Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding the Impact of Human Development on Wildlife
- III. Conservation Strategies for Reducing the Impact of Human Development on Wildlife
- IV. Best Practices for Wildlife-Friendly Development
- V. Wildlife-Friendly Agriculture and Forestry Practices
- VI. Engaging Local Communities in Wildlife Conservation
- VII. Wildlife Rehabilitation and Rescue
- VIII. Wildlife Conservation Laws and Policies
- IX. Wildlife Tourism and Responsible Wildlife Watching
I. Introduction

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on how to reduce the impact of human development on wildlife. As human activities continue to expand, it is crucial that we take proactive measures to protect and preserve the natural habitats of wildlife species. This article aims to provide you with valuable insights and practical tips on how you can contribute to the conservation efforts.
Human development, including urbanization, agriculture, and infrastructure projects, has had a significant impact on wildlife populations worldwide. Habitat loss, pollution, and climate change are just a few of the challenges that wildlife face due to human activities. However, by making conscious choices and adopting sustainable practices, we can minimize these negative effects and create a harmonious coexistence between humans and wildlife.
In this guide, we will explore various strategies and initiatives that can be implemented at individual, community, and governmental levels. From promoting responsible tourism and supporting wildlife conservation organizations to advocating for stricter environmental regulations, there are numerous ways in which we can make a positive impact.
Throughout the article, we will delve into specific topics such as habitat restoration, wildlife-friendly farming practices, and the importance of protected areas. We will also discuss the role of education and awareness in fostering a culture of environmental stewardship.
By the end of this guide, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the challenges faced by wildlife due to human development and the actionable steps you can take to mitigate these impacts. Together, we can ensure a sustainable future for both humans and wildlife.
II. Understanding the Impact of Human Development on Wildlife

Human development has had a profound impact on wildlife across the globe. As we continue to expand our cities, industries, and infrastructure, we inadvertently encroach upon and disrupt the natural habitats of countless species. This section will explore some of the key ways in which human development has negatively affected wildlife, including habitat destruction and fragmentation, pollution and contamination, and climate change.
A. Habitat Destruction and Fragmentation
One of the most significant consequences of human development on wildlife is habitat destruction and fragmentation. As we clear land for agriculture, urbanization, and industrial activities, we destroy the natural habitats that many species rely on for survival. This loss of habitat not only displaces wildlife but also disrupts entire ecosystems, leading to a decline in biodiversity.
Furthermore, the fragmentation of habitats due to human activities creates isolated patches of land that are unable to support viable populations of many species. This fragmentation restricts the movement and gene flow of wildlife, making them more susceptible to inbreeding, reduced genetic diversity, and ultimately, extinction.
For example, the construction of roads and highways often divides once contiguous habitats, making it difficult for animals to access food, water, and mates. This can lead to increased mortality rates, decreased reproductive success, and a higher risk of predation.
B. Pollution and Contamination
Another significant impact of human development on wildlife is pollution and contamination. Our industrial activities, improper waste disposal, and the use of harmful chemicals have resulted in the release of pollutants into the environment, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
Chemical pollutants, such as pesticides and heavy metals, can accumulate in the bodies of wildlife through the food chain, leading to various health issues and reproductive problems. These pollutants can also contaminate water bodies, affecting aquatic species and their habitats.
Furthermore, air pollution from industrial emissions and vehicle exhausts can have detrimental effects on wildlife, particularly on species that are sensitive to changes in air quality. Birds, for example, can suffer from respiratory problems and reduced reproductive success due to exposure to air pollutants.
C. Climate Change and Its Effects on Wildlife
Climate change, largely driven by human activities, is one of the most pressing challenges facing wildlife today. Rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and extreme weather events are altering ecosystems and disrupting the delicate balance of nature.
Many wildlife species have specific temperature and climate requirements for survival, such as hibernation periods, migration patterns, and breeding seasons. However, as the climate changes, these species are forced to adapt or face extinction.
For example, polar bears, which rely on sea ice for hunting and breeding, are facing significant challenges as the Arctic ice melts at an alarming rate. Similarly, coral reefs, which support a diverse array of marine life, are under threat due to rising ocean temperatures and ocean acidification.
Climate change also affects the availability of food and resources for wildlife. Changes in precipitation patterns can lead to droughts or floods, impacting the availability of water and vegetation. This, in turn, affects the survival and reproductive success of many species.
III. Conservation Strategies for Reducing the Impact of Human Development on Wildlife
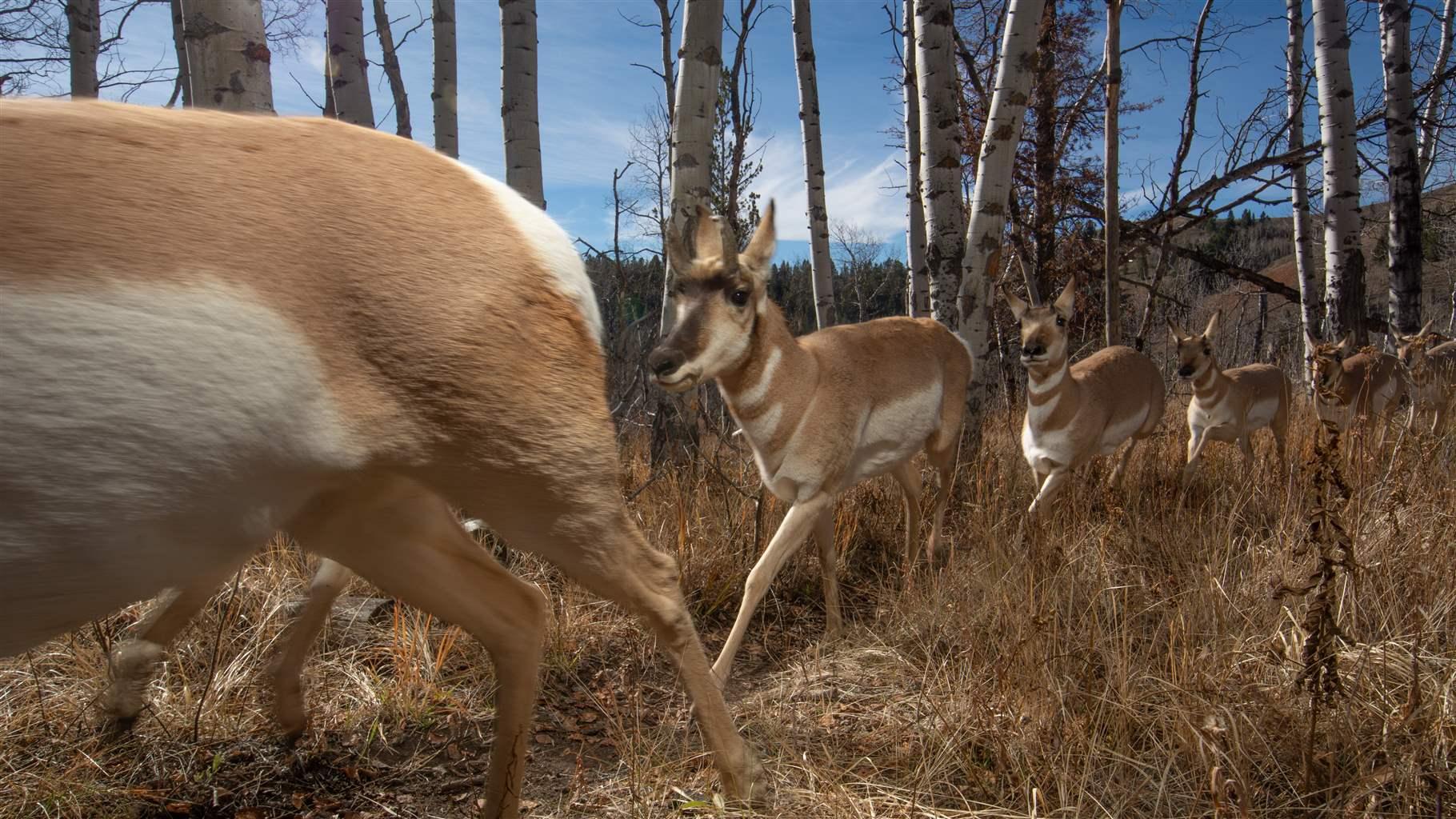

Conservation of wildlife is of utmost importance in today’s world, where human development and activities continue to encroach upon natural habitats. To mitigate the negative impact of human development on wildlife, various conservation strategies have been implemented. These strategies aim to protect wildlife, restore habitats, and promote sustainable land use practices. In this section, we will explore some of the key conservation strategies that can help reduce the impact of human development on wildlife.
A. Protected areas and wildlife reserves
Protected areas and wildlife reserves play a crucial role in safeguarding wildlife and their habitats. These designated areas are managed and protected to ensure the preservation of biodiversity. Protected areas can include national parks, wildlife sanctuaries, and nature reserves.
Within these protected areas, regulations are put in place to limit human activities that may harm wildlife. These regulations may include restrictions on hunting, fishing, and logging. By creating and effectively managing protected areas, we can provide safe havens for wildlife to thrive.
Furthermore, protected areas also serve as important educational and recreational resources for the public. They offer opportunities for people to connect with nature and learn about the importance of conservation. By raising awareness and fostering a sense of stewardship, protected areas can contribute to long-term conservation efforts.
B. Habitat restoration and conservation
Habitat restoration and conservation are vital for maintaining healthy ecosystems and preserving wildlife populations. Human development often leads to habitat destruction, fragmentation, and degradation, which can have severe consequences for wildlife.
Restoration efforts focus on rehabilitating degraded habitats and creating suitable conditions for wildlife to thrive. This can involve activities such as reforestation, wetland restoration, and removal of invasive species. By restoring habitats, we can provide essential resources, such as food and shelter, for wildlife.
Conservation efforts also aim to protect and conserve existing habitats. This involves identifying and prioritizing areas of high ecological value and implementing measures to ensure their long-term preservation. Conservation strategies may include land acquisition, habitat management, and the establishment of conservation easements.
Additionally, habitat conservation can be achieved through collaboration with local communities and stakeholders. By involving local communities in conservation efforts, we can promote sustainable practices and ensure the long-term success of conservation initiatives.
C. Sustainable land use practices
Sustainable land use practices are essential for minimizing the impact of human development on wildlife. Unsustainable land use, such as deforestation, urbanization, and intensive agriculture, can lead to habitat loss, pollution, and the depletion of natural resources.
Adopting sustainable land use practices involves balancing human needs with the conservation of wildlife and their habitats. This can be achieved through measures such as land-use planning, zoning regulations, and the promotion of sustainable agriculture.
Land-use planning involves identifying suitable areas for development while preserving ecologically sensitive areas. Zoning regulations can help ensure that development activities are carried out in a manner that minimizes harm to wildlife and their habitats.
Sustainable agriculture practices, such as organic farming and agroforestry, can help reduce the use of harmful chemicals and promote biodiversity. By implementing sustainable land use practices, we can create a harmonious balance between human development and wildlife conservation.
IV. Best Practices for Wildlife-Friendly Development

When it comes to reducing the impact of human development on wildlife, there are several best practices that can be implemented. These practices aim to create a balance between urban growth and the preservation of natural habitats. In this section, we will explore three key strategies for wildlife-friendly development: incorporating wildlife corridors in urban planning, implementing green infrastructure and sustainable design, and minimizing light and noise pollution.
A. Incorporating wildlife corridors in urban planning
One effective way to mitigate the negative effects of urban development on wildlife is by incorporating wildlife corridors into urban planning. Wildlife corridors are designated areas that connect fragmented habitats, allowing animals to move freely between different areas. These corridors can be in the form of green spaces, such as parks or nature reserves, or they can be linear features like rivers or tree-lined pathways.
By including wildlife corridors in urban planning, we can provide safe passage for animals, enabling them to access essential resources such as food, water, and shelter. These corridors also help to maintain genetic diversity within wildlife populations, as they allow for the exchange of individuals between different habitats.
When designing wildlife corridors, it is important to consider the specific needs of different species. Some animals may require larger corridors, while others may need specific types of habitats. By taking into account the ecological requirements of different species, we can create corridors that are effective in supporting a diverse range of wildlife.
B. Implementing green infrastructure and sustainable design
Another important aspect of wildlife-friendly development is the implementation of green infrastructure and sustainable design practices. Green infrastructure refers to the network of natural and semi-natural features, such as parks, green roofs, and wetlands, that provide multiple environmental benefits.
By incorporating green infrastructure into urban areas, we can create habitats that support a variety of wildlife species. For example, green roofs can provide nesting sites for birds, while wetlands can serve as breeding grounds for amphibians and insects. These green spaces also help to improve air and water quality, reduce urban heat island effects, and enhance the overall livability of cities.
Sustainable design practices, such as using native plants, minimizing the use of pesticides, and reducing water consumption, are also crucial for creating wildlife-friendly environments. Native plants provide food and shelter for local wildlife, while minimizing the use of pesticides helps to protect beneficial insects and other organisms. Additionally, reducing water consumption can help to conserve water resources, which are essential for both humans and wildlife.
C. Minimizing light and noise pollution
Light and noise pollution are two major threats to wildlife in urban areas. Artificial lights can disrupt natural light cycles, affecting the behavior and physiology of many species. For example, bright lights can disorient migrating birds, leading to collisions with buildings. Similarly, excessive noise from traffic, construction, and other human activities can disrupt animal communication, feeding patterns, and reproductive behaviors.
To minimize light pollution, it is important to use outdoor lighting fixtures that are properly shielded and directed downwards. This helps to reduce the amount of light that is emitted into the night sky and surrounding natural habitats. Additionally, using motion sensors and timers can help to ensure that lights are only on when needed, further reducing energy consumption and light pollution.
To address noise pollution, urban planners and developers can implement sound barriers, such as vegetative buffers or noise-reducing walls, to minimize the impact of noise on wildlife habitats. Additionally, creating buffer zones between noisy areas and sensitive habitats can help to reduce the exposure of wildlife to excessive noise levels.
By incorporating these best practices into urban planning and development, we can create environments that are more compatible with wildlife needs. These strategies not only help to protect and conserve biodiversity but also contribute to the overall sustainability and resilience of our cities.
V. Wildlife-Friendly Agriculture and Forestry Practices
In order to reduce the impact of human development on wildlife, it is crucial to adopt wildlife-friendly agriculture and forestry practices. These practices aim to minimize habitat destruction, preserve biodiversity, and promote sustainable land use. In this section, we will explore some key practices that can be implemented to achieve these goals.
A. Organic farming and agroforestry
Organic farming and agroforestry are two agricultural practices that prioritize environmental sustainability and wildlife conservation. Organic farming eliminates the use of synthetic fertilizers, pesticides, and genetically modified organisms (GMOs), relying instead on natural methods to enhance soil fertility and control pests.
Agroforestry, on the other hand, involves the integration of trees and shrubs into agricultural systems. This practice provides multiple benefits, such as improved soil quality, enhanced water retention, and increased biodiversity. By creating diverse habitats, agroforestry supports a wide range of wildlife species, including birds, insects, and small mammals.
Both organic farming and agroforestry contribute to the conservation of wildlife by minimizing chemical inputs, preserving natural habitats, and promoting ecological balance. These practices also offer economic benefits to farmers, such as improved soil health, reduced input costs, and increased resilience to climate change.
B. Sustainable logging and reforestation
The logging industry plays a significant role in deforestation and habitat loss, which negatively impact wildlife populations. However, sustainable logging practices can help mitigate these effects and promote responsible forest management.
Sustainable logging involves selective cutting, where only mature trees are harvested, leaving younger trees and the surrounding ecosystem intact. This approach minimizes the ecological impact and allows for natural regeneration of the forest. Additionally, sustainable logging practices prioritize the protection of endangered species and sensitive habitats.
Reforestation is another crucial aspect of reducing the impact of human development on wildlife. It involves the planting of trees in areas that have been deforested or degraded. Reforestation efforts not only restore habitats but also provide food and shelter for a variety of wildlife species.
By adopting sustainable logging practices and actively participating in reforestation initiatives, we can ensure the long-term survival of wildlife and maintain the ecological balance of our forests.
C. Integrated pest management
Integrated pest management (IPM) is an effective and environmentally friendly approach to pest control that minimizes the use of chemical pesticides. IPM focuses on preventing pest problems through a combination of techniques, including biological control, cultural practices, and the use of resistant crop varieties.
Biological control involves the introduction of natural predators, parasites, or pathogens to control pest populations. This method reduces the reliance on chemical pesticides and promotes the natural balance of ecosystems. Cultural practices, such as crop rotation and proper sanitation, help prevent pest infestations by disrupting their life cycles and reducing their habitat.
Furthermore, the use of resistant crop varieties can significantly reduce the need for chemical pesticides. By selecting plant varieties that are naturally resistant to pests and diseases, farmers can minimize crop damage and protect wildlife from the harmful effects of pesticides.
Integrated pest management not only protects crops but also preserves the health of ecosystems and the diversity of wildlife. By implementing IPM strategies, we can minimize the negative impact of pest control on wildlife and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
VI. Engaging Local Communities in Wildlife Conservation
Engaging local communities in wildlife conservation is crucial for the long-term protection and preservation of our natural resources. By involving and empowering local residents, we can create a sustainable future where humans and wildlife coexist harmoniously. In this section, we will explore three key strategies for engaging local communities in wildlife conservation: education and awareness programs, community-based conservation initiatives, and collaboration with indigenous communities.
A. Education and awareness programs
Education and awareness programs play a vital role in fostering a sense of responsibility and stewardship towards wildlife and their habitats. By providing information and knowledge about the importance of conservation, we can inspire individuals to take action and make informed decisions that benefit both wildlife and the local community.
One effective approach is to collaborate with local schools and educational institutions to incorporate wildlife conservation into their curriculum. By integrating conservation topics into the classroom, we can ensure that future generations grow up with a deep understanding and appreciation for the natural world.
Additionally, organizing workshops, seminars, and public awareness campaigns can help raise awareness among the broader community. These initiatives can cover a wide range of topics, such as the importance of biodiversity, the impact of human activities on wildlife, and sustainable practices for coexistence.
Engaging local communities through education and awareness programs not only helps in spreading knowledge but also fosters a sense of ownership and pride in protecting the local environment and its inhabitants.
B. Community-based conservation initiatives
Community-based conservation initiatives involve actively involving local residents in the decision-making and implementation processes of wildlife conservation projects. By empowering communities and recognizing their traditional knowledge and practices, we can create a sense of shared responsibility and ownership over conservation efforts.
One example of a community-based conservation initiative is the establishment of community-led wildlife sanctuaries or protected areas. These areas are managed and governed by local communities, who work together to protect and manage the wildlife and their habitats. This approach not only ensures the active participation of local residents but also provides economic opportunities through eco-tourism and sustainable livelihoods.
Another aspect of community-based conservation is the promotion of sustainable practices that benefit both the community and wildlife. This can include initiatives such as sustainable agriculture, responsible fishing practices, and the promotion of alternative livelihoods that reduce dependence on natural resources.
By involving local communities in decision-making processes and providing them with the necessary resources and support, we can create a more inclusive and effective approach to wildlife conservation.
C. Collaboration with indigenous communities
Collaborating with indigenous communities is essential for effective wildlife conservation. Indigenous communities often have a deep understanding of their local ecosystems and possess traditional knowledge and practices that have been passed down through generations.
By partnering with indigenous communities, we can tap into their expertise and wisdom, ensuring that conservation efforts are culturally sensitive and sustainable. Indigenous communities can provide valuable insights into the behavior and habitat requirements of local wildlife, as well as traditional conservation practices that have proven successful over time.
Furthermore, collaboration with indigenous communities can help address historical injustices and promote social justice in conservation. By recognizing and respecting indigenous rights, we can work towards a more equitable and inclusive approach to wildlife conservation.
Engaging local communities, implementing community-based conservation initiatives, and collaborating with indigenous communities are all essential components of reducing the impact of human development on wildlife. By working together, we can create a future where wildlife thrives, and communities benefit from a healthy and sustainable environment.
VII. Wildlife Rehabilitation and Rescue
A. Importance of wildlife rehabilitation
Wildlife rehabilitation plays a vital role in preserving and protecting the natural world. It provides a lifeline for injured, orphaned, or sick animals, giving them a chance to recover and eventually return to their natural habitats. The importance of wildlife rehabilitation cannot be overstated, as it directly contributes to the conservation of various species and helps maintain the delicate balance of ecosystems.
By providing medical care, nourishment, and a safe environment, wildlife rehabilitation centers give animals a fighting chance to survive and thrive. They also play a crucial role in educating the public about the importance of wildlife conservation and the impact of human activities on the natural world.
B. Rehabilitation techniques and best practices
Wildlife rehabilitation centers employ a range of techniques and best practices to ensure the successful rehabilitation of animals. These techniques vary depending on the species being treated and the nature of their injuries or illnesses.
One of the key aspects of wildlife rehabilitation is providing appropriate medical care. This includes diagnosing injuries or illnesses, administering medications, and performing surgeries when necessary. Wildlife rehabilitators work closely with veterinarians to ensure the animals receive the best possible care.
In addition to medical treatment, rehabilitation centers focus on providing a suitable environment for the animals to recover. This may involve creating enclosures that mimic their natural habitats, providing proper nutrition, and offering opportunities for exercise and mental stimulation.
Rehabilitation centers also prioritize the animals’ emotional well-being. They aim to minimize stress and create a supportive environment that allows the animals to regain their natural behaviors and instincts. This may involve limiting human contact, providing enrichment activities, and gradually reintroducing the animals to their natural surroundings.
C. Collaboration with wildlife rehabilitation centers
Collaboration between various stakeholders is crucial for the success of wildlife rehabilitation efforts. Wildlife rehabilitation centers often work closely with government agencies, conservation organizations, and local communities to achieve their goals.
Government agencies play a vital role in regulating and licensing wildlife rehabilitation centers. They provide guidelines and standards that ensure the welfare of the animals and the safety of the rehabilitators. Collaboration with these agencies helps maintain the integrity of the rehabilitation process and ensures compliance with legal requirements.
Conservation organizations often provide financial support and resources to wildlife rehabilitation centers. They may also assist in raising public awareness about the importance of wildlife rehabilitation and the need for conservation efforts.
Local communities can also play a significant role in supporting wildlife rehabilitation centers. They can volunteer their time, donate resources, or participate in educational programs organized by the centers. By fostering a sense of ownership and responsibility towards wildlife, communities can contribute to the long-term success of rehabilitation efforts.
VIII. Wildlife Conservation Laws and Policies
When it comes to reducing the impact of human development on wildlife, it is crucial to have strong wildlife conservation laws and policies in place. These laws and policies provide a framework for protecting and preserving wildlife, ensuring their habitats are safeguarded, and regulating activities that may harm or disrupt their natural environment. In this section, we will explore the international conventions and agreements, national wildlife protection laws, and the enforcement and penalties for wildlife crimes.
A. International Conventions and Agreements
International conventions and agreements play a vital role in promoting wildlife conservation on a global scale. These agreements bring together countries from around the world to address common concerns and establish guidelines for the protection of wildlife and their habitats.
One such agreement is the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES). CITES aims to ensure that international trade in wild animals and plants does not threaten their survival. It regulates the trade of species listed under its appendices, which include endangered and threatened species.
Another important international convention is the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands. The Ramsar Convention focuses on the conservation and wise use of wetlands, which are vital habitats for many species of wildlife. It promotes the sustainable management of wetlands to maintain their ecological character and biodiversity.
These international conventions and agreements provide a platform for countries to collaborate and share knowledge and best practices in wildlife conservation. They also help to raise awareness about the importance of protecting wildlife and ensure that efforts are coordinated on a global scale.
B. National Wildlife Protection Laws
In addition to international agreements, countries also have their own national wildlife protection laws. These laws vary from country to country but generally aim to protect wildlife and their habitats, regulate hunting and fishing activities, and prevent the illegal trade of wildlife and wildlife products.
For example, in the United States, the Endangered Species Act (ESA) is a key piece of legislation that provides protection for endangered and threatened species and their habitats. The ESA prohibits the “taking” of listed species, which includes actions such as killing, harming, or harassing them. It also prohibits the trade of products made from these species.
In India, the Wildlife Protection Act is a comprehensive legislation that provides protection to wildlife and their habitats. It prohibits hunting, capturing, and trading of wildlife species listed under the act. It also establishes protected areas, such as national parks and wildlife sanctuaries, to conserve and manage wildlife and their habitats.
These national wildlife protection laws are essential for ensuring the conservation and sustainable management of wildlife within a country’s borders. They provide legal mechanisms to enforce wildlife protection and hold individuals accountable for actions that harm or exploit wildlife.
C. Enforcement and Penalties for Wildlife Crimes
Enforcement of wildlife conservation laws is crucial to deter wildlife crimes and ensure compliance with regulations. Governments and law enforcement agencies play a vital role in monitoring and enforcing these laws, investigating wildlife crimes, and prosecuting offenders.
Penalties for wildlife crimes vary depending on the severity of the offense and the country’s legal system. They can range from fines and imprisonment to the forfeiture of assets and licenses. The severity of penalties is often determined by the level of threat posed to wildlife and the intent behind the crime.
Efforts to combat wildlife crimes are not limited to law enforcement agencies alone. Non-governmental organizations (NGOs), community-based organizations, and individuals also play a significant role in supporting enforcement efforts. They raise awareness, provide training and resources, and collaborate with law enforcement agencies to combat wildlife crimes.
It is essential to strengthen enforcement mechanisms and ensure that penalties for wildlife crimes are sufficient to deter potential offenders. Additionally, raising public awareness about the importance of wildlife conservation and the consequences of wildlife crimes can contribute to a culture of respect and protection for wildlife.
IX. Wildlife Tourism and Responsible Wildlife Watching
Wildlife tourism is a popular form of travel that allows individuals to experience and appreciate the beauty of nature and its inhabitants. However, it is important to understand the benefits and risks associated with wildlife tourism, as well as the guidelines for responsible wildlife watching. By supporting ethical wildlife tourism operators, we can ensure the conservation and protection of wildlife for future generations.
A. Benefits and risks of wildlife tourism
1. Benefits of wildlife tourism:
- Education and awareness: Wildlife tourism provides an opportunity for people to learn about different species, their habitats, and the importance of conservation.
- Economic support: Wildlife tourism contributes to the local economy by generating revenue through tourism activities, such as guided tours, accommodations, and local businesses.
- Conservation efforts: The funds generated from wildlife tourism can be used for conservation initiatives, including habitat restoration, anti-poaching efforts, and research projects.
- Community involvement: Wildlife tourism often involves local communities, providing them with employment opportunities and encouraging their participation in conservation efforts.
2. Risks of wildlife tourism:
- Disturbance of natural behavior: Unregulated wildlife tourism can disrupt the natural behavior of animals, leading to stress, aggression, and altered feeding patterns.
- Habitat degradation: Increased tourism activities can result in habitat degradation, including pollution, habitat loss, and destruction of nesting sites.
- Illegal wildlife trade: Wildlife tourism can inadvertently contribute to the illegal wildlife trade, as some operators may exploit animals for profit.
- Human-wildlife conflicts: Inadequate safety measures and irresponsible behavior by tourists can lead to human-wildlife conflicts, posing risks to both humans and animals.
B. Responsible wildlife watching guidelines
1. Respect wildlife and their habitats:
- Observe from a distance: Maintain a safe distance from wildlife to avoid causing stress or disturbance.
- Do not feed or touch animals: Feeding or touching wildlife can disrupt their natural behavior and may pose risks to both humans and animals.
- Stay on designated paths: Stick to designated trails and paths to minimize habitat disturbance and prevent trampling of vegetation.
2. Follow ethical photography practices:
- Use zoom lenses: Capture close-up shots without intruding on the animal’s personal space.
- Do not use flash: Flash photography can startle animals and potentially harm their eyes.
- Do not bait or lure animals: Avoid using bait or sound recordings to attract wildlife for photography purposes.
3. Support responsible wildlife tourism operators:
- Research before booking: Choose operators that prioritize animal welfare, conservation, and sustainable practices.
- Ask about their policies: Inquire about their policies on animal interactions, environmental impact, and community involvement.
- Report unethical practices: If you witness any unethical behavior or mistreatment of animals, report it to the relevant authorities or organizations.
C. Supporting ethical wildlife tourism operators
1. Look for certifications and affiliations:
- Check if the operator is affiliated with recognized conservation organizations or has certifications such as the Global Sustainable Tourism Council (GSTC) or the Association of Zoos and Aquariums (AZA).
2. Consider their conservation efforts:
- Find out if the operator actively supports conservation initiatives, such as habitat restoration, research projects, or anti-poaching efforts.
- Ask how they contribute to local communities and involve them in their conservation efforts.
3. Assess their animal welfare practices:
- Ensure that the operator follows ethical guidelines for animal care, including providing appropriate habitats, veterinary care, and enrichment activities.
- Ask about their policies on breeding, animal transfers, and interactions with tourists.
By following these guidelines and supporting ethical wildlife tourism operators, we can enjoy the beauty of wildlife while ensuring their conservation and protection. Responsible wildlife watching allows us to appreciate nature without compromising the well-being of animals or their habitats.
In this section, we will explore three case studies that highlight successful wildlife conservation projects. These examples demonstrate the positive impact of conservation efforts on endangered species, the restoration of degraded habitats, and community-led initiatives.
Example 1: Conservation efforts for endangered species
One remarkable case study of successful wildlife conservation is the efforts made to protect endangered species such as the Sumatran tiger and the black rhinoceros. In Sumatra, Indonesia, conservation organizations have collaborated with local communities and government agencies to establish protected areas and implement anti-poaching measures.
These conservation efforts have yielded positive results, with an increase in the population of Sumatran tigers and black rhinoceros. Through the use of camera traps and monitoring systems, researchers have been able to track the movements and behavior of these endangered species, providing valuable insights for their long-term conservation.
Additionally, education and awareness programs have been implemented to engage local communities in the conservation efforts. By involving the community in wildlife monitoring and protection, there has been a significant reduction in poaching activities and an increase in support for conservation initiatives.
Example 2: Restoration of degraded habitats
Another inspiring case study focuses on the restoration of degraded habitats, particularly in areas affected by deforestation and habitat fragmentation. One successful project took place in the Amazon rainforest, where a team of conservationists and local communities worked together to restore a large tract of land that had been cleared for agriculture.
The project involved reforestation efforts, including the planting of native tree species and the creation of wildlife corridors to connect fragmented habitats. Over time, the restored area has seen a remarkable recovery, with the return of numerous plant and animal species, including endangered ones like the golden lion tamarin.
This case study highlights the importance of restoring degraded habitats to provide suitable environments for wildlife. By creating corridors and promoting biodiversity, conservationists can help species thrive and ensure their long-term survival.
Example 3: Community-led conservation initiatives
Community-led conservation initiatives have proven to be effective in various parts of the world. One notable example is the Maasai Mara Wildlife Conservancies in Kenya. These conservancies are managed and governed by local Maasai communities, who have taken the lead in protecting wildlife and their habitats.
The Maasai communities have implemented sustainable land management practices, such as rotational grazing and controlled burns, to maintain the health of the ecosystem. They have also established wildlife conservancies, which generate income through eco-tourism and provide employment opportunities for the local population.
Through these initiatives, the Maasai communities have successfully reduced human-wildlife conflicts and improved the conservation status of key species, including lions, elephants, and giraffes. The involvement of the local communities has been crucial in ensuring the long-term success and sustainability of these conservation efforts.
