Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Predatory Mammals and Their Impact on Prey Populations
- III. Keystone Predators and Trophic Cascades
- IV. Predatory Mammals and Biodiversity
- V. Human-Wildlife Conflict and Predatory Mammals
- VI. The Role of Predatory Mammals in Ecosystem Services
- VII. Predatory Mammals and Habitat Restoration
- VIII. Predatory Mammals and Climate Change
- IX. FAQs
- 1. What are some examples of predatory mammals?
- 2. How do predatory mammals hunt their prey?
- 3. What is the relationship between predatory mammals and keystone species?
- 4. How do predatory mammals contribute to biodiversity?
- 5. What are some conservation efforts to protect predatory mammals?
- 6. How can human-wildlife conflict be mitigated?
- 7. What are some ecosystem services provided by predatory mammals?
- 8. How do predatory mammals contribute to habitat restoration?
- 9. How does climate change affect predatory mammal populations?
- 10. What can be done to conserve predatory mammals in the face of climate change?
I. Introduction
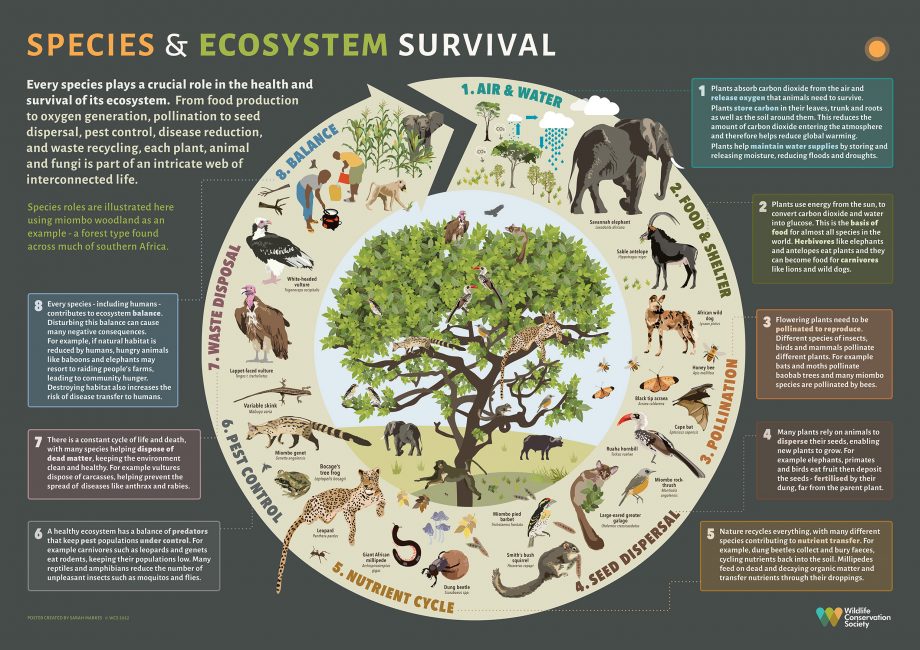
Predatory mammals play a crucial role in maintaining balance within ecosystems. These carnivorous animals, such as lions, tigers, and wolves, are essential for regulating prey populations and preventing overgrazing or overpopulation. By controlling the numbers of herbivores and smaller predators, they help maintain a healthy and diverse ecosystem.
One of the key benefits of predatory mammals is their ability to control the population of herbivores. Without natural predators, herbivorous animals can multiply rapidly, leading to overgrazing of vegetation and depletion of resources. This can have a cascading effect on the entire ecosystem, impacting the availability of food and shelter for other species. Predatory mammals act as a natural check on herbivore populations, ensuring that they do not exceed the carrying capacity of their environment.
In addition to regulating herbivore populations, predatory mammals also help control the numbers of smaller predators. These smaller predators, such as foxes and raccoons, can have a significant impact on local ecosystems if their populations are left unchecked. By preying on these smaller predators, larger predatory mammals help maintain a balance in the predator-prey relationship, preventing any one species from dominating the ecosystem.
Furthermore, predatory mammals contribute to the overall health and diversity of ecosystems by targeting weak or sick individuals within prey populations. This natural selection process helps ensure that only the fittest individuals survive and reproduce, leading to stronger and more resilient prey populations over time.
II. Predatory Mammals and Their Impact on Prey Populations

Predatory mammals play a crucial role in maintaining balance in ecosystems by controlling prey populations. Their hunting strategies, role in controlling prey populations, and specific prey relationships vary across species. In this section, we will explore these aspects in more detail.
A. Hunting strategies of predatory mammals
Predatory mammals have evolved a wide range of hunting strategies to effectively capture their prey. These strategies are often influenced by factors such as the mammal’s size, habitat, and prey availability. Let’s take a look at some common hunting strategies employed by predatory mammals:
- Ambush: Some predatory mammals, like the leopard, rely on stealth and camouflage to surprise their prey. They patiently wait in concealed positions before launching a sudden attack.
- Pursuit: Other mammals, such as the cheetah, are built for speed. They use their incredible agility and speed to chase down prey over short distances.
- Cooperative hunting: Certain predatory mammals, like the African wild dog, hunt in packs. They work together to surround and exhaust their prey, increasing their chances of a successful hunt.
- Stalking: Predatory mammals like the lion use stalking as a hunting strategy. They silently approach their prey, taking advantage of cover and minimizing the chances of detection.
These hunting strategies demonstrate the adaptability and resourcefulness of predatory mammals in securing their next meal.
B. Role of predatory mammals in controlling prey populations
Predatory mammals play a vital role in maintaining the balance of prey populations within an ecosystem. By preying on herbivores, they help regulate the size and distribution of prey populations. This, in turn, has several important ecological implications:
- Preventing overgrazing: Herbivores, if left unchecked, can overgraze an area, leading to the depletion of vegetation and habitat degradation. Predatory mammals help control herbivore populations, preventing overgrazing and promoting healthier ecosystems.
- Controlling disease spread: Predatory mammals often target weaker or sick individuals within prey populations. By removing these individuals, they help reduce the spread of diseases and parasites among prey species.
- Enhancing biodiversity: By regulating prey populations, predatory mammals contribute to the overall biodiversity of an ecosystem. This allows for a more balanced and diverse range of species within the ecosystem.
The presence of predatory mammals is therefore crucial for maintaining the overall health and stability of ecosystems.
C. Examples of predatory mammals and their prey relationships
Throughout the world, numerous predatory mammals have established unique prey relationships. These relationships are often shaped by factors such as geographical location, habitat type, and available prey species. Let’s explore some examples of predatory mammals and their prey relationships:
| Predatory Mammal | Prey Species |
|---|---|
| African lion | Wildebeest, zebra, buffalo |
| Gray wolf | Elk, deer, moose |
| Polar bear | Seals, walrus |
| Tiger | Deer, wild boar, water buffalo |
These examples highlight the diverse range of prey species targeted by predatory mammals in different parts of the world.
III. Keystone Predators and Trophic Cascades
In this section, we will delve into the fascinating world of keystone predators and their role in maintaining balance through trophic cascades. Keystone predators play a crucial role in shaping ecosystems and regulating populations of other species. Let’s explore the definition and characteristics of keystone predators, how they maintain balance through trophic cascades, and examine some intriguing case studies that highlight their ecological impact.
A. Definition and Characteristics of Keystone Predators
Keystone predators are species that have a disproportionately large impact on their ecosystems relative to their abundance. They exert control over the structure and dynamics of the community by regulating the population sizes of their prey species. The removal or decline of keystone predators can lead to significant changes in the ecosystem, often resulting in imbalances and cascading effects throughout the food web.
One of the key characteristics of keystone predators is their ability to influence the behavior and distribution of other species. They often shape the landscape by creating a “landscape of fear,” where their presence alone can alter the behavior and movements of prey species. This, in turn, affects the distribution and abundance of other organisms within the ecosystem.
Another important characteristic of keystone predators is their role in maintaining biodiversity. By controlling the population sizes of their prey, they prevent any one species from dominating the ecosystem. This allows for a greater variety of species to coexist and thrive, leading to a more resilient and diverse ecosystem.
B. How Keystone Predators Maintain Balance Through Trophic Cascades
Trophic cascades are powerful ecological processes that occur when changes in the abundance of one species have cascading effects on other species within the food web. Keystone predators play a crucial role in initiating and maintaining trophic cascades by controlling the population sizes of their prey.
When keystone predators are present in an ecosystem, they keep the populations of their prey in check. This prevents the prey species from overgrazing or overexploiting their resources, which can have detrimental effects on other species and the overall health of the ecosystem. By regulating the population sizes of their prey, keystone predators indirectly benefit other organisms within the community.
For example, let’s consider the case of sea otters in kelp forest ecosystems. Sea otters are considered keystone predators because they feed on sea urchins, which are herbivores that graze on kelp. When sea otters are abundant, they keep the sea urchin population in check, preventing them from overgrazing the kelp forests. This allows the kelp forests to thrive, providing habitat and food for a diverse array of species, including fish, invertebrates, and other marine organisms.
Without the presence of sea otters, the sea urchin population can explode, leading to the overgrazing of kelp forests. This can have cascading effects throughout the ecosystem, as the loss of kelp forests impacts the abundance and distribution of other species. By maintaining a balance between sea otters, sea urchins, and kelp, trophic cascades ensure the stability and health of the entire ecosystem.
C. Case Studies of Keystone Predators and Their Ecological Impact
There are numerous case studies that highlight the ecological impact of keystone predators in various ecosystems around the world. Let’s explore a few notable examples:
1. Gray Wolves in Yellowstone National Park: The reintroduction of gray wolves to Yellowstone National Park in the 1990s had a profound impact on the ecosystem. As top predators, wolves regulate the populations of herbivores such as elk, which in turn affects vegetation and other species. The presence of wolves led to a decrease in elk populations, allowing for the recovery of vegetation and the return of other species, including beavers and songbirds.
2. African Lions in Savanna Ecosystems: African lions are apex predators in savanna ecosystems and play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of the food web. Their presence influences the behavior and distribution of herbivores, which in turn affects vegetation and other species. Studies have shown that the decline of lion populations can lead to an increase in herbivore populations, resulting in overgrazing and habitat degradation.
3. Orcas in Marine Ecosystems: Orcas, also known as killer whales, are apex predators in marine ecosystems and have a significant impact on the structure and dynamics of the food web. They feed on a variety of prey species, including seals, sea lions, and other marine mammals. The presence of orcas influences the abundance and distribution of these prey species, which in turn affects the populations of their prey’s prey. This cascading effect helps maintain the balance and health of the entire marine ecosystem.
These case studies highlight the critical role that keystone predators play in maintaining balance and stability within ecosystems. Their presence or absence can have far-reaching effects on the structure and dynamics of the community, underscoring the importance of conserving and protecting these species for the health of our planet.
IV. Predatory Mammals and Biodiversity
As a wildlife biologist with a deep passion for understanding the intricate relationships within ecosystems, I have dedicated my career to studying the role of predatory mammals in maintaining balance and promoting biodiversity. Predatory mammals play a crucial role in the delicate web of life, and their decline can have far-reaching effects on ecosystems.
A. Role of predatory mammals in promoting biodiversity
Predatory mammals, such as wolves, lions, and bears, have long been recognized as keystone species in their respective habitats. These animals are at the top of the food chain and exert a significant influence on the populations of their prey species. By controlling the abundance and distribution of prey, predatory mammals help maintain a healthy balance in ecosystems.
One of the key ways in which predatory mammals promote biodiversity is through the regulation of herbivore populations. By preying on herbivores, these predators prevent overgrazing and allow vegetation to regenerate. This, in turn, creates habitat heterogeneity, which is essential for supporting a wide range of plant and animal species.
Predatory mammals also play a crucial role in shaping the behavior and distribution of their prey. The fear of predation influences the feeding, mating, and movement patterns of herbivores, which can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem. For example, the presence of wolves in Yellowstone National Park has led to changes in the behavior of elk, resulting in a reduction in browsing pressure on aspen trees and an increase in the abundance of songbirds that rely on aspen habitat.
Furthermore, predatory mammals contribute to biodiversity by preventing the dominance of certain species. Without the presence of predators, certain herbivores can become overabundant and outcompete other species for resources. This can lead to a decrease in species diversity and disrupt the balance of the ecosystem.
B. Effects of the decline of predatory mammal populations on ecosystems
The decline of predatory mammal populations can have profound effects on ecosystems, often resulting in a loss of biodiversity and ecological imbalance. One of the most well-known examples of such effects is the decline of the gray wolf population in North America.
Historically, gray wolves were widespread across much of North America, playing a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. However, due to habitat loss and human persecution, wolf populations have declined significantly. This decline has had cascading effects on ecosystems, leading to an increase in the abundance of herbivores, such as deer and elk, and a decrease in the diversity of plant and animal species.
Without the presence of wolves to regulate herbivore populations, overgrazing has become a significant issue in many areas. This has resulted in the degradation of vegetation, loss of habitat for other species, and a decline in overall biodiversity. Additionally, the absence of predators has allowed certain herbivores to become overabundant, leading to increased competition for resources and potential population crashes.
Furthermore, the decline of predatory mammal populations can disrupt ecological processes and alter the structure of ecosystems. For example, the absence of predators can lead to an increase in mesopredator populations, such as raccoons and coyotes, which can have negative impacts on smaller prey species and disrupt the balance of the food chain.
C. Conservation efforts to protect predatory mammals and biodiversity
Recognizing the importance of predatory mammals in maintaining biodiversity, conservation organizations and governments have implemented various efforts to protect these species and their habitats.
One of the most effective conservation strategies is the establishment of protected areas and national parks. These areas provide a safe haven for predatory mammals and their prey, allowing them to thrive without human interference. Additionally, these protected areas often serve as important research sites, providing valuable insights into the ecology and behavior of these species.
Another crucial conservation approach is the reintroduction of predatory mammals into their former habitats. This has been successful in the case of the gray wolf in Yellowstone National Park, where reintroduction efforts have led to a recovery of the wolf population and positive ecological impacts.
Furthermore, public education and awareness campaigns play a vital role in promoting the conservation of predatory mammals. By raising awareness about the importance of these species and their role in maintaining biodiversity, we can foster a sense of stewardship and encourage individuals to take action to protect them.
V. Human-Wildlife Conflict and Predatory Mammals
Human-wildlife conflict is a complex issue that arises from interactions between humans and predatory mammals. As human populations continue to expand and encroach upon natural habitats, conflicts with predatory mammals become more frequent. These conflicts can have serious implications for both humans and wildlife, leading to economic losses, damage to property, and even loss of life.
A. Conflicts arising from interactions between humans and predatory mammals
Interactions between humans and predatory mammals often result in conflicts due to competition for resources and differences in behavior. Predatory mammals, such as wolves, bears, and big cats, require large territories to hunt and establish their territories. However, as human activities encroach upon these territories, conflicts arise.
One common conflict is predation on livestock. Predatory mammals may target domestic animals, such as sheep and cattle, leading to significant economic losses for farmers and ranchers. This can create animosity towards these predators and result in retaliatory killings.
Another conflict arises when predatory mammals come into close proximity to human settlements. This can lead to attacks on humans, especially in areas where there is limited prey availability. Such incidents can instill fear and anxiety among local communities, impacting their livelihoods and well-being.
Additionally, conflicts can arise when predatory mammals raid crops or damage property. For example, bears may raid beehives or destroy fruit orchards, causing financial losses for farmers.
It is important to understand the underlying causes of these conflicts in order to develop effective strategies for mitigation.
B. Strategies for mitigating human-wildlife conflict
Mitigating human-wildlife conflict requires a multi-faceted approach that takes into account the needs of both humans and wildlife. Here are some strategies that have been successful in reducing conflicts:
- 1. Habitat management: Protecting and restoring natural habitats for predatory mammals can help reduce conflicts. This includes creating wildlife corridors, establishing protected areas, and implementing sustainable land-use practices.
- 2. Livestock protection: Implementing measures to protect livestock from predation can help reduce economic losses for farmers. This can include the use of guard animals, such as dogs or llamas, and the installation of predator-proof fencing.
- 3. Early warning systems: Developing and implementing early warning systems can help alert communities to the presence of predatory mammals in the vicinity. This can allow for timely actions, such as temporarily confining livestock or avoiding areas where conflicts are likely to occur.
- 4. Education and awareness: Educating local communities about the importance of predatory mammals and their role in maintaining ecosystem balance can help foster coexistence. This can include workshops, outreach programs, and the dissemination of educational materials.
- 5. Compensation and insurance: Providing compensation or insurance schemes for farmers who experience losses due to predation can help alleviate financial burdens and reduce the likelihood of retaliatory killings.
It is important to tailor these strategies to the specific context and needs of each region, taking into account local socio-economic factors and cultural beliefs.
C. Case studies of successful human-predatory mammal coexistence
Several case studies have demonstrated successful coexistence between humans and predatory mammals. These examples highlight the effectiveness of various strategies in reducing conflicts:
- 1. The Yellowstone National Park: The reintroduction of gray wolves in Yellowstone National Park in the United States has led to a remarkable recovery of the ecosystem. By managing the park as a natural habitat for wolves, the park authorities have successfully reduced conflicts with local communities while promoting the ecological balance.
- 2. The Snow Leopard Conservancy: In the high mountains of Central Asia, the Snow Leopard Conservancy works with local communities to protect snow leopards and their habitats. Through community-based conservation initiatives, such as livestock insurance programs and the establishment of predator-proof corrals, conflicts have been minimized, and coexistence has been achieved.
- 3. The Living with Lions Project: In Kenya, the Living with Lions Project focuses on reducing conflicts between local Maasai communities and lions. By implementing measures such as the construction of predator-proof bomas (livestock enclosures) and providing compensation for livestock losses, the project has successfully promoted coexistence and reduced retaliatory killings.
These case studies demonstrate the importance of adopting a holistic approach that involves local communities, conservation organizations, and government agencies in finding sustainable solutions for human-wildlife conflict.
VI. The Role of Predatory Mammals in Ecosystem Services
Predatory mammals play a crucial role in maintaining balance within ecosystems. They provide a range of ecosystem services that benefit both the natural environment and humans. Understanding the importance of these services is essential for conservation efforts and sustainable management of ecosystems.
A. Ecosystem services provided by predatory mammals
Predatory mammals contribute to various ecosystem services that are vital for the functioning of ecosystems. One of the key services they provide is the regulation of prey populations. By preying on herbivores, predatory mammals help control their numbers and prevent overgrazing, which can lead to habitat degradation and loss of biodiversity.
Additionally, predatory mammals play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of predator-prey relationships. Their presence helps prevent the dominance of certain prey species, ensuring a more diverse and resilient ecosystem. This, in turn, promotes the stability and health of ecosystems.
Another important ecosystem service provided by predatory mammals is the facilitation of nutrient cycling. Through predation, they contribute to the decomposition of prey carcasses, which releases nutrients back into the ecosystem. This process helps maintain the fertility of the soil and supports the growth of vegetation.
Predatory mammals also contribute to the dispersal of seeds. Some species, such as foxes and coyotes, consume fruits and berries and then disperse the seeds through their scat. This aids in the regeneration of plant species and contributes to the overall biodiversity of the ecosystem.
B. Examples of ecosystem services and their benefits to humans
The ecosystem services provided by predatory mammals have direct and indirect benefits for humans. One of the most significant benefits is the regulation of pests. Predatory mammals help control populations of rodents and other small mammals that can cause damage to crops and spread diseases. By reducing pest populations, they contribute to agricultural productivity and human health.
Predatory mammals also play a role in disease regulation. By preying on infected individuals, they can help prevent the spread of diseases within both wildlife populations and human communities. This is particularly important in the case of zoonotic diseases, which can be transmitted between animals and humans.
Furthermore, the presence of predatory mammals in ecosystems can have positive economic impacts. For example, ecotourism centered around observing and photographing these charismatic species can generate revenue and support local economies. Many people are willing to travel to areas where they have the opportunity to see predators in their natural habitats, contributing to the conservation of these species and their habitats.
C. The economic value of ecosystem services provided by predatory mammals
The economic value of the ecosystem services provided by predatory mammals is often underestimated. However, studies have shown that these services can have significant economic implications. For example, the regulation of pests by predatory mammals can result in substantial savings for the agricultural industry by reducing the need for chemical pesticides.
In addition, the presence of predators in natural areas can enhance the value of protected areas for tourism. Many national parks and wildlife reserves attract visitors who are interested in observing and experiencing the presence of these iconic species. This tourism revenue can contribute to local economies and support conservation efforts.
Furthermore, the ecosystem services provided by predatory mammals contribute to the overall resilience and sustainability of ecosystems. By maintaining the balance of predator-prey relationships and promoting biodiversity, they help ensure the long-term health and functioning of ecosystems. This, in turn, provides a range of benefits for human well-being, including clean air and water, climate regulation, and recreational opportunities.
VII. Predatory Mammals and Habitat Restoration
Predatory mammals play a crucial role in habitat restoration, contributing to the overall balance and health of ecosystems. These mammals, such as wolves, bears, and big cats, have a significant impact on their surrounding environments through their hunting behaviors and interactions with other species. In this section, we will explore how predatory mammals contribute to habitat restoration, provide examples of habitat restoration projects involving these mammals, and discuss the benefits of habitat restoration for both predatory mammals and ecosystems as a whole.
A. How predatory mammals contribute to habitat restoration
Predatory mammals have a direct impact on the populations of their prey species. By hunting and controlling the numbers of herbivores, they help maintain a balanced ecosystem. For example, wolves are known to regulate the population of deer and elk, preventing overgrazing and allowing vegetation to regenerate. This, in turn, benefits other species that rely on these habitats, such as birds and small mammals.
Furthermore, predatory mammals also influence the behavior and distribution of their prey. The fear of predation can cause prey species to alter their foraging patterns and avoid certain areas, allowing vegetation to recover. This creates a ripple effect throughout the ecosystem, leading to increased biodiversity and overall ecosystem health.
B. Examples of habitat restoration projects involving predatory mammals
Several habitat restoration projects have successfully incorporated predatory mammals to restore ecosystems. One notable example is the reintroduction of gray wolves to Yellowstone National Park in the United States. After their reintroduction in 1995, the wolves played a crucial role in controlling the population of elk, which had been overgrazing the park’s vegetation. As a result, the vegetation recovered, leading to improved habitat conditions for other species, including beavers, birds, and fish.
Another example is the conservation efforts for the Iberian lynx in Spain. The Iberian lynx is a critically endangered species, and its decline has had negative effects on the ecosystems it inhabits. Habitat restoration projects in Spain aim to restore the lynx’s natural habitat by reintroducing suitable prey species and implementing conservation measures. By restoring the lynx’s habitat, these projects contribute to the overall restoration of the ecosystem and help maintain a balanced predator-prey relationship.
C. Benefits of habitat restoration for predatory mammals and ecosystems
Habitat restoration not only benefits prey species but also provides essential resources and opportunities for predatory mammals. Restored habitats offer a diverse range of prey species, ensuring an adequate food supply for these predators. Additionally, restored habitats can provide suitable shelter and breeding grounds for predatory mammals, allowing them to thrive and reproduce.
From an ecological perspective, habitat restoration contributes to the overall health and resilience of ecosystems. Restored habitats support a higher level of biodiversity, as they provide suitable conditions for a variety of species to coexist. This, in turn, enhances ecosystem stability and resilience, making it more resistant to disturbances such as climate change or invasive species.
VIII. Predatory Mammals and Climate Change
In recent years, the impact of climate change on various ecosystems has become a topic of great concern. One area that has been significantly affected is the population of predatory mammals. These majestic creatures play a crucial role in maintaining the balance of our ecosystems, and their decline could have far-reaching consequences. In this section, we will explore the impact of climate change on predatory mammal populations, their role in mitigating climate change effects, and strategies for conserving them in the face of this global challenge.
Impact of Climate Change on Predatory Mammal Populations
Climate change has led to a multitude of changes in ecosystems around the world. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and habitat loss have all contributed to the decline of many species, including predatory mammals. These animals are highly specialized and rely on specific habitats and prey to survive. As their habitats shrink or become fragmented, their populations are at risk of decline.
One of the most significant impacts of climate change on predatory mammals is the alteration of their prey dynamics. Changes in temperature and precipitation patterns can disrupt the delicate balance between predator and prey, leading to mismatches in timing and availability of food resources. For example, a study conducted on Arctic fox populations in the Canadian Arctic found that the decline in lemming populations, their primary prey, was linked to changes in snow cover duration caused by climate change. This disruption in the prey-predator relationship can have cascading effects on the entire ecosystem.
Furthermore, climate change can also directly affect the physiological and behavioral patterns of predatory mammals. For instance, polar bears, which rely on sea ice for hunting seals, are facing increased challenges as the Arctic sea ice melts at an alarming rate. This forces polar bears to travel longer distances in search of food, leading to increased energy expenditure and reduced reproductive success. Similarly, warmer temperatures can affect the hunting efficiency of large cats, such as lions and tigers, as their prey may become more elusive or change their behavior in response to changing environmental conditions.
Role of Predatory Mammals in Mitigating Climate Change Effects
While climate change poses significant threats to predatory mammals, these animals also play a vital role in mitigating the effects of climate change on ecosystems. Predatory mammals help maintain the balance of their respective ecosystems by regulating prey populations. By keeping herbivore populations in check, they prevent overgrazing and maintain the health of vegetation, which in turn helps sequester carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
Additionally, predatory mammals contribute to nutrient cycling and ecosystem resilience. Their feeding behaviors and hunting patterns help redistribute nutrients across the landscape, promoting the growth of diverse plant communities. This, in turn, enhances the capacity of ecosystems to adapt to changing environmental conditions, including those caused by climate change.
Furthermore, the presence of healthy populations of predatory mammals can also have indirect positive effects on other species within their ecosystems. For example, studies have shown that the presence of large predators, such as wolves, can help reduce the browsing pressure on trees by herbivores like deer. This allows for the regeneration of forests, which act as carbon sinks and play a crucial role in mitigating climate change.
Strategies for Conserving Predatory Mammals in the Face of Climate Change
Conserving predatory mammals in the face of climate change requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses both the direct and indirect impacts of this global challenge. Here are some strategies that can help protect and preserve these magnificent creatures:
- Habitat conservation: Protecting and restoring the habitats of predatory mammals is crucial for their survival. This includes preserving large, intact landscapes and creating wildlife corridors that allow for the movement of these animals between different habitats.
- Prey conservation: Ensuring the availability of prey species is essential for the survival of predatory mammals. This can be achieved through sustainable management of prey populations and protecting their habitats from degradation.
- Climate change mitigation: Taking action to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change is vital for the long-term survival of predatory mammals. This includes transitioning to renewable energy sources, promoting sustainable land-use practices, and advocating for policies that address climate change at a global scale.
- Community engagement: Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is crucial for the success of any conservation initiative. By involving communities in decision-making processes and providing them with alternative livelihood options, we can ensure the long-term support and participation of local stakeholders in protecting predatory mammals.
- Research and monitoring: Continued research and monitoring are essential for understanding the impacts of climate change on predatory mammals and developing effective conservation strategies. This includes studying their behavior, population dynamics, and habitat requirements, as well as monitoring the effectiveness of conservation interventions.
IX. FAQs
1. What are some examples of predatory mammals?
Predatory mammals are a diverse group of animals that have evolved to hunt and feed on other animals. Some examples of predatory mammals include lions, tigers, wolves, cheetahs, leopards, jaguars, bears, hyenas, and foxes. These animals have specialized adaptations such as sharp teeth, strong jaws, keen senses, and powerful bodies that enable them to capture and kill their prey.
2. How do predatory mammals hunt their prey?
Predatory mammals use a variety of hunting techniques to capture their prey. Some species, like lions and wolves, hunt in groups and use cooperative strategies to bring down larger prey. They work together to surround and overpower their target. Other predators, such as cheetahs and leopards, rely on their speed and agility to chase down and capture their prey. They use stealth and camouflage to get close to their target before launching a surprise attack.
3. What is the relationship between predatory mammals and keystone species?
Predatory mammals play a crucial role as keystone species in many ecosystems. Keystone species are those that have a disproportionately large impact on their environment relative to their abundance. Predatory mammals help regulate the populations of their prey species, preventing them from becoming overabundant and causing imbalances in the ecosystem. By controlling the population of herbivores, they indirectly influence plant communities and maintain the overall health and diversity of the ecosystem.
4. How do predatory mammals contribute to biodiversity?
Predatory mammals contribute to biodiversity by playing a vital role in maintaining the balance of ecosystems. They help control the population of prey species, which in turn affects the abundance and distribution of other organisms in the ecosystem. By keeping herbivore populations in check, predatory mammals prevent overgrazing and habitat degradation, allowing for the survival of a wide range of plant and animal species. Their presence ensures the stability and resilience of the ecosystem.
5. What are some conservation efforts to protect predatory mammals?
Conservation efforts to protect predatory mammals involve a combination of strategies aimed at preserving their habitats, reducing human-wildlife conflicts, and promoting sustainable hunting practices. These efforts include the establishment of protected areas, the implementation of laws and regulations to prohibit the hunting and trade of endangered species, the promotion of education and awareness programs, and the development of community-based conservation initiatives. Collaboration between governments, conservation organizations, and local communities is essential for the success of these conservation efforts.
6. How can human-wildlife conflict be mitigated?
Human-wildlife conflict arises when there is competition or conflict between humans and predatory mammals over resources or when predatory mammals pose a threat to human safety or livelihoods. To mitigate human-wildlife conflict, various measures can be taken, such as implementing effective livestock protection methods, promoting the use of non-lethal deterrents, establishing wildlife corridors to reduce habitat fragmentation, and providing compensation or alternative livelihood options for communities affected by wildlife depredation. It is important to find a balance between the needs of local communities and the conservation of predatory mammals.
7. What are some ecosystem services provided by predatory mammals?
Predatory mammals provide several ecosystem services that are essential for the functioning and well-being of ecosystems. They help regulate prey populations, preventing overgrazing and maintaining the balance of plant communities. They also act as scavengers, consuming carrion and helping to break down organic matter, which contributes to nutrient cycling. Additionally, predatory mammals can influence the behavior and distribution of their prey species, which can have cascading effects on other organisms within the ecosystem.
8. How do predatory mammals contribute to habitat restoration?
Predatory mammals can contribute to habitat restoration by controlling the populations of herbivores that may be causing damage to ecosystems. By reducing the abundance of herbivores, predatory mammals help restore the balance between plants and animals, allowing for the recovery of degraded habitats. Their presence can also promote the regeneration of plant species and the restoration of natural ecological processes. In some cases, reintroducing predatory mammals to areas where they have been extirpated can have positive effects on ecosystem health and biodiversity.
9. How does climate change affect predatory mammal populations?
Climate change can have significant impacts on predatory mammal populations. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and altered habitats can affect the availability of prey species and disrupt the delicate balance between predators and their prey. Changes in climate can also lead to shifts in the distribution and abundance of prey species, which can impact the foraging and reproductive success of predatory mammals. Additionally, climate change can result in habitat loss and fragmentation, further threatening the survival of these species.
10. What can be done to conserve predatory mammals in the face of climate change?
Conserving predatory mammals in the face of climate change requires a multi-faceted approach. It involves reducing greenhouse gas emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change, protecting and restoring habitats that are crucial for the survival of these species, implementing adaptive management strategies to address changing ecological conditions, and promoting connectivity between habitats to allow for the movement of predators in response to shifting environmental conditions. Collaboration between scientists, policymakers, and local communities is vital for the effective conservation of predatory mammals in a changing climate.
