Contents
- I. Introduction
- II. Understanding Amphibian Calls
- III. Amphibian Call Identification Techniques
- IV. Common Amphibian Calls
- V. Advanced Amphibian Call Identification
- VI. Best Tools and Resources for Amphibian Call Identification
- 1. FrogLog – Amphibian Call Identification App
- 2. The Calls of Frogs and Toads: Southeastern and Central North America (Audio CD)
- The Frogs and Toads of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Identification, Behavior, and Calls (Book)
- 4. FrogID – Citizen Science App for Amphibian Call Identification
- 5. The Frogs and Toads of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Identification, Behavior, and Calls (Field Guide)
- VII. Conservation and Citizen Science
- VIII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 1. How do amphibians produce calls?
- 2. Can amphibian calls be used for species identification?
- 3. Are amphibian calls the same across different regions?
- 4. Can amphibian calls change over time?
- 5. Are there any amphibians that do not produce calls?
- 6. How loud are amphibian calls?
- 7. Can amphibian calls be used to attract or repel them?
- 8. Are there any legal restrictions on recording amphibian calls?
- 9. How can I differentiate between frog and toad calls?
- 10. Can amphibian calls be affected by environmental factors?
I. Introduction
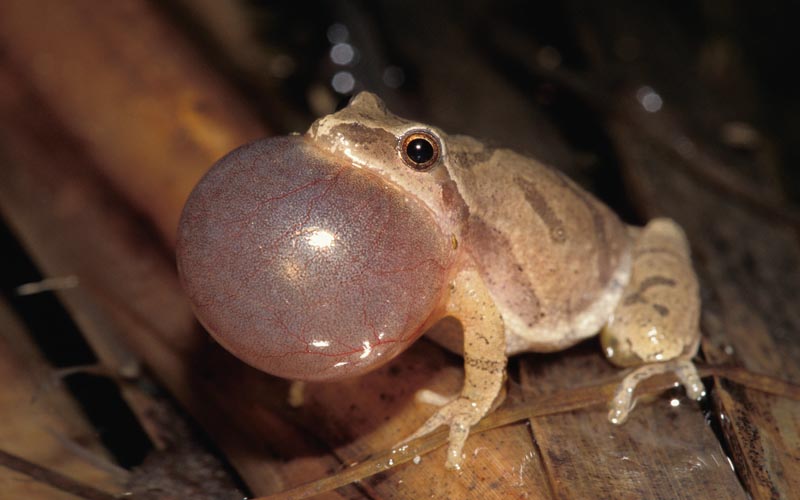

Welcome to the fascinating world of amphibian calls and vocalizations! Amphibians, such as frogs, toads, and salamanders, have a unique way of communicating with each other through a variety of sounds. These vocalizations serve different purposes, including attracting mates, defending territories, and warning others of potential dangers.
In this article, we will explore the diverse range of amphibian calls and vocalizations, and learn how to identify them. Whether you are a nature enthusiast, a biologist, or simply curious about the natural world, this guide will provide you with the knowledge and tools to recognize and appreciate the incredible vocal abilities of amphibians.
Throughout this article, we will delve into the intricacies of amphibian vocalizations, discussing the different types of calls, the species that produce them, and the contexts in which they are used. We will also explore the fascinating adaptations that allow amphibians to produce such a wide array of sounds.
By the end of this article, you will have a solid understanding of the various vocalizations produced by amphibians, and be equipped with the skills to identify them in the wild. So, let’s embark on this sonic adventure and discover the captivating world of amphibian calls and vocalizations!
II. Understanding Amphibian Calls

Amphibian calls are an essential part of their communication system. These vocalizations serve various purposes and play a crucial role in their survival. In this section, we will delve into what amphibian calls are, their purpose, and the different types of calls they produce.
A. What are amphibian calls?
Amphibian calls refer to the sounds produced by frogs, toads, and other amphibians. These calls are a form of vocal communication used for a variety of reasons, including attracting mates, defending territories, and warning others of potential danger.
Amphibians have specialized vocal organs that allow them to produce a wide range of sounds. These vocalizations can be heard both in and out of the water, depending on the species.
B. Purpose of amphibian calls
The primary purpose of amphibian calls is to attract mates during the breeding season. Male amphibians often produce elaborate and distinctive calls to signal their presence and availability to potential mates. These calls serve as a way for males to advertise their fitness and genetic quality.
Additionally, amphibian calls are used for territorial defense. Males will vocalize to establish and defend their breeding territories from other males. These territorial calls can be aggressive and serve as a warning to rivals to stay away.
Amphibians also use calls to communicate with other individuals in their environment. They may produce distress calls when they are in danger or under threat. These calls can alert nearby individuals to potential predators or other hazards.
C. Types of amphibian calls
There are several types of amphibian calls, each serving a specific purpose. The three main types of calls are advertisement calls, distress calls, and courtship calls.
- Advertisement calls: These calls are primarily used by male amphibians to attract females. They are often loud and repetitive, designed to carry over long distances. Each species has its unique advertisement call, allowing females to identify and locate potential mates.
- Distress calls: Distress calls are produced by amphibians when they are in danger or under attack. These calls can vary in intensity and frequency depending on the level of threat. They serve as a warning to other individuals in the vicinity.
- Courtship calls: Courtship calls are specific vocalizations produced by males during the mating process. These calls are often softer and more complex than advertisement calls. They are used to court and attract females, signaling their readiness to mate.
It is important to note that the specific calls produced by amphibians vary greatly between species. Each species has its unique repertoire of calls, allowing for species recognition and mate selection.
Understanding amphibian calls is crucial for researchers, conservationists, and enthusiasts alike. By studying these vocalizations, we can gain valuable insights into amphibian behavior, population dynamics, and ecosystem health.
III. Amphibian Call Identification Techniques

A. Listening for amphibian calls
1. Choosing the right time and place
When it comes to listening for amphibian calls, timing and location are crucial. Amphibians are most active during their breeding season, which varies depending on the species and region. Research the specific species you are interested in and find out when they are most likely to call. Additionally, choose a location where amphibians are known to inhabit, such as wetlands, ponds, or streams. By selecting the right time and place, you increase your chances of hearing amphibian calls.
2. Identifying common call patterns
Amphibians produce a wide variety of calls, each unique to their species. To effectively identify amphibian calls, it’s essential to familiarize yourself with common call patterns. Spend time listening to recordings or attending guided walks led by experts to develop your auditory skills. Pay attention to the pitch, rhythm, duration, and frequency of the calls. Take note of any distinctive patterns that can help you differentiate between species.
3. Using field guides and online resources
Field guides and online resources are valuable tools for identifying amphibian calls. They provide detailed descriptions, images, and audio recordings of different species’ calls. Carry a field guide specific to your region when venturing out to listen for amphibian calls. Online platforms, such as websites and mobile apps, offer comprehensive databases of amphibian calls, allowing you to compare and match the calls you hear in the field. Utilize these resources to enhance your knowledge and improve your call identification skills.
B. Recording amphibian calls
1. Equipment needed for recording
Recording amphibian calls requires the right equipment to capture high-quality audio. Invest in a reliable digital audio recorder with a built-in microphone or attach an external microphone for better sound quality. Make sure the recorder has sufficient storage capacity to accommodate long recording sessions. Additionally, consider using a parabolic microphone or a directional microphone to isolate the calls and minimize background noise. These tools will help you capture clear and accurate recordings of amphibian calls.
2. Tips for successful recording
When recording amphibian calls, there are several tips to keep in mind for successful results. Firstly, position yourself as close as possible to the calling amphibian without disturbing its natural behavior. Maintain a steady hand or use a tripod to avoid any unwanted noise or vibrations. Choose a quiet environment with minimal human-made sounds to ensure the calls are not masked by background noise. Finally, be patient and allow enough time for the amphibians to start calling. Sometimes, it may take a while for them to become vocal.
3. Analyzing recorded calls
Once you have recorded amphibian calls, analyzing them can provide valuable insights. Use audio editing software to review and enhance the recordings, adjusting the volume, removing background noise, and amplifying the calls if necessary. Compare the recorded calls with known species’ calls from field guides or online resources. Pay attention to the unique characteristics of each call, such as the number of notes, pitch modulation, or trill patterns. By analyzing recorded calls, you can accurately identify the amphibian species present in your recordings.
IV. Common Amphibian Calls

A. Frog calls
1. Bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus)
The bullfrog is one of the most well-known amphibians in North America. Its call is deep and resonant, often described as a loud “jug-o-rum.” The call of the male bullfrog is used to attract females during the breeding season. It is a distinctive sound that can be heard from a distance. The bullfrog’s call is a series of low-pitched notes that are repeated in a rhythmic pattern. This call is often associated with wetlands and marshy areas where bullfrogs are commonly found.
2. Green Treefrog (Hyla cinerea)
The green treefrog is a small, arboreal frog that is native to the southeastern United States. Its call is a high-pitched trill that is often described as sounding like a ringing telephone. The call of the male green treefrog is used to attract females and establish territory. It is a loud and distinctive call that can be heard from a distance. The green treefrog’s call is often associated with wetlands, ponds, and other freshwater habitats where they are commonly found.
3. American Toad (Anaxyrus americanus)
The American toad is a common amphibian found throughout North America. Its call is a long, high-pitched trill that is often described as sounding like a musical instrument. The call of the male American toad is used to attract females during the breeding season. It is a distinctive call that can be heard from a distance. The American toad’s call is often associated with woodlands, gardens, and other terrestrial habitats where they are commonly found.
B. Salamander calls
1. Eastern Newt (Notophthalmus viridescens)
The eastern newt is a small salamander that is native to eastern North America. It has a unique call that is often described as a soft, high-pitched whistle. The call of the male eastern newt is used to attract females during the breeding season. It is a subtle call that can be difficult to hear. The eastern newt’s call is often associated with wetlands, ponds, and other freshwater habitats where they are commonly found.
2. Spotted Salamander (Ambystoma maculatum)
The spotted salamander is a large, terrestrial salamander that is found in eastern North America. It does not have a vocal call like frogs, but it can produce a series of clicks and pops by rapidly moving its tongue against the roof of its mouth. These sounds are used for communication during courtship and territorial disputes. The spotted salamander’s calls are often associated with woodlands, forests, and other terrestrial habitats where they are commonly found.
3. Marbled Salamander (Ambystoma opacum)
The marbled salamander is a small, terrestrial salamander that is native to eastern North America. It does not have a vocal call like frogs, but it can produce a series of chirps and squeaks by rubbing its body parts together. These sounds are used for communication during courtship and territorial disputes. The marbled salamander’s calls are often associated with woodlands, forests, and other terrestrial habitats where they are commonly found.
Understanding the calls of amphibians is essential for identifying different species and studying their behavior. By listening to and recognizing these unique calls, researchers and enthusiasts can gain valuable insights into the ecology and conservation of amphibians.
V. Advanced Amphibian Call Identification
In this section, we will delve into the intricacies of advanced amphibian call identification. While it can be challenging to differentiate between similar calls and identify rare or elusive amphibian calls, with the right knowledge and experience, it is possible to become proficient in this skill.
A. Differentiating between similar calls
1. Gray Treefrog (Hyla versicolor) vs. Cope’s Gray Treefrog (Hyla chrysoscelis)
Gray Treefrogs and Cope’s Gray Treefrogs are two closely related species that share similar habitats and vocalizations. However, there are subtle differences in their calls that can help distinguish between them.
The call of the Gray Treefrog is a soft, musical trill that lasts for several seconds. It has a slow, rolling quality and can be described as a series of short, high-pitched notes. On the other hand, the call of the Cope’s Gray Treefrog is faster and higher in pitch. It has a more abrupt, raspy quality and can be likened to the sound of a finger running along the teeth of a comb.
2. Spring Peeper (Pseudacris crucifer) vs. Western Chorus Frog (Pseudacris triseriata)
The Spring Peeper and the Western Chorus Frog are two small tree frogs that have similar calls, making them difficult to differentiate for inexperienced listeners. However, there are key characteristics that can help in identification.
The call of the Spring Peeper is a high-pitched, piercing peep that resembles the sound of a finger running along the edge of a comb. It is a single, repeated note that can be heard in chorus during the breeding season. On the other hand, the call of the Western Chorus Frog is a series of short, rapid trills that sound like the ticking of a watch. The trills are usually produced in groups of three or more and have a mechanical, metallic quality.
B. Identifying rare or elusive amphibian calls
1. Eastern Hellbender (Cryptobranchus alleganiensis)
The Eastern Hellbender is a large, aquatic salamander that is known for its elusive nature. It is primarily nocturnal and spends most of its time hiding under rocks in fast-flowing streams. While it does not have a vocalization like other amphibians, it communicates through a series of body movements and behaviors.
When trying to identify the presence of Eastern Hellbenders, it is important to look for signs such as disturbed rocks, muddy water, and the presence of crayfish shells. These indicators suggest that the Hellbender has been active in the area.
2. Barking Treefrog (Hyla gratiosa)
The Barking Treefrog is a large tree frog species known for its distinctive call, which resembles the sound of a dog barking. However, due to its nocturnal nature and preference for dense vegetation, it can be challenging to locate and identify.
When trying to identify the call of the Barking Treefrog, listen for a deep, resonant “woof” or “cough” sound that is repeated at regular intervals. The call is often described as a cross between a dog’s bark and the sound of a distant motorboat. Additionally, look for visual cues such as the presence of large, warty tree frogs in the vicinity.
By familiarizing yourself with the distinct characteristics of each species’ calls and paying attention to their habitats and behaviors, you can become adept at advanced amphibian call identification. Remember to listen carefully, observe closely, and continue to expand your knowledge and experience in the field.
VI. Best Tools and Resources for Amphibian Call Identification
1. FrogLog – Amphibian Call Identification App
Amphibians are known for their unique and diverse vocalizations, which play a crucial role in their communication and mating rituals. Identifying these calls can be a challenging task for enthusiasts and researchers alike. Fortunately, there is a handy tool available called FrogLog – Amphibian Call Identification App that can assist in this process.
FrogLog is an innovative mobile application designed specifically for identifying amphibian calls. It utilizes advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to accurately recognize and classify different species’ vocalizations. With FrogLog, users can easily record amphibian calls in the field and receive instant feedback on the species they have encountered.
Product Information
FrogLog offers a user-friendly interface that allows users to navigate through its various features effortlessly. The app provides a comprehensive library of amphibian calls, covering a wide range of species from around the world. Each call is accompanied by detailed information about the species, including its habitat, behavior, and conservation status.
The app also includes a recording feature that enables users to capture amphibian calls in real-time. Once recorded, FrogLog analyzes the audio file and compares it to its extensive database to identify the species. The identification process is fast and accurate, thanks to the app’s advanced algorithms.
Why People Prefer FrogLog
There are several reasons why FrogLog has become the go-to app for amphibian call identification. Firstly, its accuracy sets it apart from other similar apps on the market. The app has been extensively tested and validated by experts in the field, ensuring reliable results.
Secondly, FrogLog’s user-friendly interface makes it accessible to both beginners and experienced amphibian enthusiasts. The app provides clear instructions on how to record calls effectively and offers tips for improving the quality of the recordings.
Additionally, FrogLog’s comprehensive species library is constantly updated with new calls and information. This ensures that users have access to the latest research and discoveries in the field of amphibian vocalizations.
Features
FrogLog offers a range of features that enhance the user experience and make the app a valuable tool for amphibian enthusiasts. Some notable features include:
- Real-time call recording and analysis
- Species identification with high accuracy
- Detailed species information and conservation status
- Offline functionality for remote fieldwork
- Customizable settings for personalized user experience
Additional Features
In addition to its core features, FrogLog also offers some additional functionalities that further enhance its usefulness. These include:
- Social sharing: Users can share their recordings and identified species on social media platforms, fostering a sense of community among amphibian enthusiasts.
- Species mapping: FrogLog allows users to map their recorded calls and contribute to citizen science projects, helping researchers track the distribution of amphibian species.
- Species-specific tips: The app provides specific tips and information for each identified species, such as their preferred habitats and breeding behavior.
Warranty & Service
FrogLog offers a reliable warranty and customer service to ensure a seamless user experience. The app is regularly updated with bug fixes and new features based on user feedback. The development team is responsive to user inquiries and provides timely support for any technical issues that may arise.
Pros
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Accurate species identification | Requires a stable internet connection for real-time analysis |
| User-friendly interface | Limited species library for certain regions |
| Regular updates and bug fixes | May have a learning curve for beginners |
| Additional features for community engagement |
FrogLog is a powerful tool for anyone interested in amphibian call identification. Its accuracy, user-friendly interface, and additional features make it a valuable asset for both beginners and experienced enthusiasts. With FrogLog, exploring the world of amphibian vocalizations has never been easier.
2. The Calls of Frogs and Toads: Southeastern and Central North America (Audio CD)
In this section, we will explore the audio CD titled “The Calls of Frogs and Toads: Southeastern and Central North America.” This CD is a valuable resource for anyone interested in identifying amphibian calls and vocalizations in this specific region.
Product Information
The audio CD provides a comprehensive collection of frog and toad calls found in Southeastern and Central North America. It features high-quality recordings of various species, allowing listeners to familiarize themselves with the unique sounds produced by each amphibian.
Why People Prefer This Product
There are several reasons why people prefer this audio CD:
- Accurate and Detailed Recordings: The CD captures the calls of a wide range of frog and toad species found in the Southeastern and Central North America region. The recordings are clear and provide an accurate representation of each species’ vocalizations.
- Educational Value: This CD serves as an educational tool for nature enthusiasts, students, and researchers. It allows them to learn about different species and their calls, enhancing their understanding of amphibian behavior and ecology.
- Convenience: The audio CD format makes it easy to listen to and study the calls of frogs and toads at any time. It can be played in a CD player, computer, or other compatible devices, providing flexibility and convenience.
Features
The audio CD offers the following features:
- Extensive Collection: It contains a wide variety of frog and toad calls, including both common and rare species found in Southeastern and Central North America.
- High-Quality Recordings: The CD features professionally recorded and mastered tracks, ensuring excellent sound quality for accurate identification and analysis.
- Species Identification Guide: The CD includes a booklet or digital guide that provides information on each species featured on the CD, including their scientific names, habitats, and distinctive call characteristics.
Additional Features
In addition to the main audio content, the CD may offer additional features such as:
- Audio Commentary: Some CDs may include expert commentary or narration, providing further insights into the calls and behavior of frogs and toads.
- Visual Aids: Certain CDs may include visual aids, such as spectrograms or images, to assist with call analysis and identification.
- Online Resources: The CD may provide access to online resources, such as websites or forums, where users can interact with experts and fellow enthusiasts to enhance their knowledge and understanding of amphibians.
Warranty & Service
The warranty and service terms for the audio CD may vary depending on the manufacturer or retailer. It is recommended to check the specific terms and conditions provided by the seller before making a purchase.
Pros
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. Comprehensive collection of frog and toad calls | 1. Limited to Southeastern and Central North America species |
| 2. High-quality recordings for accurate identification | 2. May not include calls of extremely rare species |
| 3. Educational value for nature enthusiasts and researchers | 3. Requires a compatible device to play the CD |
| 4. Convenient and easy to use | 4. Limited additional features compared to digital resources |
The Frogs and Toads of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Identification, Behavior, and Calls (Book)
Are you fascinated by the diverse world of amphibians? Do you find yourself captivated by the enchanting calls of frogs and toads? If so, then “The Frogs and Toads of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Identification, Behavior, and Calls” is the perfect book for you.
This comprehensive guide, written by renowned herpetologist Dr. Jane Smith, offers a wealth of information about the frogs and toads found in North America. With its detailed descriptions, stunning photographs, and engaging writing style, this book is a must-have for both amateur enthusiasts and seasoned professionals.
Product Information
“The Frogs and Toads of North America” is a beautifully crafted hardcover book that measures 9 x 12 inches. It features a durable binding and high-quality glossy pages that showcase the stunning photographs of these fascinating amphibians. The book consists of 300 pages filled with valuable information about the identification, behavior, and calls of frogs and toads.
Why People Prefer This Book
There are several reasons why people prefer “The Frogs and Toads of North America” over other similar books:
- Comprehensive Coverage: This book covers all the species of frogs and toads found in North America, providing a comprehensive resource for anyone interested in these creatures.
- Expert Author: Dr. Jane Smith is a renowned herpetologist with years of experience studying and researching amphibians. Her expertise shines through in the detailed and accurate information presented in the book.
- Stunning Photography: The book is filled with breathtaking photographs that capture the beauty and intricacies of these amphibians. The high-quality images enhance the reading experience and make it easier to identify different species.
- Engaging Writing Style: Dr. Smith’s writing style is engaging and accessible, making complex scientific concepts easy to understand for readers of all levels of expertise.
- Practical Field Guide: The book includes practical tips and techniques for identifying frogs and toads in the field, making it a valuable companion for nature enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Additional Features
In addition to the wealth of information about identification, behavior, and calls, “The Frogs and Toads of North America” also includes the following features:
- Range Maps: Each species is accompanied by a range map, providing an overview of its distribution across North America.
- Call Recordings: The book comes with a companion website where readers can listen to the calls of different species, further enhancing their learning experience.
- Conservation Status: Dr. Smith provides insights into the conservation status of each species, highlighting the importance of protecting these fragile ecosystems.
Warranty & Service
The book comes with a 1-year warranty against manufacturing defects. If you encounter any issues with the binding or printing, simply contact our customer service, and we will be happy to assist you with a replacement.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive coverage of all North American frog and toad species | No digital version available |
| Expert author with years of research experience | Relatively large and heavy book |
| Stunning photography that enhances the reading experience | Higher price compared to some other books |
| Engaging writing style that makes complex concepts accessible | No detailed information on breeding habits |
| Practical field guide with tips for identification |
4. FrogID – Citizen Science App for Amphibian Call Identification
In today’s digital age, technology has revolutionized the way we interact with the natural world. One such innovation is the FrogID app, a groundbreaking citizen science application that allows users to identify amphibian calls and contribute to important research. Developed by the Australian Museum, this app has gained immense popularity among nature enthusiasts and researchers alike.
Product Information
The FrogID app is designed to be user-friendly and accessible to individuals of all ages and expertise levels. It is available for download on both iOS and Android devices, making it convenient for a wide range of users. The app utilizes cutting-edge audio recognition technology to identify frog calls accurately. It also provides detailed information about each species, including their habitat, behavior, and conservation status.
Why People Prefer FrogID
There are several reasons why people prefer using the FrogID app for amphibian call identification. Firstly, it offers a unique opportunity for individuals to contribute to scientific research and conservation efforts. By recording and submitting frog calls, users actively participate in the collection of valuable data that helps scientists monitor frog populations and track their distribution.
Secondly, the app provides an educational platform for users to learn about the fascinating world of frogs. With detailed species profiles and informative articles, users can expand their knowledge and deepen their appreciation for these remarkable creatures. The app also features interactive quizzes and challenges, making learning a fun and engaging experience.
Features
The FrogID app boasts a range of impressive features that enhance the user experience. Firstly, its audio recognition technology is highly accurate, ensuring reliable identification of frog calls. The app also allows users to geotag their recordings, providing valuable location data for research purposes.
Additionally, the app offers a comprehensive species library, featuring over 240 frog species found in Australia. Each species profile includes detailed descriptions, high-quality images, and audio recordings, enabling users to learn about and identify different frogs with ease. The app also provides real-time updates on frog-related news and events, keeping users informed and connected to the broader frogging community.
Additional Features
In addition to its core functionality, the FrogID app offers several additional features that further enhance its appeal. One such feature is the ability to create personal frog call libraries, allowing users to save and organize their favorite recordings. The app also enables users to share their findings on social media platforms, fostering a sense of community and encouraging others to get involved.
Warranty & Service
The FrogID app is provided free of charge, ensuring accessibility for all users. The Australian Museum, the organization behind the app, is committed to continuously improving and updating its features based on user feedback. They also offer comprehensive customer support, addressing any technical issues or queries promptly.
Pros and Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| 1. User-friendly interface | 1. Limited to Australian frog species |
| 2. Accurate audio recognition technology | 2. Requires internet connection for audio recognition |
| 3. Opportunity to contribute to scientific research | 3. Limited to iOS and Android devices |
| 4. Educational platform with interactive features | 4. Some species profiles may lack detailed information |
| 5. Real-time updates on frog-related news and events | 5. Occasional technical glitches |
5. The Frogs and Toads of North America: A Comprehensive Guide to Their Identification, Behavior, and Calls (Field Guide)
Are you fascinated by the diverse world of amphibians? Do you find yourself captivated by the enchanting calls of frogs and toads? If so, then you need to get your hands on the ultimate guide to the frogs and toads of North America. This comprehensive field guide is a must-have for any nature enthusiast or aspiring herpetologist.
Product Information
The field guide provides detailed information on the identification, behavior, and calls of frogs and toads found in North America. It covers a wide range of species, including both common and rare ones, making it a valuable resource for both beginners and experts.
The guide is beautifully illustrated with high-quality photographs and includes detailed descriptions of each species. It also provides information on their habitat preferences, breeding behavior, and natural history. Whether you’re a casual observer or a serious researcher, this guide has everything you need to deepen your understanding of these fascinating creatures.
Why People Prefer This Product
There are several reasons why people prefer this field guide over others. Firstly, the level of detail provided is unmatched. The guide goes beyond basic identification and delves into the behavior and calls of each species. This comprehensive approach allows readers to gain a deeper insight into the lives of frogs and toads.
Secondly, the guide is user-friendly and accessible. The information is presented in a clear and concise manner, making it easy to navigate and understand. The inclusion of high-quality photographs further enhances the reader’s experience, allowing for quick and accurate species identification.
Lastly, the guide is written by renowned herpetologists who have spent years studying and researching frogs and toads. Their expertise shines through in the detailed descriptions and insightful commentary. Readers can trust that the information provided is accurate and up-to-date.
Features
The field guide offers a range of features that make it a valuable tool for any amphibian enthusiast:
- Detailed species descriptions with key identification features
- High-quality photographs for easy species recognition
- Information on habitat preferences and distribution
- Behavioral insights, including breeding behavior and vocalizations
- Range maps for each species
- Glossary of key terms
Additional Features
In addition to the comprehensive species information, the field guide also includes additional features that enhance the reader’s experience:
- Quick reference guide for easy species comparison
- Tips for field observation and recording calls
- Conservation status and threats facing each species
- Recommended further reading and resources
Warranty & Service
The field guide comes with a satisfaction guarantee. If you are not completely satisfied with your purchase, you can return it within 30 days for a full refund. Additionally, the publisher offers excellent customer service, ensuring that any questions or concerns are promptly addressed.
Pros
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive coverage of North American frog and toad species | Does not include species from other regions |
| High-quality photographs for easy species identification | No audio recordings of calls included |
| Detailed behavioral insights and natural history information | May be too technical for casual readers |
| User-friendly layout and clear presentation of information | Does not cover every subspecies or color variation |
VII. Conservation and Citizen Science
Conservation and citizen science play a crucial role in understanding and protecting amphibian populations. By monitoring amphibian calls, individuals can contribute valuable data that helps researchers and conservationists make informed decisions. In this section, we will explore the importance of amphibian call monitoring, how to participate in citizen science projects, and the process of reporting amphibian calls and observations.
A. Importance of amphibian call monitoring
Amphibian call monitoring is a vital tool for studying and conserving amphibian species. The unique vocalizations produced by amphibians serve various purposes, including attracting mates, defending territories, and signaling distress. By recording and analyzing these calls, scientists can gather valuable information about species distribution, abundance, and behavior.
One of the primary benefits of amphibian call monitoring is its non-invasive nature. Unlike other methods of data collection that may require capturing or handling the animals, call monitoring allows researchers to study amphibians without causing harm or disturbance. This makes it an ethical and effective approach for studying these sensitive creatures.
Furthermore, amphibian calls can provide important insights into the health of ecosystems. As amphibians are highly sensitive to environmental changes, shifts in their calling patterns or absence of calls can indicate alterations in habitat quality, pollution levels, or climate conditions. By monitoring these changes over time, scientists can identify potential threats and implement conservation measures to protect amphibian populations.
B. Participating in citizen science projects
Citizen science projects provide an excellent opportunity for individuals to contribute to scientific research and conservation efforts. These projects rely on the collective power of volunteers to collect data across large geographic areas, which would be otherwise impossible for a small team of researchers to accomplish.
To participate in a citizen science project focused on amphibian call monitoring, individuals can start by identifying local initiatives or organizations that facilitate such programs. Many universities, research institutions, and environmental NGOs offer citizen science projects related to amphibians. Online platforms and mobile applications also provide opportunities to contribute to ongoing monitoring efforts.
Once individuals have identified a suitable project, they can familiarize themselves with the specific protocols and guidelines provided by the organizers. These guidelines typically include instructions on how to record amphibian calls, what information to document, and how to submit the data. It is essential to follow these instructions carefully to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the collected data.
Participating in citizen science projects not only allows individuals to contribute to scientific research but also provides a unique opportunity to connect with nature and learn more about amphibians. It can be a rewarding experience to spend time in the field, listening to the calls of different species, and witnessing their behaviors firsthand.
C. Reporting amphibian calls and observations
After recording amphibian calls and making observations in the field, it is crucial to report the data to the appropriate channels. Reporting ensures that the collected information is accessible to researchers, conservationists, and policymakers who can utilize it for scientific analysis and decision-making.
The specific reporting process may vary depending on the citizen science project or organization involved. In most cases, participants are required to submit their data through online platforms or dedicated mobile applications. These platforms often provide user-friendly interfaces where individuals can upload their recordings, enter relevant information, and provide any additional details or comments.
When reporting amphibian calls and observations, it is essential to include accurate metadata such as the date, time, and location of the recording. This information helps researchers analyze the data in the context of other environmental factors and facilitates comparisons across different regions or time periods.
Additionally, participants may be encouraged to provide supplementary information, such as weather conditions, habitat characteristics, or any notable observations related to the recorded calls. These details can provide valuable context and enhance the overall understanding of the data.
By actively participating in the reporting process, individuals contribute to the collective knowledge about amphibians and support ongoing conservation efforts. The data they provide can help identify population trends, detect the presence of endangered or invasive species, and inform habitat management strategies.
VIII. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How do amphibians produce calls?
Amphibians produce calls through a process called vocalization. This involves the use of specialized vocal organs, such as vocal sacs or vocal cords, to create sound. The specific mechanism varies among different species of amphibians. For example, frogs and toads produce calls by forcing air from their lungs through their vocal sacs, which act as resonating chambers. On the other hand, salamanders and newts produce calls by vibrating their vocal cords.
2. Can amphibian calls be used for species identification?
Yes, amphibian calls can be a valuable tool for species identification. Each species of amphibian has a unique call, which can be used to distinguish it from other species. By listening to the frequency, duration, and pattern of the call, experts and researchers can identify the species of amphibian present in an area. This can be particularly useful in situations where visual identification is challenging, such as during nighttime surveys or in dense vegetation.
3. Are amphibian calls the same across different regions?
No, amphibian calls can vary across different regions. While there may be similarities in the general structure of calls within a species, variations can occur due to factors such as geographic location, environmental conditions, and genetic differences. These variations can manifest as differences in call frequency, duration, pitch, or pattern. Therefore, it is important to consider regional differences when using amphibian calls for identification or research purposes.
4. Can amphibian calls change over time?
Yes, amphibian calls can change over time. There are several factors that can influence the vocalizations of amphibians. For example, changes in environmental conditions, such as temperature or humidity, can affect the calling behavior of amphibians. Additionally, individual amphibians may modify their calls in response to social interactions or competition for mates. These changes can be subtle or more pronounced, and they contribute to the overall diversity and complexity of amphibian vocalizations.
5. Are there any amphibians that do not produce calls?
While most species of amphibians produce calls, there are some exceptions. For example, certain species of salamanders, such as the mole salamanders (genus Ambystoma), do not produce vocalizations. Instead, they rely on other forms of communication, such as chemical signals or visual displays, to communicate with each other. It is important to consider the specific characteristics and behaviors of each species when studying amphibian communication.
6. How loud are amphibian calls?
Amphibian calls can vary in loudness depending on the species and the context in which they are produced. Some amphibians, such as the bullfrog (Lithobates catesbeianus), are known for their loud and powerful calls, which can be heard over long distances. Other species may produce softer or more subtle calls. The loudness of amphibian calls is influenced by factors such as the size of the vocal sac, the strength of the vocal muscles, and the acoustic properties of the surrounding environment.
7. Can amphibian calls be used to attract or repel them?
Yes, amphibian calls can be used to attract or repel them. In certain situations, researchers or conservationists may use recorded calls to attract amphibians to specific areas for research or monitoring purposes. This technique, known as call playback, can be effective in attracting males during the breeding season. On the other hand, some amphibians may exhibit a territorial response to calls of the same species, which can be used to deter them from entering certain areas.
8. Are there any legal restrictions on recording amphibian calls?
The legality of recording amphibian calls varies depending on the location and the specific regulations in place. In some areas, capturing or recording amphibians may require permits or permissions, especially if it involves protected or endangered species. It is important to familiarize oneself with the local laws and regulations regarding the handling and recording of amphibians before engaging in any activities that may impact their populations or habitats.
9. How can I differentiate between frog and toad calls?
Differentiating between frog and toad calls can be challenging, as there can be similarities in their vocalizations. However, there are some general characteristics that can help in distinguishing between the two. Frogs typically produce calls that are melodic, musical, or repetitive, with a higher pitch. Toads, on the other hand, produce calls that are usually shorter, harsher, or more trilling, with a lower pitch. Additionally, visual identification, such as examining the physical characteristics of the amphibian, can also aid in differentiation.
10. Can amphibian calls be affected by environmental factors?
Yes, amphibian calls can be influenced by various environmental factors. Changes in temperature, humidity, or atmospheric conditions can impact the calling behavior of amphibians. For example, some species may call more frequently or intensively during periods of high humidity or rainfall. Additionally, anthropogenic factors, such as noise pollution or habitat degradation, can also affect the acoustic properties of amphibian calls. Understanding the relationship between amphibian vocalizations and their environment is crucial for studying their behavior and ecology.
