Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Definition and Types of Protected Areas
- III. Role of Protected Areas in Mammal Conservation
- IV. Case Studies: Successful Mammal Conservation in Protected Areas
- V. Threats to Mammals in Protected Areas
- VI. Conservation Strategies for Protected Areas
- VII. Monitoring and Research in Protected Areas
- VIII. Challenges and Limitations of Protected Areas for Mammal Conservation
- IX. Collaboration and International Efforts in Mammal Conservation
I. Introduction

Protected areas play a crucial role in the conservation of mammal species around the world. These areas, also known as nature reserves or national parks, are designated spaces that are managed to preserve the natural environment and protect the wildlife within them. They serve as havens for various mammal species, providing them with suitable habitats and ensuring their survival.
The importance of protected areas for mammal conservation cannot be overstated. These areas offer a range of benefits, including:
- Preservation of biodiversity: Protected areas help safeguard the diverse range of mammal species found in different regions. By providing a safe and undisturbed environment, these areas allow for the maintenance of healthy populations and the preservation of genetic diversity.
- Habitat protection: Many mammal species rely on specific habitats for their survival. Protected areas ensure the preservation of these habitats, which are often threatened by human activities such as deforestation and urbanization.
- Prevention of species extinction: Protected areas act as refuges for endangered mammal species. By providing a safe space, these areas help prevent the extinction of species that are at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching, and climate change.
- Research and education: Protected areas serve as living laboratories for scientists and researchers studying mammal species. They provide valuable opportunities for studying animal behavior, population dynamics, and ecological interactions. Additionally, these areas offer educational opportunities for visitors, raising awareness about the importance of mammal conservation.
II. Definition and Types of Protected Areas

A. Definition of protected areas
Protected areas are designated regions that are managed and conserved to preserve their natural, cultural, or historical significance. These areas play a crucial role in safeguarding biodiversity, maintaining ecological balance, and providing habitat for various species. They are established with the aim of protecting and preserving the unique features and values of the area, ensuring their long-term sustainability.
Protected areas can include national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, biosphere reserves, and nature reserves. Each category has its own specific objectives and management strategies, but they all share the common goal of conserving the natural environment and its inhabitants.
B. Categories of protected areas
1. National parks
National parks are extensive areas of land and/or water that are protected and managed by the government for the conservation of natural and cultural resources. These areas are typically chosen for their exceptional beauty, unique ecosystems, or significant historical or cultural value.
Within national parks, strict regulations are enforced to ensure the preservation of the area’s natural features. Activities such as hunting, logging, and mining are usually prohibited, while recreational activities like hiking, camping, and wildlife viewing are encouraged in designated areas.
2. Wildlife sanctuaries
Wildlife sanctuaries are designated areas that provide a safe haven for wildlife species, particularly those that are endangered or vulnerable. These sanctuaries aim to protect and conserve the natural habitats of these species, allowing them to thrive and reproduce without disturbance.
Wildlife sanctuaries often have specific management plans in place to address the needs of the resident species. This may include habitat restoration, predator control, and monitoring programs to ensure the well-being of the wildlife population.
3. Biosphere reserves
Biosphere reserves are unique areas that integrate conservation, sustainable development, and scientific research. These reserves aim to reconcile the conservation of biodiversity with the sustainable use of natural resources and the promotion of local livelihoods.
Biosphere reserves are typically divided into three zones: a core area where strict conservation measures are enforced, a buffer zone where limited human activities are allowed, and a transition zone where sustainable development practices are encouraged.
4. Nature reserves
Nature reserves are protected areas that are established primarily for the conservation of biodiversity and natural ecosystems. These reserves are often home to rare and endangered species, and they serve as important refuges for these plants and animals.
Nature reserves may have specific management plans in place to protect and restore the habitats within their boundaries. This can include measures such as habitat restoration, invasive species control, and monitoring programs to assess the health of the ecosystem.
III. Role of Protected Areas in Mammal Conservation
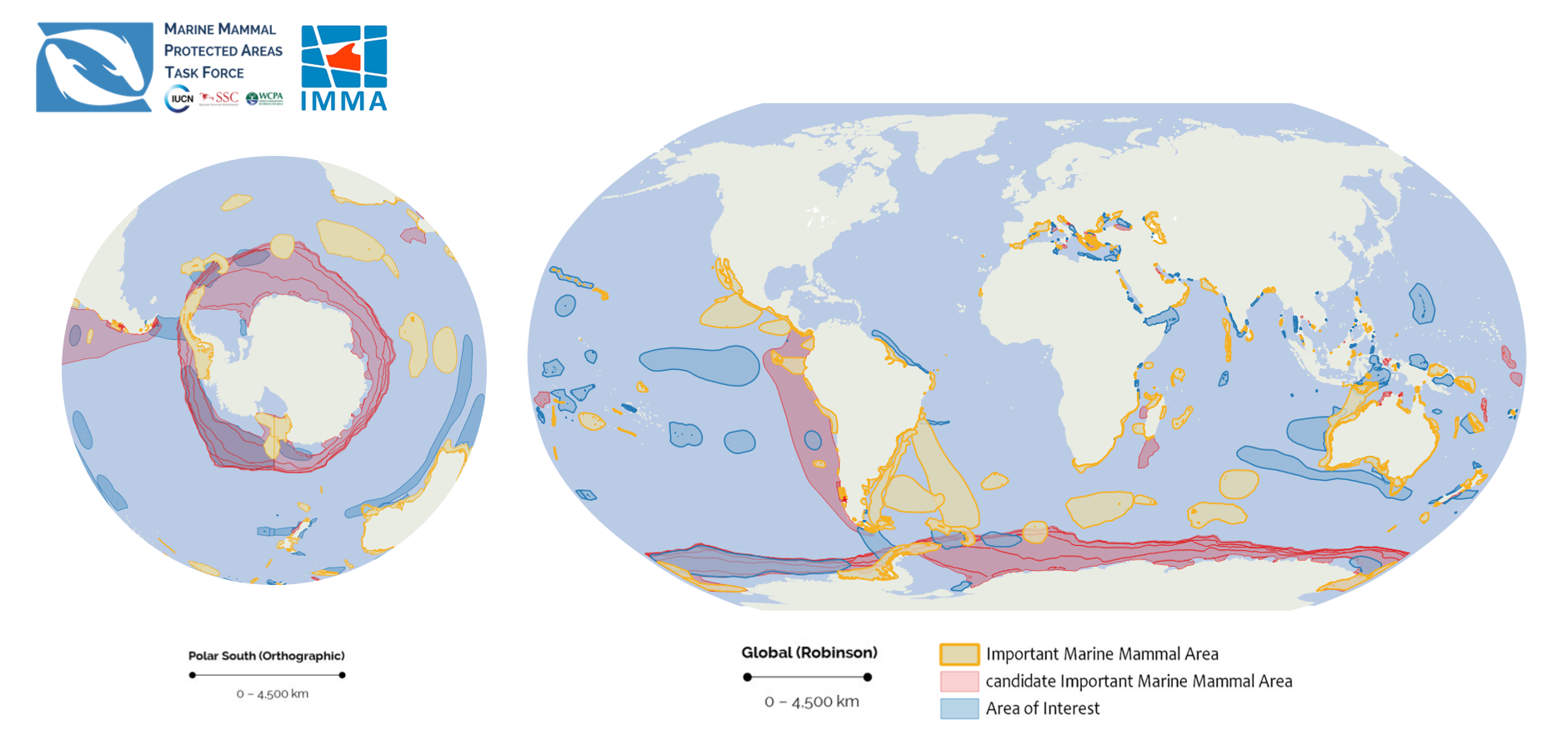
Protected areas play a crucial role in the conservation of mammal species around the world. These areas, which include national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and nature reserves, provide a safe haven for many endangered and threatened mammal species. In this section, we will explore the various ways in which protected areas contribute to mammal conservation.
A. Habitat preservation
One of the primary functions of protected areas is to preserve the natural habitats of mammal species. These areas are often characterized by a diverse range of ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, wetlands, and coastal areas, which provide essential resources for the survival of mammals. By protecting these habitats from human activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and pollution, protected areas ensure the availability of suitable habitats for a wide variety of mammal species.
For example, the Amazon rainforest, which is protected by numerous national parks and reserves, is home to a vast array of mammal species, including jaguars, tapirs, and sloths. The preservation of this habitat is crucial for the survival of these species, as it provides them with food, shelter, and breeding grounds.
Protected areas also play a vital role in maintaining the connectivity of habitats. Many mammal species require large home ranges and migrate between different areas in search of food, mates, or suitable habitats for their young. By creating a network of protected areas, conservationists can ensure that these species have access to the resources they need to survive and thrive.
B. Biodiversity conservation
Protected areas are hotspots of biodiversity, harboring a wide range of plant and animal species, including mammals. By conserving these areas, we can protect not only individual mammal species but also the entire ecosystems they inhabit. This is important because ecosystems are complex webs of interactions, and the loss of one species can have far-reaching consequences for others.
For instance, in African savannas, protected areas such as national parks and game reserves are crucial for the conservation of iconic mammal species like elephants, lions, and rhinos. These species are not only important in their own right but also play key roles in maintaining the balance of the ecosystem. Elephants, for example, are known as ecosystem engineers because they shape their environment by creating water holes and clearing vegetation, which benefits other species.
Protected areas also serve as living laboratories for scientific research and monitoring. By studying mammal populations within these areas, scientists can gain valuable insights into their behavior, ecology, and conservation needs. This knowledge can then be used to develop effective conservation strategies and management plans for both protected and non-protected areas.
C. Population management and recovery
Protected areas provide a safe space for the management and recovery of mammal populations. Many mammal species are threatened by factors such as habitat loss, poaching, and climate change. By establishing protected areas, conservationists can create refuges where these species can breed and increase their numbers.
For example, the Wolong National Nature Reserve in China is home to the endangered giant panda. Through dedicated conservation efforts, including habitat restoration, anti-poaching measures, and captive breeding programs, the population of giant pandas in Wolong has been steadily increasing. This success story demonstrates the importance of protected areas in the recovery of threatened mammal species.
Protected areas also play a crucial role in reintroducing mammal species into their former habitats. This is often done through carefully planned translocation programs, where individuals are captured from healthy populations and released into suitable protected areas. These programs have been successful in reintroducing species such as the black-footed ferret and the California condor back into the wild.
IV. Case Studies: Successful Mammal Conservation in Protected Areas

Protected areas play a crucial role in the conservation of mammal species around the world. These designated areas provide a safe haven for wildlife, allowing them to thrive and ensuring their long-term survival. In this section, we will explore three case studies that highlight the importance of protected areas in mammal conservation.
A. Serengeti National Park: Preserving African wildlife
Serengeti National Park, located in Tanzania, is renowned for its vast savannahs and diverse wildlife. It is home to numerous mammal species, including the iconic African elephant, lion, and giraffe. The park’s protected status has been instrumental in preserving these species and their habitats.
One of the park’s notable success stories is the conservation of the African elephant population. In the past, these majestic creatures faced significant threats from poaching and habitat loss. However, thanks to the strict protection measures implemented within Serengeti National Park, the elephant population has rebounded. Today, visitors to the park can witness large herds of elephants roaming freely, a testament to the effectiveness of protected areas in safeguarding these magnificent animals.
Furthermore, Serengeti National Park is also crucial for the conservation of big cat species, such as lions and cheetahs. The park provides a vast and undisturbed habitat for these predators, allowing them to hunt, breed, and maintain healthy populations. Without the protection offered by the park, these iconic African species would be at a much higher risk of extinction.
B. Great Barrier Reef Marine Park: Protecting marine mammals
The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park, located off the coast of Queensland, Australia, is not only a haven for coral reefs but also a vital habitat for marine mammals. This protected area encompasses a vast expanse of ocean, providing shelter, feeding grounds, and breeding areas for a variety of marine species.
One of the most notable marine mammals found within the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park is the dugong, also known as the “sea cow.” These gentle herbivores rely on seagrass meadows for their survival. The park’s protected status ensures the preservation of these vital habitats, allowing dugongs to thrive and maintain healthy populations.
In addition to dugongs, the marine park is also home to various dolphin and whale species. These intelligent and highly social creatures rely on the park’s waters for feeding, breeding, and migration. By safeguarding their habitat, the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park plays a crucial role in the conservation of these magnificent marine mammals.
C. Yellowstone National Park: Restoring wolf populations
Yellowstone National Park, located primarily in the U.S. state of Wyoming, is not only a stunning natural landscape but also a prime example of successful mammal conservation. One of the park’s most notable success stories is the restoration of wolf populations.
Wolves were once a common sight in Yellowstone but were eradicated from the park in the early 20th century due to hunting and predator control programs. However, in 1995, a reintroduction program was launched, bringing wolves back to the park. This initiative aimed to restore the natural balance of the ecosystem, as wolves play a vital role in regulating prey populations and shaping the landscape.
The reintroduction of wolves to Yellowstone National Park has had far-reaching effects. It has led to a reduction in overgrazing by herbivores such as elk, allowing vegetation to recover and creating a more diverse habitat for other species. The presence of wolves has also had positive cascading effects on other wildlife, such as beavers and songbirds, further enhancing the park’s biodiversity.
Yellowstone National Park serves as a powerful example of how protected areas can not only conserve existing mammal populations but also restore and revitalize ecosystems that have been disrupted by human activities.
V. Threats to Mammals in Protected Areas
Protected areas play a crucial role in conserving mammal species and their habitats. However, these areas are not immune to threats that can negatively impact the survival of mammals. In this section, we will explore some of the major threats faced by mammals in protected areas.
A. Habitat loss and fragmentation
Habitat loss and fragmentation are among the most significant threats to mammal populations in protected areas. As human activities continue to encroach upon natural habitats, the available space for mammals to thrive diminishes. Deforestation, urbanization, and agricultural expansion are some of the primary drivers of habitat loss.
When habitats are fragmented, it becomes challenging for mammals to move freely, find food, and establish territories. Fragmentation can lead to isolation of populations, reducing genetic diversity and increasing the risk of inbreeding. It also disrupts ecological processes and can result in the loss of important habitat corridors.
Protected areas must address the issue of habitat loss and fragmentation through effective land-use planning, habitat restoration, and the establishment of wildlife corridors. Collaborative efforts between governments, conservation organizations, and local communities are essential to mitigate these threats and ensure the long-term survival of mammal species.
B. Poaching and illegal wildlife trade
Poaching and the illegal wildlife trade pose significant threats to mammal populations in protected areas. The demand for wildlife products, such as ivory, rhino horn, and exotic pets, drives the illegal hunting and capture of mammals. This unsustainable exploitation can lead to population declines and even extinction.
Protected areas are often targeted by poachers due to their rich biodiversity and the relative isolation of some regions. Lack of resources and inadequate enforcement can make it challenging to combat poaching effectively. However, many protected areas have implemented anti-poaching measures, such as increased patrols, surveillance technology, and community engagement, to address this threat.
International cooperation and stricter law enforcement are crucial in combating the illegal wildlife trade. Public awareness campaigns and education programs can also help reduce the demand for wildlife products and promote ethical wildlife tourism as an alternative source of income for local communities.
C. Climate change and its impact on mammal habitats
Climate change is a global threat that affects mammal habitats in protected areas. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events can alter ecosystems and disrupt the delicate balance between species and their environment.
As habitats shift or become unsuitable for certain species, mammals may face challenges in finding suitable food sources, water, and shelter. Climate change can also lead to the spread of diseases and the introduction of invasive species, further impacting mammal populations.
Protected areas need to adapt to the changing climate by implementing climate-smart conservation strategies. This may include habitat restoration, assisted migration, and the creation of climate-resilient landscapes. Collaboration with scientific institutions and local communities can provide valuable insights and help develop effective adaptation plans.
VI. Conservation Strategies for Protected Areas
Protected areas play a crucial role in conserving mammal species and their habitats. To ensure the long-term survival of these species, effective conservation strategies need to be implemented. In this section, we will explore three key conservation strategies for protected areas: ecosystem-based management, community involvement and local engagement, and sustainable tourism and revenue generation.
A. Ecosystem-based management
Ecosystem-based management is a holistic approach to conservation that focuses on maintaining the health and integrity of entire ecosystems. It recognizes the interconnectedness of all living organisms and the importance of preserving their natural habitats. By protecting the entire ecosystem, rather than individual species, ecosystem-based management ensures the long-term survival of mammal populations.
One of the key principles of ecosystem-based management is the restoration and maintenance of natural ecological processes. This includes managing invasive species, controlling pollution, and restoring degraded habitats. By restoring natural processes, protected areas can provide suitable habitats for a wide range of mammal species.
Another important aspect of ecosystem-based management is the establishment of ecological corridors. These corridors connect fragmented habitats, allowing for the movement of mammal populations and facilitating gene flow. By maintaining connectivity between different protected areas, ecosystem-based management promotes genetic diversity and enhances the resilience of mammal populations.
B. Community involvement and local engagement
Effective conservation of protected areas requires the active participation and support of local communities. Engaging local communities in conservation efforts not only fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility but also promotes sustainable practices that benefit both people and wildlife.
Community involvement can take various forms, including education and awareness programs, capacity building, and the establishment of community-based conservation initiatives. By involving local communities in decision-making processes and empowering them to take an active role in conservation, protected areas can benefit from their traditional knowledge and expertise.
Furthermore, local engagement can help address the root causes of threats to protected areas. By addressing issues such as poverty, lack of alternative livelihoods, and unsustainable resource use, protected areas can gain the support and cooperation of local communities. This, in turn, leads to more effective conservation outcomes and ensures the long-term sustainability of protected areas.
C. Sustainable tourism and revenue generation
Tourism can be a powerful tool for conservation when managed sustainably. Protected areas that attract tourists can generate revenue that can be reinvested in conservation efforts. This revenue can be used to improve infrastructure, enhance monitoring and enforcement, and support local communities.
Sustainable tourism practices ensure that the ecological integrity of protected areas is not compromised. This includes limiting visitor numbers, implementing strict regulations, and promoting responsible behavior among tourists. By minimizing the negative impacts of tourism, protected areas can continue to provide habitats for mammal species while also benefiting from the economic opportunities that tourism brings.
Furthermore, sustainable tourism can raise awareness about the importance of protected areas and the need for their conservation. Tourists who visit protected areas can become advocates for conservation, spreading the message and supporting conservation initiatives in their own communities.
VII. Monitoring and Research in Protected Areas
In order to effectively conserve mammal populations and assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts, monitoring and research play a crucial role in protected areas. By tracking mammal populations, studying their behavior and ecology, and evaluating the impact of conservation initiatives, we can gain valuable insights into the status and trends of mammal species within these areas.
A. Tracking mammal populations
Tracking mammal populations is essential for understanding their distribution, abundance, and habitat preferences. This information helps us identify key areas for conservation and prioritize management strategies. There are various methods used to track mammal populations, including:
- Camera trapping: This technique involves setting up motion-activated cameras in strategic locations to capture images of mammals in their natural habitat. It provides valuable data on species presence, behavior, and population size.
- Footprint surveys: By examining tracks and signs left by mammals, researchers can estimate their abundance and identify the species present in a particular area.
- Radio telemetry: This method involves attaching radio transmitters to individual animals to track their movements and gather information on their home range, habitat use, and behavior.
By combining these tracking methods, researchers can obtain comprehensive data on mammal populations, which can inform conservation strategies and help monitor the success of management efforts over time.
B. Studying behavior and ecology
Studying the behavior and ecology of mammals in protected areas provides valuable insights into their natural history, social structure, and ecological interactions. This knowledge is crucial for developing effective conservation plans and understanding the ecological roles of different species. Researchers use various techniques to study mammal behavior and ecology, including:
- Observational studies: Researchers spend time in the field observing mammals and recording their behavior, social interactions, and feeding habits. This information helps us understand how mammals interact with their environment and other species.
- Radio tracking: By using radio telemetry, researchers can track individual animals and gather data on their movements, habitat use, and behavior patterns. This information is particularly useful for studying migratory species or those with large home ranges.
- Genetic analysis: DNA analysis allows researchers to study the genetic diversity, relatedness, and population structure of mammal species. This information helps us understand their evolutionary history and inform conservation strategies.
By studying the behavior and ecology of mammals in protected areas, we can gain a deeper understanding of their needs and vulnerabilities, which is essential for effective conservation planning.
C. Assessing the effectiveness of conservation efforts
Assessing the effectiveness of conservation efforts is crucial for adaptive management and ensuring the long-term viability of mammal populations in protected areas. By evaluating the impact of conservation initiatives, we can identify successful strategies and make informed decisions about future management actions. There are several approaches used to assess the effectiveness of conservation efforts, including:
- Population monitoring: Regular monitoring of mammal populations allows us to track changes over time and assess the impact of conservation interventions. This can involve population surveys, demographic studies, and trend analysis.
- Habitat assessment: Evaluating the quality and extent of habitat within protected areas helps us understand the factors influencing mammal populations. This information guides habitat restoration and management efforts.
- Community engagement: Involving local communities in conservation initiatives is essential for long-term success. Assessing the level of community participation and support helps measure the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
By continuously monitoring and evaluating the effectiveness of conservation efforts, we can adapt management strategies to ensure the persistence of mammal populations in protected areas.
VIII. Challenges and Limitations of Protected Areas for Mammal Conservation
Protected areas play a crucial role in conserving mammal species and their habitats. However, they also face several challenges and limitations that need to be addressed in order to ensure their effectiveness in conservation efforts. In this section, we will discuss three key challenges that protected areas encounter: lack of funding and resources, conflicts between conservation and human activities, and invasive species and disease transmission.
A. Lack of funding and resources
One of the major challenges faced by protected areas is the lack of adequate funding and resources. Conservation initiatives require substantial financial support to carry out activities such as habitat restoration, anti-poaching efforts, and research. However, many protected areas struggle to secure sufficient funding to meet these needs.
This lack of funding often leads to limited staff capacity, inadequate infrastructure, and insufficient equipment and technology. Without proper resources, protected areas may struggle to effectively monitor and manage mammal populations, enforce regulations, and implement conservation strategies.
To address this challenge, it is crucial for governments, non-governmental organizations, and other stakeholders to prioritize funding and resource allocation for protected areas. This can be achieved through increased government support, public-private partnerships, and international collaborations. Additionally, innovative financing mechanisms, such as ecotourism and carbon offset programs, can provide alternative sources of funding for conservation efforts.
B. Conflicts between conservation and human activities
Protected areas often face conflicts between conservation objectives and human activities. Human populations living in or near protected areas may rely on natural resources for their livelihoods, leading to conflicts over land use, hunting, fishing, and resource extraction.
These conflicts can have detrimental impacts on mammal populations and their habitats. Illegal hunting and poaching, for example, can result in the decline of vulnerable and endangered species. Habitat destruction and fragmentation caused by human activities can also disrupt ecological processes and threaten the survival of mammal populations.
To address these conflicts, it is important to promote sustainable livelihood options for local communities living in and around protected areas. This can be achieved through the implementation of community-based conservation initiatives, which involve local communities in decision-making processes and provide them with incentives to participate in conservation efforts.
Furthermore, effective law enforcement and awareness campaigns are essential to combat illegal activities and raise public awareness about the importance of protected areas for mammal conservation.
C. Invasive species and disease transmission
Invasive species and disease transmission pose significant threats to mammal populations within protected areas. Invasive species, such as non-native predators and plants, can outcompete native species for resources and disrupt ecological balance.
Disease transmission, particularly zoonotic diseases that can be transmitted between animals and humans, can have devastating effects on mammal populations. Outbreaks of diseases such as rabies, bovine tuberculosis, and Ebola have been reported in protected areas, leading to population declines and even local extinctions.
To mitigate the impacts of invasive species and disease transmission, protected areas need to implement strict biosecurity measures. This includes monitoring and controlling the introduction of non-native species, implementing disease surveillance programs, and promoting public health measures to prevent the spread of zoonotic diseases.
Collaboration between protected area management authorities, research institutions, and veterinary services is crucial to effectively address these challenges and develop strategies for the prevention and control of invasive species and diseases.
IX. Collaboration and International Efforts in Mammal Conservation
In the global effort to conserve and protect mammal species, collaboration and international initiatives play a crucial role. Various organizations and agreements have been established to promote conservation efforts and ensure the long-term survival of mammals. In this section, we will explore three key entities that are actively involved in mammal conservation on an international scale.
A. International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN)
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) is a leading global authority on environmental conservation. Established in 1948, the IUCN brings together governments, NGOs, scientists, and experts from around the world to address pressing conservation challenges. The IUCN maintains the Red List of Threatened Species, which assesses the conservation status of various species, including mammals.
Through its Species Survival Commission (SSC), the IUCN focuses on species-specific conservation efforts. The SSC’s Specialist Groups, such as the IUCN SSC Primate Specialist Group and the IUCN SSC Cat Specialist Group, work to gather scientific data, conduct research, and develop conservation strategies for specific mammal groups. These efforts contribute to the overall understanding and conservation of mammal species worldwide.
B. Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD)
The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) is an international treaty that aims to conserve biodiversity, promote sustainable use of natural resources, and ensure equitable sharing of benefits derived from genetic resources. The CBD recognizes the importance of protecting mammal species and their habitats as part of broader conservation goals.
Under the CBD, countries commit to developing and implementing national strategies and action plans for biodiversity conservation. These plans often include measures to protect and manage mammal populations and their habitats. By fostering collaboration and knowledge-sharing among member countries, the CBD encourages international cooperation in mammal conservation.
C. Global initiatives for protected area expansion
Protected areas are crucial for the conservation of mammal species, providing safe havens for their survival and promoting biodiversity. Several global initiatives are dedicated to expanding protected areas and improving their management to benefit mammals and other wildlife.
One such initiative is the World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA), managed by the IUCN and the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP). The WDPA serves as a comprehensive source of information on protected areas worldwide, helping governments, researchers, and conservation organizations make informed decisions about conservation planning and management.
Additionally, the Global Environment Facility (GEF) supports projects that focus on expanding protected areas and enhancing their effectiveness. Through funding and technical assistance, the GEF helps countries establish new protected areas, strengthen their management capacities, and improve the connectivity between protected areas to facilitate the movement of mammal populations.
Other initiatives, such as the Alliance for Zero Extinction (AZE) and the Global Wildlife Conservation (GWC), also contribute to protected area expansion efforts. These organizations work to identify and protect areas that are critical for the survival of endangered mammal species, ensuring their long-term conservation.
Protected areas play a crucial role in not only conserving wildlife and natural habitats but also in providing economic benefits to local communities. These benefits can be seen in various aspects, including ecotourism and job creation, sustainable development and poverty alleviation, and the cultural and spiritual significance of protected areas.
A. Ecotourism and Job Creation
One of the key economic benefits of protected areas for local communities is the promotion of ecotourism and the subsequent job creation opportunities. Protected areas often attract tourists who are interested in experiencing the beauty of nature and observing wildlife in their natural habitats. This influx of tourists creates a demand for various services, such as accommodation, transportation, food, and guiding services.
Local communities living near protected areas can tap into this tourism potential by offering these services and creating employment opportunities for their residents. For example, local individuals can become tour guides, providing valuable insights into the flora and fauna found within the protected area. Others can establish small businesses, such as guesthouses or restaurants, to cater to the needs of tourists.
By engaging in ecotourism activities, local communities can not only generate income but also develop new skills and knowledge related to tourism management. This can lead to the overall socio-economic development of the community, as individuals become more empowered and financially stable.
B. Sustainable Development and Poverty Alleviation
Protected areas contribute to sustainable development by providing opportunities for local communities to engage in activities that promote long-term economic growth while preserving the natural environment. Sustainable development aims to meet the needs of the present generation without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Through sustainable resource management practices, local communities can benefit from the natural resources within protected areas without depleting them. For example, sustainable harvesting of non-timber forest products, such as medicinal plants or wild fruits, can provide a source of income for local communities while ensuring the continued availability of these resources for future generations.
Furthermore, protected areas can serve as a source of alternative livelihoods for communities that rely heavily on activities such as logging or hunting, which can be detrimental to the environment. By promoting sustainable livelihood options, protected areas can help alleviate poverty and reduce dependence on unsustainable practices.
C. Cultural and Spiritual Significance of Protected Areas
Protected areas often hold cultural and spiritual significance for local communities. These areas may be associated with traditional beliefs, rituals, or practices that have been passed down through generations. They serve as important cultural heritage sites, connecting people to their ancestral roots and preserving their cultural identity.
For many indigenous communities, protected areas are not just places of ecological importance but also sacred sites. These areas are believed to be inhabited by ancestral spirits or deities and are considered sacred grounds. The conservation of these areas ensures the preservation of cultural heritage and the continuation of traditional practices and knowledge.
Local communities can benefit from the cultural and spiritual significance of protected areas by engaging in cultural tourism. This form of tourism allows visitors to learn about the local traditions, customs, and beliefs, providing a unique and authentic experience. By sharing their cultural heritage with visitors, local communities can generate income and promote intercultural understanding.
