, raising awareness about the benefits of renewable energy and educating the public on its importance can drive the demand for clean energy.
C. Implementing green transportation systems
The transportation sector is a significant contributor to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Implementing green transportation systems is crucial for pollution prevention and reducing our carbon footprint.
One effective strategy is promoting the use of electric vehicles (EVs). EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and improving air quality. Governments can incentivize the purchase of EVs through subsidies and tax credits, as well as investing in charging infrastructure to support their widespread adoption.
Another green transportation strategy is promoting public transportation and active modes of transportation, such as walking and cycling. Encouraging people to use public transportation reduces the number of private vehicles on the road, leading to decreased traffic congestion and lower emissions. Additionally, investing in infrastructure for pedestrians and cyclists can make these modes of transportation more accessible and safer.
Furthermore, implementing smart transportation systems that optimize traffic flow and reduce idling can contribute to pollution prevention. Intelligent traffic management systems, such as adaptive traffic signals and real-time traffic information, can help reduce congestion and minimize emissions from vehicles stuck in traffic.
VIII. Impact of Pollution on Human Health
Pollution is a pressing issue that affects not only the environment but also human health. The adverse effects of pollution on human health are well-documented and cannot be ignored. In this section, we will explore the various health risks associated with air pollution, the effects of water pollution on human health, and the link between pollution and chronic diseases.
A. Health risks associated with air pollution
Air pollution is a major concern worldwide, and its impact on human health is significant. Breathing in polluted air can have detrimental effects on the respiratory system, cardiovascular system, and overall well-being. The following are some of the health risks associated with air pollution:
- Respiratory problems: Prolonged exposure to polluted air can lead to respiratory issues such as asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Fine particulate matter and toxic gases present in polluted air can irritate the airways and cause inflammation.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Air pollution has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart attacks, strokes, and high blood pressure. The fine particles in polluted air can enter the bloodstream and cause inflammation, leading to the development of cardiovascular problems.
- Allergies and skin problems: Polluted air can trigger allergies and skin problems in susceptible individuals. The presence of pollutants such as pollen, mold spores, and chemicals can cause allergic reactions and skin irritations.
- Impaired lung development: Children exposed to air pollution may experience impaired lung development, leading to long-term respiratory issues. The pollutants in the air can hinder the growth and function of the lungs, affecting respiratory health throughout their lives.
- Increased risk of cancer: Certain air pollutants, such as benzene and formaldehyde, are known carcinogens. Prolonged exposure to these pollutants can increase the risk of developing lung cancer, bladder cancer, and other types of cancer.
It is crucial to address air pollution and implement measures to reduce emissions for the sake of protecting human health.
B. Water pollution and its effects on human health
Water pollution is another significant issue that poses risks to human health. Contaminated water can harbor harmful substances and pathogens that can cause various health problems. The following are some of the effects of water pollution on human health:
- Waterborne diseases: Contaminated water can transmit diseases such as cholera, typhoid, dysentery, and hepatitis. Pathogens like bacteria, viruses, and parasites thrive in polluted water sources and can cause severe illnesses when ingested.
- Heavy metal poisoning: Industrial waste and improper disposal of chemicals can lead to the contamination of water sources with heavy metals like lead, mercury, and arsenic. Ingesting water containing high levels of these metals can lead to poisoning and long-term health complications.
- Impaired neurological development: Children exposed to water pollution may experience impaired neurological development. Certain pollutants, such as lead, can affect brain development and lead to cognitive and behavioral problems.
- Endocrine disruption: Some pollutants found in water sources, such as certain pesticides and pharmaceuticals, can disrupt the endocrine system. This disruption can interfere with hormone regulation and lead to reproductive issues, developmental problems, and other health concerns.
- Contaminated seafood: Water pollution can contaminate aquatic ecosystems, leading to the accumulation of pollutants in fish and other seafood. Consuming contaminated seafood can expose individuals to toxins and pollutants, causing adverse health effects.
Efforts must be made to prevent water pollution, ensure access to clean and safe water sources, and implement proper wastewater treatment systems.
C. Link between pollution and chronic diseases
There is a growing body of evidence linking pollution to chronic diseases. Chronic diseases are long-term conditions that often develop over time and can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Pollution, both air and water, can contribute to the development and progression of chronic diseases. The following are some examples of chronic diseases associated with pollution:
- Asthma: Air pollution, particularly fine particulate matter and pollutants like nitrogen dioxide, can trigger asthma attacks and worsen symptoms in individuals with asthma. Prolonged exposure to polluted air can also increase the risk of developing asthma.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Air pollution has been linked to an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, including heart disease, stroke, and high blood pressure. The pollutants in the air can promote inflammation, oxidative stress, and the formation of plaques in the arteries.
- Cancer: Certain pollutants, such as air pollutants and chemicals found in water sources, have been associated with an increased risk of cancer. Prolonged exposure to these pollutants can lead to the development of various types of cancer.
- Neurological disorders: Some pollutants, including heavy metals like lead and mercury, have been linked to neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, and cognitive impairments.
- Respiratory diseases: Air pollution can contribute to the development and exacerbation of respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and lung cancer. Fine particulate matter and toxic gases present in polluted air can damage the respiratory system.
Reducing pollution levels and implementing effective pollution control measures are crucial in preventing and managing chronic diseases.
